Visualizing Proximity: The Power of Maps in Defining and Displaying Radius
Related Articles: Visualizing Proximity: The Power of Maps in Defining and Displaying Radius
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Visualizing Proximity: The Power of Maps in Defining and Displaying Radius. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Visualizing Proximity: The Power of Maps in Defining and Displaying Radius
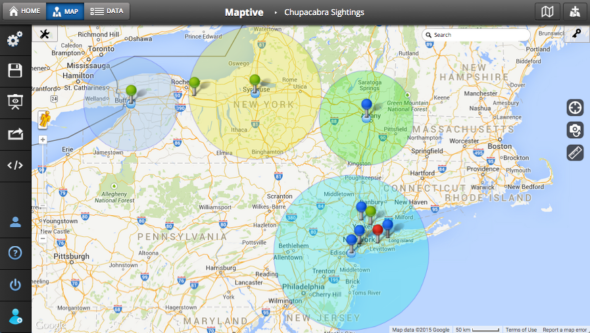
Maps are fundamental tools for understanding our world, providing visual representations of geographic information. Beyond simply depicting landmasses and borders, maps can be enhanced to convey specific data, enabling us to analyze and interpret complex spatial relationships. One particularly useful application involves the visualization of radius from a location, offering a powerful means to communicate proximity, accessibility, and spatial boundaries.
Understanding Radius Visualization
At its core, radius visualization on a map involves defining a circular area around a central point. This circle represents a specific distance from the location, allowing users to easily identify all points within that range. The radius can be measured in various units, such as kilometers, miles, or even time, depending on the application.
Applications of Radius Visualization
The ability to visually represent radius from a location finds application in a diverse range of fields, each leveraging its unique capabilities to address specific needs.
1. Business and Marketing:
- Market Analysis: Businesses can utilize radius maps to analyze potential customer bases, identifying demographics and market trends within a defined area.
- Targeted Advertising: Radius maps enable businesses to target advertising campaigns to specific geographic areas, ensuring maximum reach and impact.
- Location Optimization: Determining the optimal location for new stores, restaurants, or offices can be facilitated by radius maps, allowing businesses to assess customer density and accessibility.
2. Emergency Response and Disaster Management:
- Evacuation Zones: Radius maps are crucial in disaster management, delineating evacuation zones around potential hazards like wildfires or chemical spills.
- Resource Allocation: Emergency response teams can utilize radius maps to efficiently allocate resources, ensuring timely assistance to affected areas.
- Search and Rescue Operations: Radius maps are vital in search and rescue operations, allowing teams to focus their efforts within a defined area, maximizing the chances of finding missing individuals.
3. Urban Planning and Development:
- Infrastructure Planning: Radius maps assist in planning for infrastructure development, identifying areas needing improved transportation, utilities, or public services.
- Community Development: Radius maps can be used to identify areas with high population density, guiding community development initiatives and resource allocation.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: Radius maps help assess the potential environmental impact of projects, identifying areas that may be affected by pollution or habitat loss.
4. Healthcare and Public Health:
- Disease Surveillance: Radius maps are employed in tracking the spread of infectious diseases, identifying potential outbreaks and implementing containment measures.
- Healthcare Access: Radius maps help assess healthcare access in specific regions, highlighting areas with limited access to healthcare facilities.
- Public Health Campaigns: Radius maps are useful in targeting public health campaigns to specific populations, ensuring effective communication and intervention.
5. Real Estate and Property Management:
- Property Valuation: Radius maps can help determine property values by factoring in proximity to amenities, schools, and transportation hubs.
- Neighborhood Analysis: Radius maps facilitate the assessment of neighborhood desirability, considering factors like crime rates, school quality, and access to parks.
- Market Segmentation: Radius maps allow real estate professionals to segment the market, targeting specific buyer demographics based on location preferences.
Benefits of Radius Visualization
The use of radius maps offers numerous advantages, making them an invaluable tool for various applications:
- Clear Communication: Radius maps provide a visually intuitive way to communicate spatial information, making it easily understandable for a wide audience.
- Data Visualization: By representing data in a spatial context, radius maps allow for a deeper understanding of relationships and trends within a defined area.
- Targeted Analysis: Radius maps enable focused analysis, allowing users to explore specific areas and identify patterns within those boundaries.
- Decision Support: Radius maps provide valuable insights, facilitating informed decision-making in areas like business strategy, emergency response, and urban planning.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Radius maps serve as a common ground for discussion and collaboration, allowing stakeholders to visualize and understand shared data.
Technical Aspects of Radius Visualization
Creating radius maps involves several technical considerations, depending on the desired level of detail and functionality:
- Mapping Software: Various mapping software applications are available, offering features for creating radius visualizations, including Google Maps, ArcGIS, and Mapbox.
- Data Sources: Accurate data is crucial for creating effective radius maps. Sources can include geographic data sets, population statistics, and spatial analysis tools.
- Visualization Techniques: Radius maps can be customized using various visualization techniques, such as color gradients, line thickness, and marker size to represent different data values.
- User Interface: Intuitive user interfaces allow users to easily define the radius, select the central location, and customize the map’s appearance.
FAQs on Radius Visualization
1. What are the different types of radius visualizations?
Radius visualizations can be categorized based on the shape and type of data represented:
- Circular Radius: The most common type, representing a circular area around a central point.
- Polygon Radius: Represents an area with irregular boundaries, often used to define zones with specific characteristics.
- Isoline Radius: Displays lines of equal value, such as contour lines on a topographic map.
2. How is the radius determined?
The radius is typically defined by the user based on the specific application and the desired distance from the central location.
3. What are the limitations of radius visualization?
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of the radius map depends on the quality of the underlying data.
- Scale: Radius maps may not be suitable for representing large distances or areas with complex terrain.
- Simplification: Radius maps often simplify complex spatial relationships, potentially overlooking important details.
Tips for Effective Radius Visualization
- Define the Purpose: Clearly identify the goal of the radius visualization before creating the map.
- Choose the Right Software: Select mapping software that provides the necessary features and functionality for your application.
- Use Accurate Data: Ensure the data used for the map is reliable and up-to-date.
- Optimize Visualization: Choose appropriate colors, symbols, and techniques to effectively communicate the information.
- Provide Context: Include relevant information, such as labels, legends, and scale bars to provide context for the visualization.
Conclusion
Radius visualization on maps offers a powerful means to communicate proximity, accessibility, and spatial boundaries. Its applications span various fields, from business and marketing to emergency response and urban planning. By leveraging the visual power of maps, radius visualization provides a clear and intuitive way to analyze spatial data, facilitating informed decision-making and effective communication. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further advancements in radius visualization techniques, leading to even more sophisticated and insightful applications in the future.

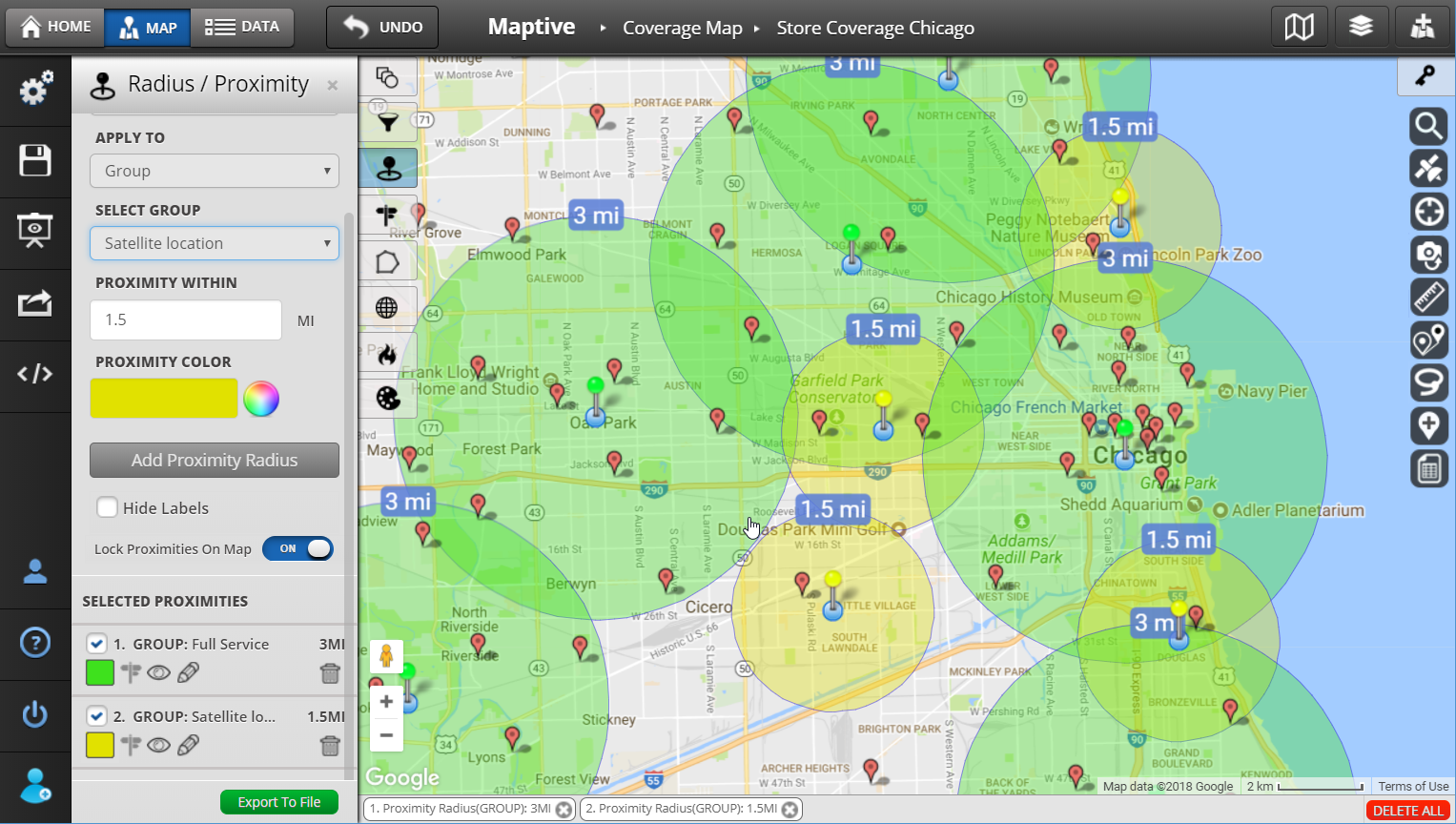
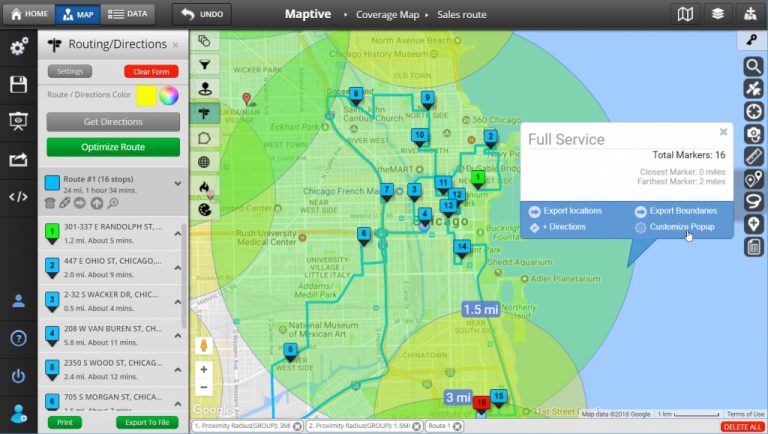


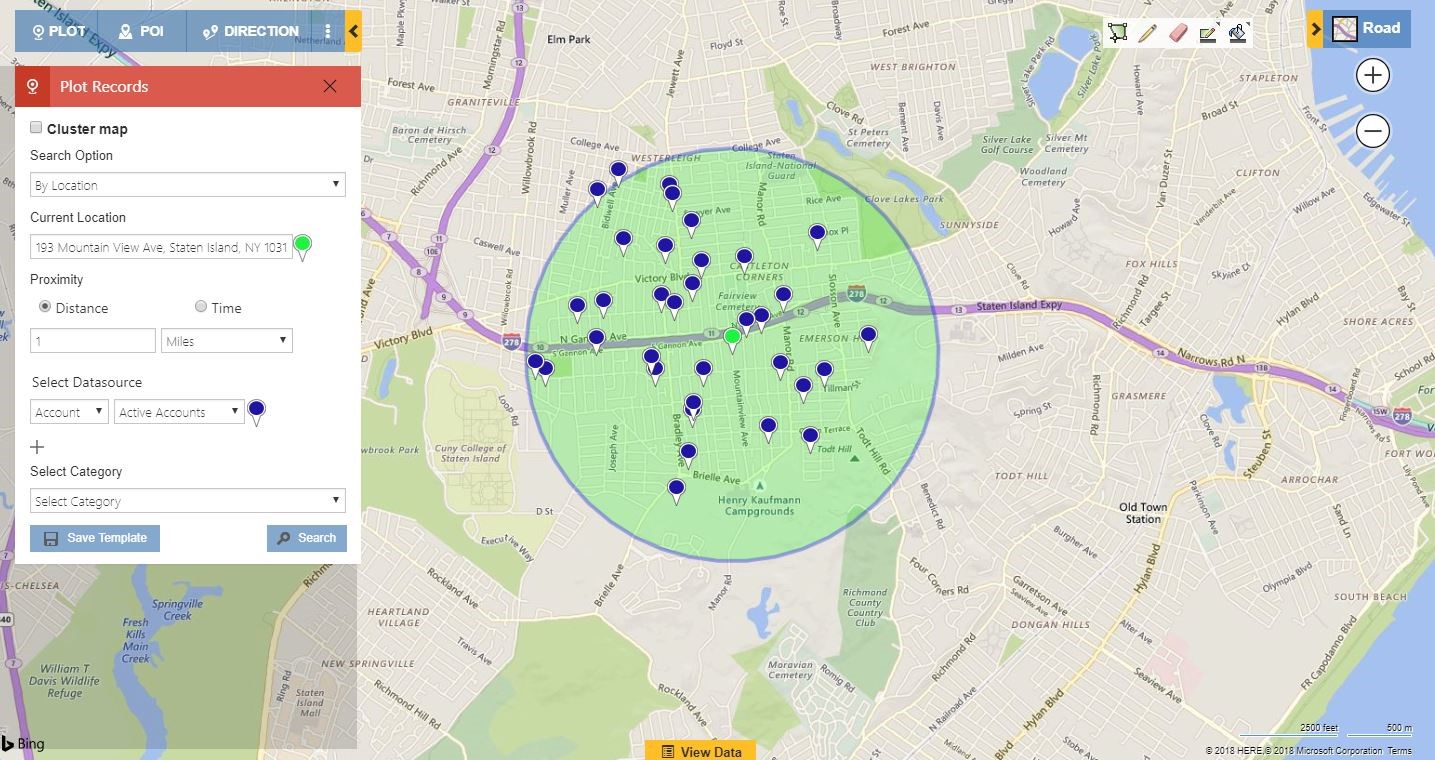

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Visualizing Proximity: The Power of Maps in Defining and Displaying Radius. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!