Unveiling the World on a Flat Surface: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projections
Related Articles: Unveiling the World on a Flat Surface: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projections
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the World on a Flat Surface: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projections. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the World on a Flat Surface: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projections
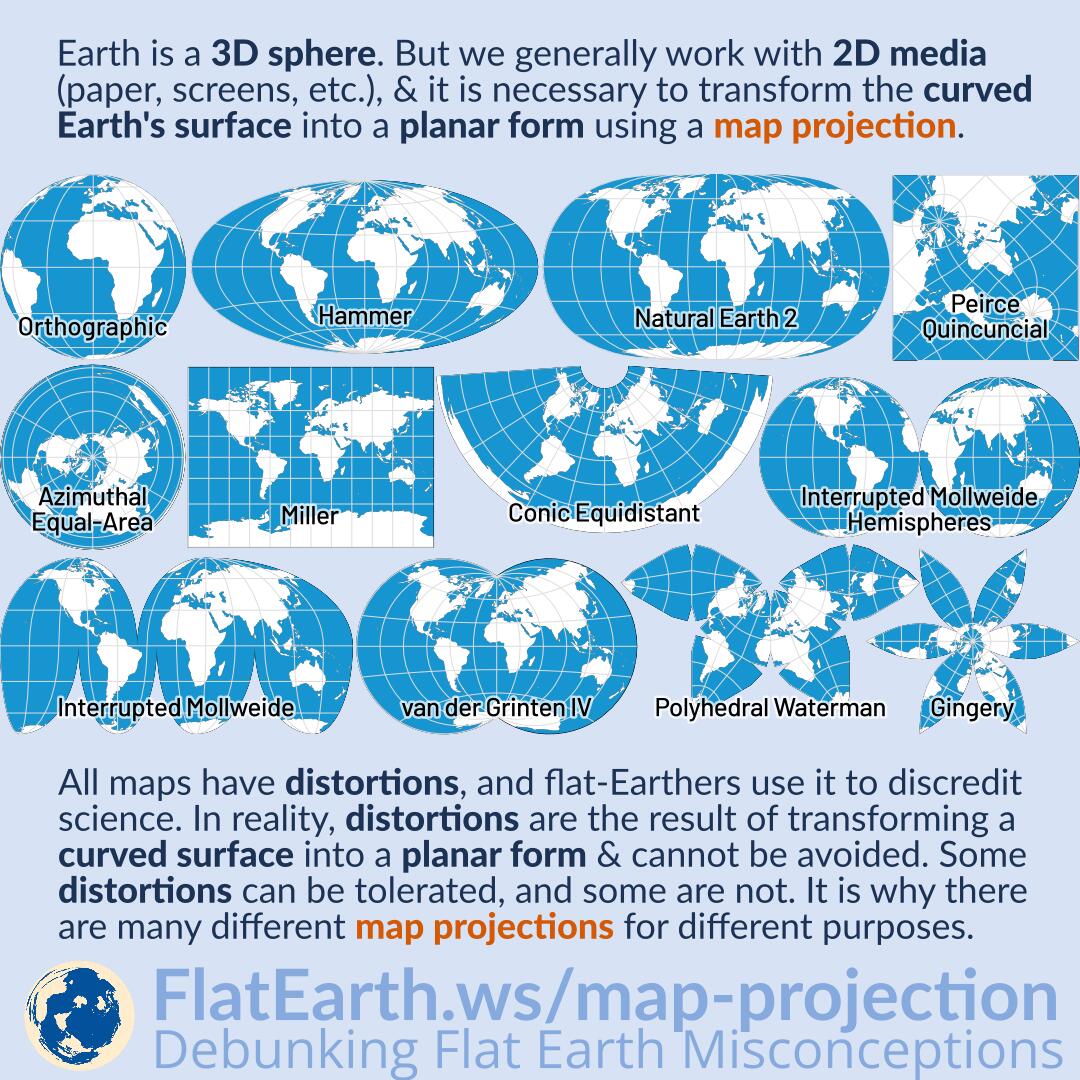
The Earth, a sphere, is a challenging subject to represent on a flat surface. This is where map projections come into play. Map projections are mathematical formulas that transform the Earth’s three-dimensional surface onto a two-dimensional plane, enabling us to visualize our planet on maps. Understanding these projections is crucial for accurately interpreting and utilizing geographic data.
The Challenge of Flattening the Globe
Imagine trying to flatten an orange peel without tearing or stretching it. This is the inherent challenge of representing the Earth’s curved surface on a flat map. No projection can perfectly capture all aspects of the Earth’s shape and size, leading to distortions in area, shape, distance, or direction.
Types of Map Projections
Map projections are broadly categorized based on the surface onto which the Earth is projected. The three primary categories are:
-
Cylindrical Projections: These projections imagine a cylinder wrapped around the globe, with the Earth’s surface projected onto the cylinder. Examples include the Mercator projection, commonly used for navigation due to its preservation of angles and shapes along lines of longitude.
-
Conic Projections: Conic projections utilize a cone that intersects the Earth at two points. This projection often preserves areas and shapes well near the points of intersection, but introduces distortions as one moves away from these points. The Lambert conformal conic projection, commonly used for topographic maps, is an example.
-
Azimuthal Projections: These projections use a flat plane that touches the Earth at a single point, known as the tangent point. Azimuthal projections are often used for polar regions or global representations, with distortions increasing as one moves away from the tangent point. The azimuthal equidistant projection, which preserves distances from the tangent point, is a common example.
Understanding Distortion
Distortion, an inherent characteristic of all map projections, manifests in various ways:
-
Area Distortion: Areas on the map may be exaggerated or diminished compared to their true size.
-
Shape Distortion: Shapes, particularly in regions far from the projection’s point of reference, may be elongated or compressed.
-
Distance Distortion: Distances between points on the map may not reflect the actual distances on the Earth.
-
Direction Distortion: Angles and bearings may be distorted, making it difficult to determine accurate directions.
Choosing the Right Projection
Selecting the appropriate map projection depends on the specific purpose of the map. Some key considerations include:
-
Intended Use: A navigation map requires a projection that preserves angles, while a map showing population density requires a projection that accurately represents areas.
-
Geographic Area: The region of interest plays a crucial role in choosing a projection. For example, a map of the United States may benefit from a conic projection, while a map of the entire globe may require an azimuthal projection.
-
Desired Distortion: The type and extent of distortion that can be tolerated must be considered.
Benefits of Understanding Map Projections
Understanding map projections is crucial for:
-
Accurate Interpretation of Maps: Recognizing the distortions inherent in a projection allows for a more accurate understanding of the information presented on a map.
-
Effective Geographic Analysis: Selecting the appropriate projection for a particular analysis ensures the reliability of the results.
-
Informed Decision-Making: Understanding the limitations of map projections helps in making informed decisions based on geographic data.
FAQs
Q: Why are there different map projections?
A: Different projections are designed to minimize specific distortions for different purposes. No single projection can accurately represent all aspects of the Earth on a flat surface.
Q: What is the most accurate map projection?
A: There is no single "most accurate" projection. Each projection introduces different types of distortions, and the best choice depends on the intended use of the map.
Q: Can I create my own map projection?
A: Yes, it is possible to create custom map projections. However, this requires advanced mathematical knowledge and software.
Q: How can I tell what projection a map uses?
A: Maps often include a projection description or a projection code in the map’s metadata.
Tips for Using Map Projections
-
Be aware of the distortions: Always consider the inherent distortions of the projection being used.
-
Choose the appropriate projection: Select a projection that minimizes the distortions relevant to the map’s purpose.
-
Consult multiple projections: Comparing maps created using different projections can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the geographic data.
Conclusion
Map projections are essential tools for representing the Earth’s surface on a flat map. Understanding the different types of projections, their inherent distortions, and the factors influencing their selection enables accurate interpretation and effective utilization of geographic data. By acknowledging the limitations of these projections, we can leverage their power to visualize and analyze our world with greater precision and insight.

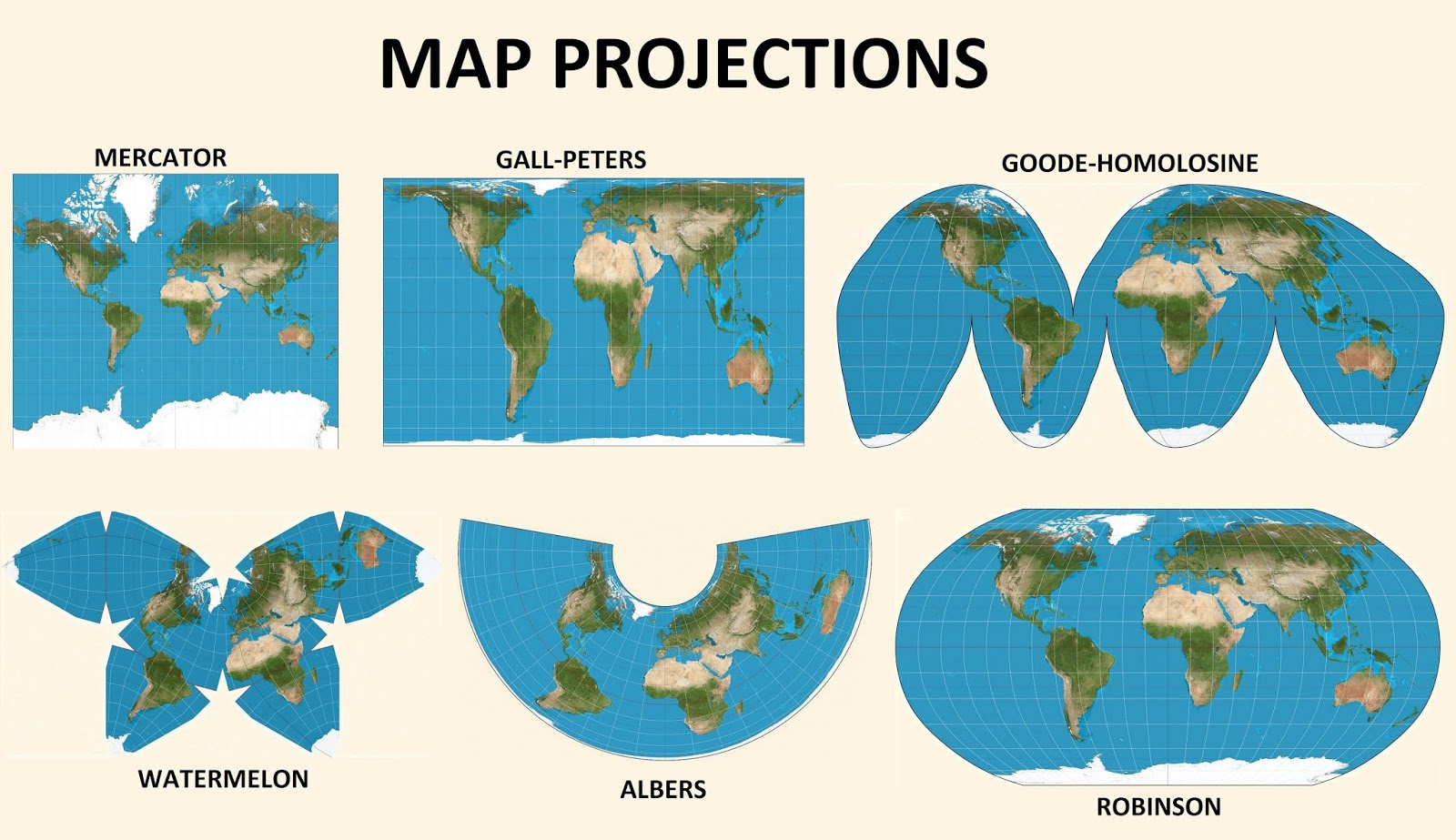

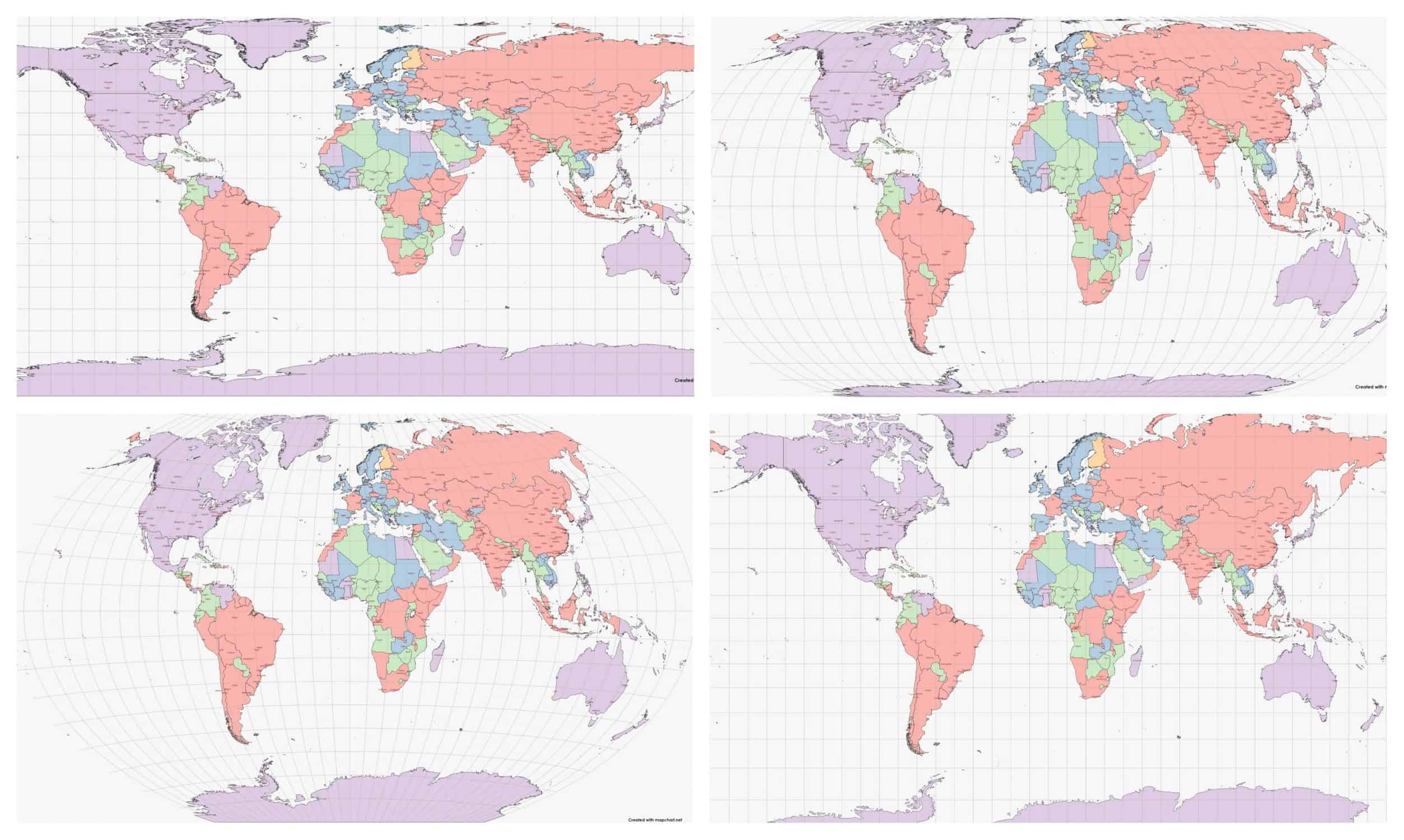
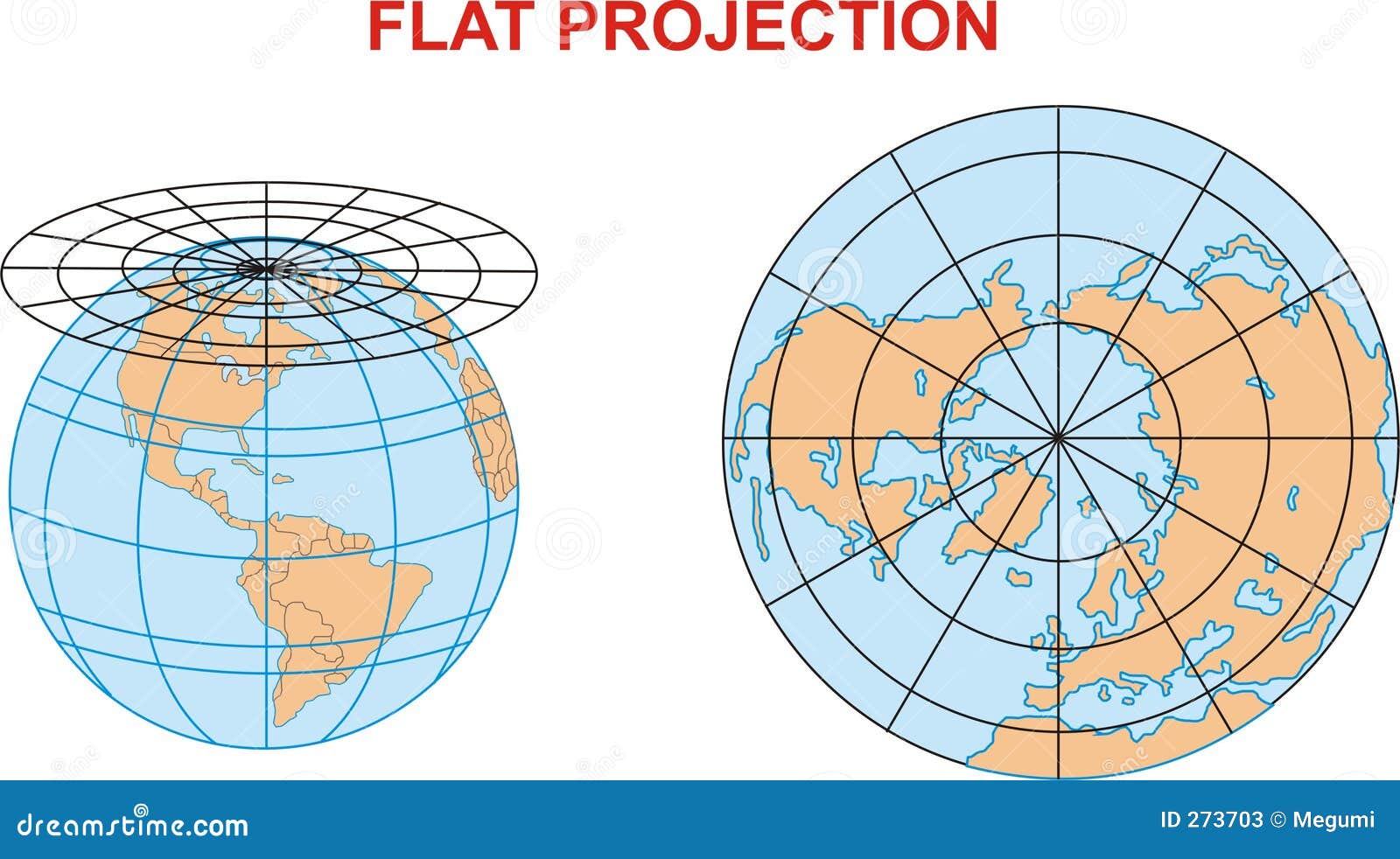



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the World on a Flat Surface: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projections. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!