Unveiling the World: An Exploration of Map Projections and Their Visual Representations
Related Articles: Unveiling the World: An Exploration of Map Projections and Their Visual Representations
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the World: An Exploration of Map Projections and Their Visual Representations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the World: An Exploration of Map Projections and Their Visual Representations
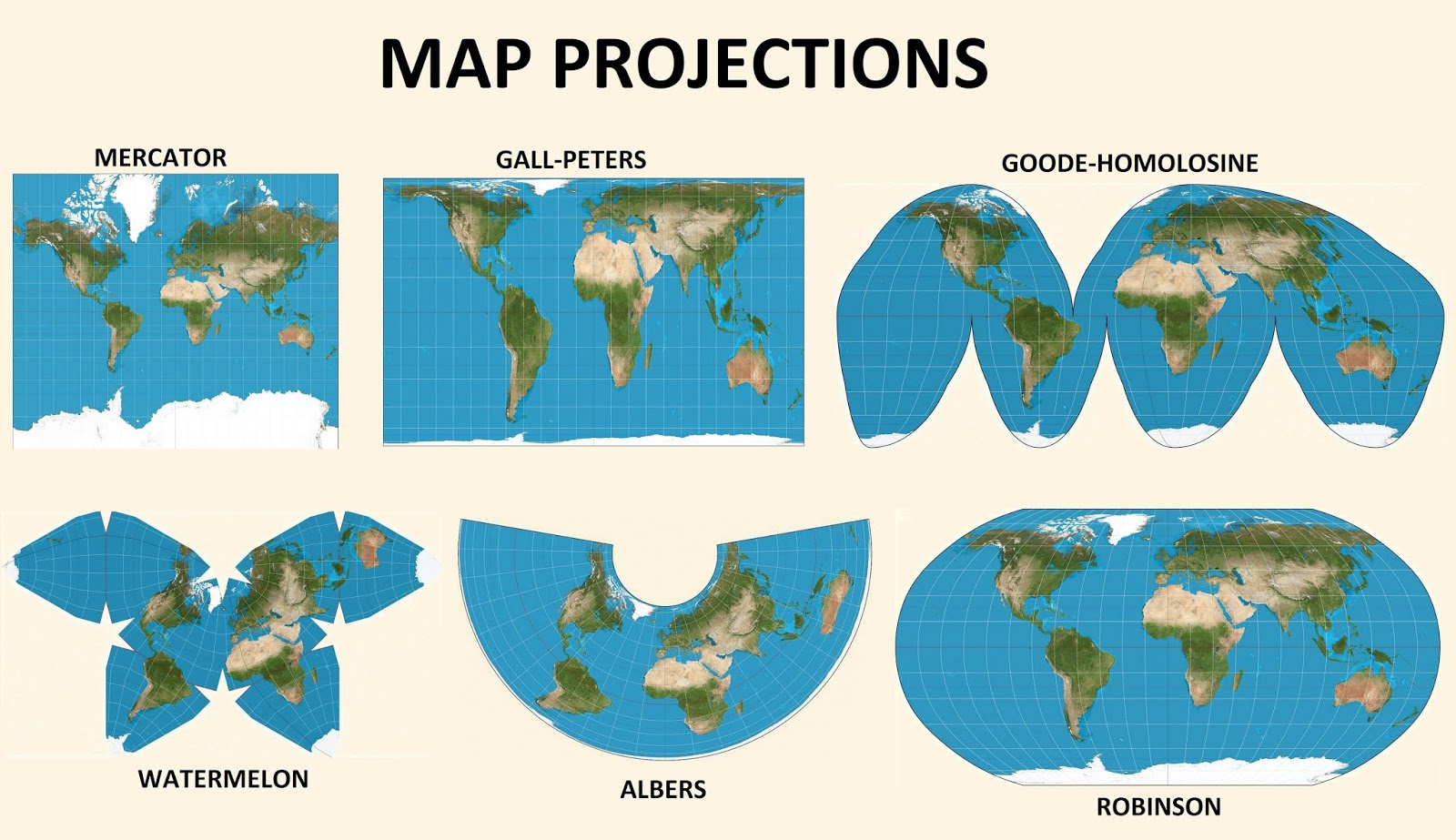
The Earth, a sphere of boundless beauty and complexity, presents a unique challenge to cartographers: how to represent its three-dimensional form on a two-dimensional surface. This challenge has led to the development of map projections, ingenious mathematical transformations that translate the curved surface of the Earth onto a flat plane. While these projections are essential for visualizing our planet, they inevitably introduce distortions, a consequence of the inherent incompatibility between spheres and flat surfaces.
The Essence of Map Projections:
Imagine trying to flatten an orange peel without tearing it. This seemingly impossible task mirrors the challenge of map projections. To create a map, cartographers must choose a projection, a specific mathematical formula that dictates how the Earth’s surface is transformed onto a plane. This process invariably involves compromises, as it is impossible to preserve all properties of the Earth’s surface – such as area, shape, distance, and direction – simultaneously.
Understanding the Distortions:
The choice of projection determines the type and extent of distortions introduced. Some projections prioritize preserving area, while others focus on maintaining shape or direction. For example, the Mercator projection, widely used for navigation, accurately represents angles and shapes along the equator but significantly exaggerates the size of landmasses towards the poles. Conversely, the Gall-Peters projection, designed to depict accurate areas, distorts shapes and distances.
Types of Map Projections:
Map projections are broadly categorized based on their geometric properties:
- Cylindrical Projections: These projections wrap a cylinder around the globe, projecting the Earth’s features onto the cylinder’s surface. The Mercator projection is a prime example of this type.
- Conic Projections: These projections use a cone that intersects the globe, projecting the Earth’s features onto the cone’s surface. Conic projections are well-suited for representing mid-latitude regions.
- Azimuthal Projections: These projections project the Earth’s features onto a plane tangent to the globe at a specific point. Azimuthal projections are ideal for depicting polar regions.
Visualizing Map Projections Through Video:
Video plays a crucial role in understanding and appreciating the complexities of map projections. By animating the projection process, videos offer a dynamic and engaging way to demonstrate how different projections distort the Earth’s surface. They can visually illustrate the trade-offs involved in choosing a specific projection, highlighting the distortions introduced in area, shape, distance, and direction.
Importance of Map Projections Video:
Beyond their educational value, map projections videos serve several important purposes:
- Enhanced Understanding: Videos provide a clear and intuitive way to explain the concept of map projections, making it accessible to a broader audience.
- Visualization of Distortions: Animations vividly showcase the distortions inherent in different projections, helping viewers understand their limitations.
- Comparison of Projections: Videos can effectively compare different projections side-by-side, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses.
- Promoting Critical Thinking: By visualizing the inherent biases in map projections, videos encourage viewers to think critically about the information presented in maps.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: Why are there so many different map projections?
A: Different map projections are designed to prioritize specific properties, such as area, shape, or direction. The choice of projection depends on the intended use of the map.
Q: Is there a "perfect" map projection?
A: No, there is no perfect map projection that can accurately represent all properties of the Earth’s surface. Every projection involves compromises and distortions.
Q: How can I choose the right map projection for my needs?
A: Consider the purpose of the map and the properties that are most important to preserve. Consult with a cartographer or use online resources to find suitable projections.
Tips for Using Map Projections Video Effectively:
- Choose videos with clear explanations and animations.
- Focus on the key distortions introduced by each projection.
- Compare different projections side-by-side to highlight their differences.
- Encourage viewers to critically analyze the information presented in maps.
Conclusion:
Map projections are essential tools for understanding and representing our planet. While they inevitably introduce distortions, they provide valuable insights into the Earth’s shape, size, and relationships. Video plays a crucial role in explaining these concepts, offering a dynamic and engaging way to visualize the complexities of map projections and their impact on our perception of the world. By understanding the limitations and strengths of different projections, we can develop a more critical and informed understanding of the maps we encounter in our daily lives.





![]()


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the World: An Exploration of Map Projections and Their Visual Representations. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!