Visualizing Proximity: Understanding and Utilizing Map Radius Graphics
Related Articles: Visualizing Proximity: Understanding and Utilizing Map Radius Graphics
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Visualizing Proximity: Understanding and Utilizing Map Radius Graphics. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Visualizing Proximity: Understanding and Utilizing Map Radius Graphics
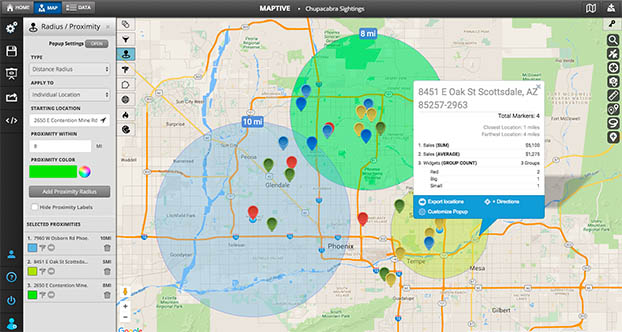
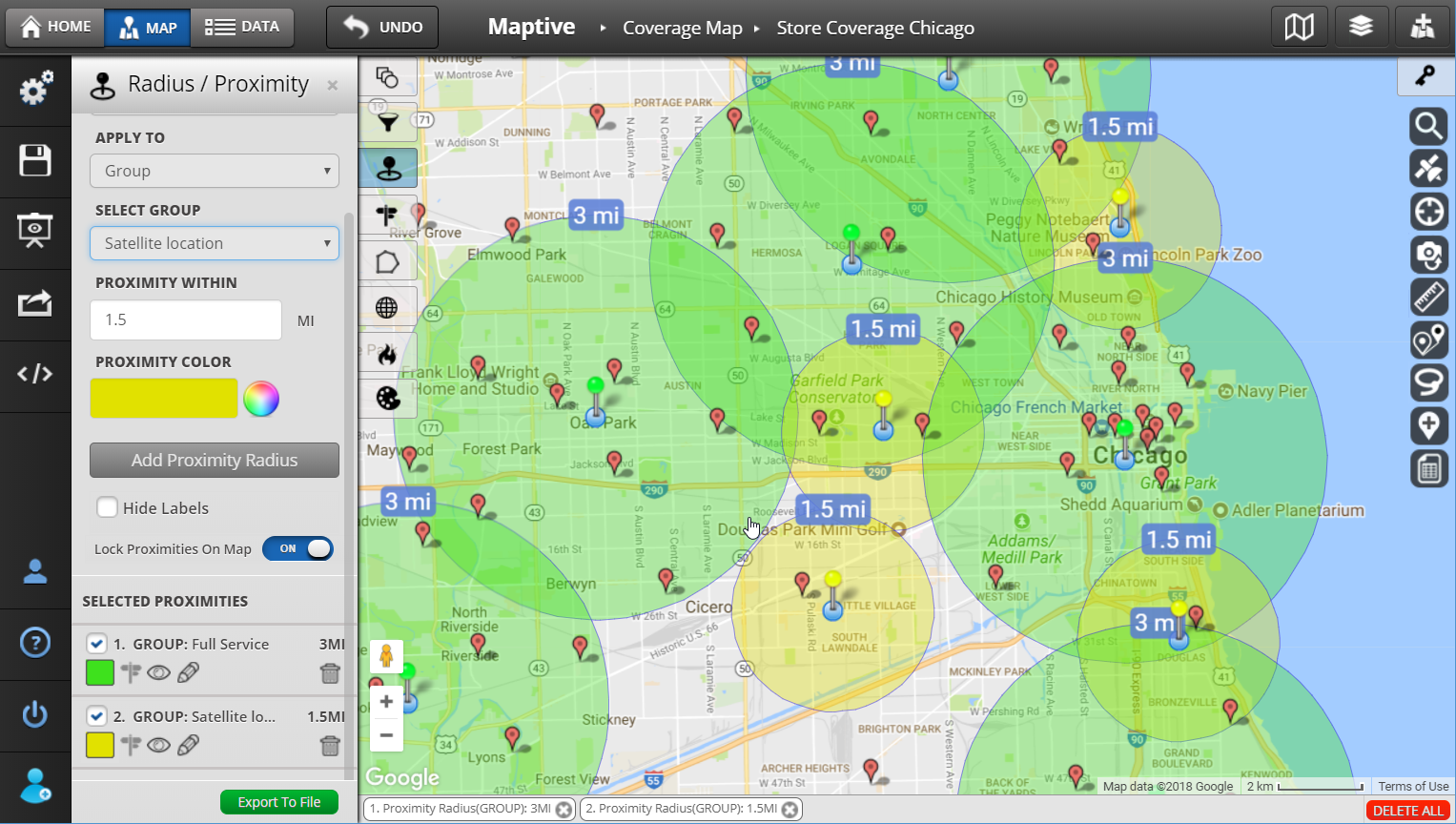
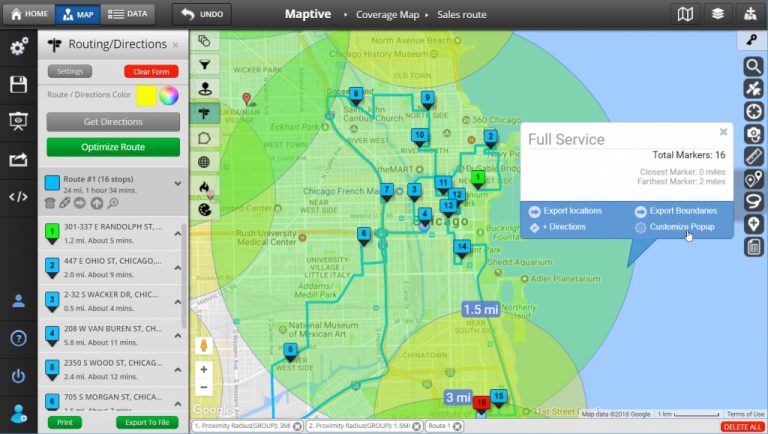
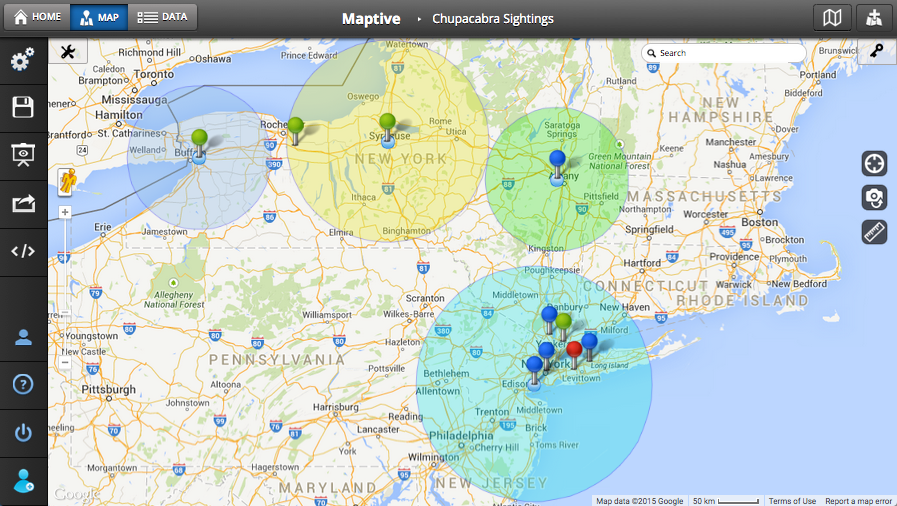
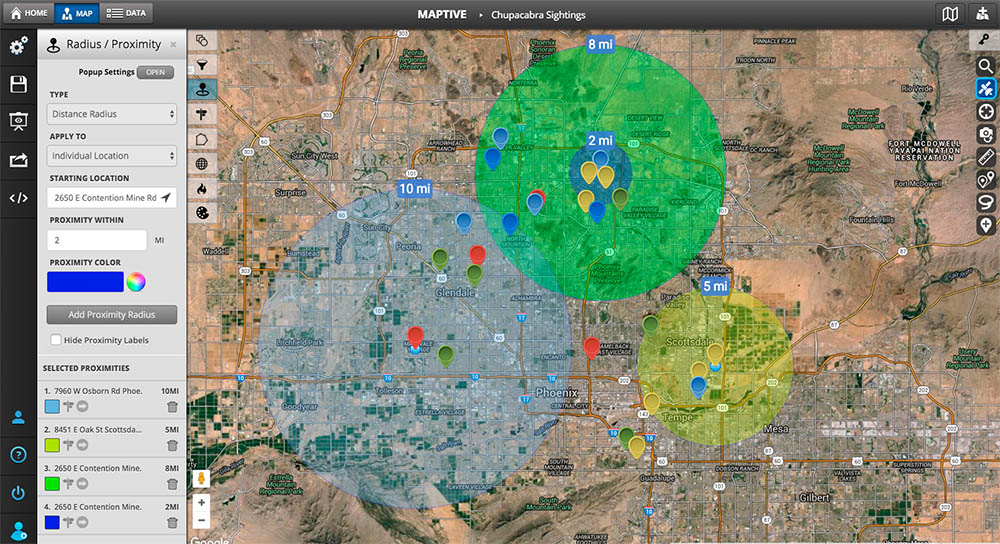
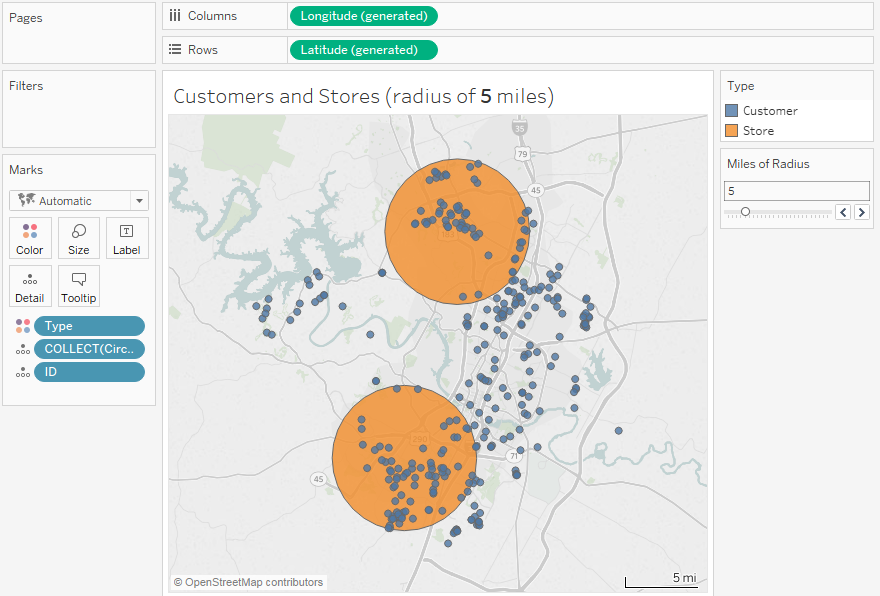
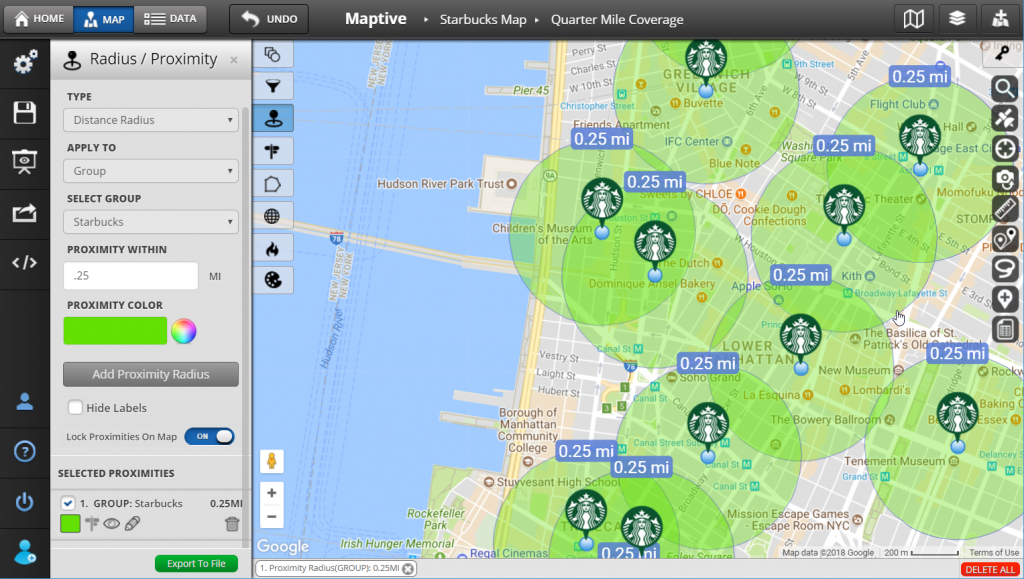
In the realm of data visualization, map radius graphics stand as a powerful tool for conveying spatial relationships and proximity. These graphics, often referred to as "circle maps," "heatmaps," or "buffer zones," depict areas of influence or coverage around a central point. They are essential for visualizing and understanding various geographic phenomena, from service areas and delivery zones to population density and disease outbreaks.
Understanding the Mechanics of Map Radius Graphics
At their core, map radius graphics utilize circles or polygons to represent a defined radius around a specific location. The radius itself is typically measured in units such as kilometers, miles, or even time, depending on the context. The size and shape of the circle or polygon directly correlate with the chosen radius, visually illustrating the extent of the area under consideration.
Applications of Map Radius Graphics: Unveiling Spatial Patterns
The versatility of map radius graphics extends across a multitude of fields, each leveraging their unique capabilities to reveal spatial patterns and insights. Here are some prominent applications:
-
Business and Marketing: Map radius graphics are indispensable for businesses seeking to optimize their service areas, target customer demographics, and analyze market competition. They allow businesses to visualize the reach of their operations, identify potential growth areas, and assess the feasibility of expansion.
-
Transportation and Logistics: In transportation and logistics, map radius graphics are crucial for route optimization, delivery planning, and fleet management. They facilitate the visualization of delivery zones, service areas, and potential congestion points, enabling efficient resource allocation and minimizing delivery times.
-
Urban Planning and Development: Urban planners rely on map radius graphics to analyze population density, assess the impact of infrastructure projects, and plan for future growth. They enable the visualization of service accessibility, transportation networks, and the potential impact of development on surrounding areas.
-
Emergency Management and Disaster Response: In emergency situations, map radius graphics play a vital role in coordinating response efforts, identifying affected areas, and prioritizing resources. They help visualize the potential impact of disasters, determine evacuation zones, and track the spread of emergencies.
-
Environmental Studies and Conservation: Environmental scientists utilize map radius graphics to analyze the impact of pollution, assess the distribution of endangered species, and monitor the effectiveness of conservation efforts. They provide a visual representation of environmental hazards, sensitive ecosystems, and the spatial extent of environmental changes.
Creating Effective Map Radius Graphics: Key Considerations
The effectiveness of map radius graphics hinges on several crucial considerations, ensuring clarity, accuracy, and meaningful insights:
-
Data Accuracy and Quality: The accuracy of the underlying data is paramount. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to misleading visualizations and flawed conclusions. It is crucial to ensure that the data used for generating map radius graphics is reliable, up-to-date, and relevant to the intended purpose.
-
Radius Definition and Units: The choice of radius and its units should be carefully considered. The radius should be appropriate for the context and the intended audience. For example, a business may use a radius measured in kilometers to represent its delivery zone, while an environmental study might use a radius measured in miles to represent the impact of a pollutant.
-
Map Base and Projection: The choice of map base and projection is essential for accurate representation of spatial relationships. Different projections can distort the shape and size of features, leading to misinterpretations. It is important to select a projection that minimizes distortion and accurately reflects the intended geographic area.
-
Visualization Techniques and Color Schemes: The choice of visualization techniques and color schemes can significantly influence the effectiveness of map radius graphics. Using appropriate colors, patterns, and symbols can enhance clarity, improve readability, and facilitate the identification of key patterns and trends.
-
Contextual Information and Labels: Providing contextual information and labels is crucial for understanding the meaning of the visualization. This includes details about the data source, the radius definition, the units used, and any relevant legends or annotations.
FAQs Regarding Map Radius Graphics
Q: What are the benefits of using map radius graphics?
A: Map radius graphics offer several benefits, including:
- Visual Clarity: They provide a clear and intuitive way to visualize spatial relationships and proximity.
- Data-Driven Insights: They enable the extraction of valuable insights from geographic data, revealing patterns and trends that might otherwise be overlooked.
- Decision-Making Support: They provide a visual framework for informed decision-making, supporting strategic planning and resource allocation.
- Enhanced Communication: They facilitate effective communication of spatial information to a diverse audience, regardless of technical expertise.
Q: What are some limitations of map radius graphics?
A: While powerful, map radius graphics have certain limitations:
- Oversimplification: They can oversimplify complex spatial relationships, potentially obscuring important nuances.
- Data Sensitivity: The accuracy and quality of the underlying data directly influence the reliability of the visualization.
- Projection Distortion: Different map projections can distort the shape and size of features, potentially affecting the interpretation of the data.
- Contextual Understanding: It is crucial to provide sufficient contextual information to avoid misinterpretations and ensure a comprehensive understanding of the visualization.
Q: How can I create effective map radius graphics?
A: Creating effective map radius graphics involves several key steps:
- Identify the purpose and audience: Define the specific goal of the visualization and tailor it to the intended audience.
- Gather and prepare the data: Ensure the data is accurate, complete, and relevant to the intended purpose.
- Select the appropriate map base and projection: Choose a projection that minimizes distortion and accurately represents the geographic area.
- Define the radius and units: Select a radius that is meaningful and relevant to the context.
- Choose visualization techniques and color schemes: Utilize appropriate colors, patterns, and symbols to enhance clarity and readability.
- Add contextual information and labels: Provide clear labels, legends, and annotations to ensure understanding.
Tips for Utilizing Map Radius Graphics
- Consider the audience: Tailor the visualization to the intended audience, ensuring clarity and accessibility.
- Use a consistent color scheme: Employ a consistent color scheme to enhance readability and facilitate comparisons.
- Provide clear labels and legends: Include labels, legends, and annotations to guide the interpretation of the visualization.
- Use interactive features: Incorporate interactive features such as zoom, pan, and tooltips to enhance user engagement and exploration.
- Focus on the message: Ensure the visualization effectively communicates the intended message, highlighting key patterns and insights.
Conclusion
Map radius graphics serve as a valuable tool for visualizing spatial relationships and proximity. Their ability to reveal patterns, support decision-making, and facilitate communication makes them indispensable across a wide range of fields. By adhering to best practices for data accuracy, visualization techniques, and contextual information, users can effectively leverage map radius graphics to unlock meaningful insights and enhance understanding of geographic phenomena. As data visualization continues to evolve, map radius graphics are poised to remain a vital component of our ability to understand and interact with the spatial world around us.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Visualizing Proximity: Understanding and Utilizing Map Radius Graphics. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!