Unveiling the World: A Guide to Map Projections
Related Articles: Unveiling the World: A Guide to Map Projections
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the World: A Guide to Map Projections. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the World: A Guide to Map Projections
![]()
The world, in its entirety, is a three-dimensional sphere. Representing this complex shape on a flat surface, a two-dimensional map, necessitates a transformation. This is where map projections come into play. They are mathematical formulas that translate the Earth’s curved surface onto a flat plane, enabling us to visualize and understand geographical information. However, this transformation inevitably introduces distortions, as it is impossible to perfectly represent a sphere on a flat surface without altering some aspects of the original shape.
Understanding the Distortion:
The essence of a map projection lies in its ability to preserve certain properties of the Earth while compromising others. These properties include:
- Area: Preserving the relative size of landmasses.
- Shape: Maintaining the accurate shape of geographical features.
- Distance: Representing accurate distances between points.
- Direction: Preserving the correct bearing between locations.
No single projection can perfectly preserve all these properties simultaneously. Consequently, each projection prioritizes specific features, leading to varying degrees of distortion in others.
A Visual Journey Through Projections:
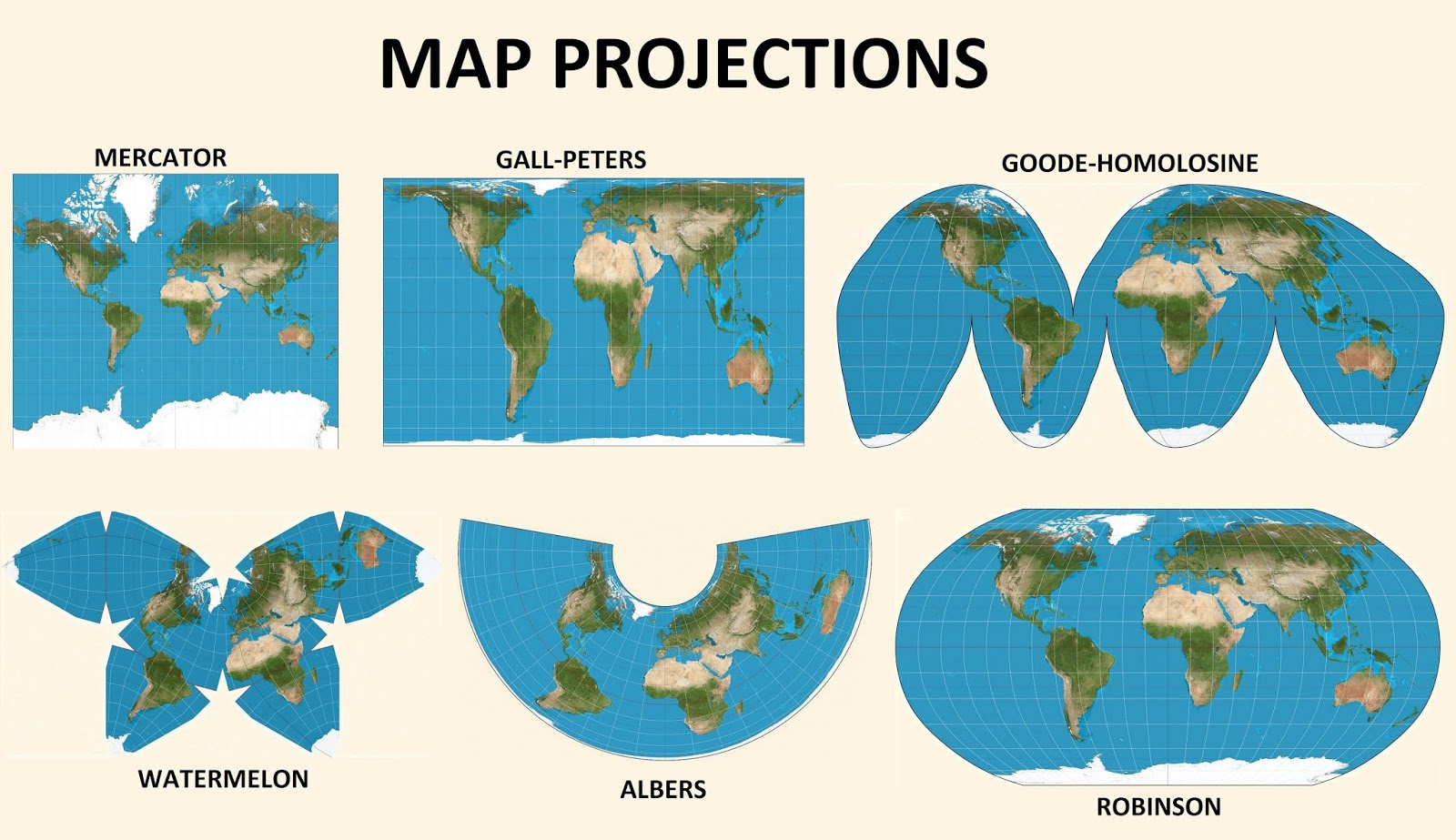
A map projections poster serves as a visual guide to understanding the diverse world of map projections. It typically showcases various projections, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses. Here are some common projections featured on such posters:
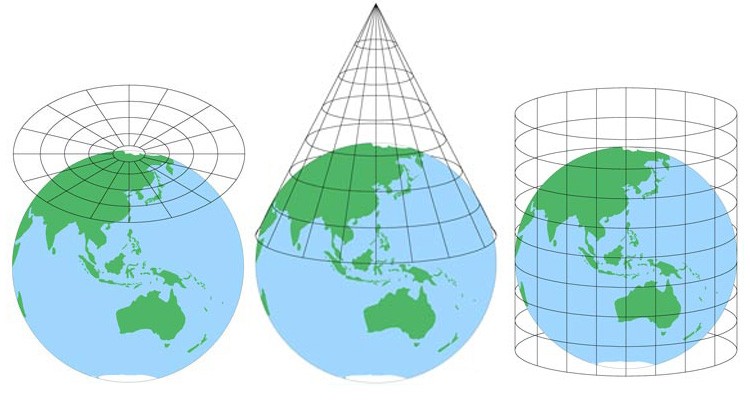
1. Cylindrical Projections:
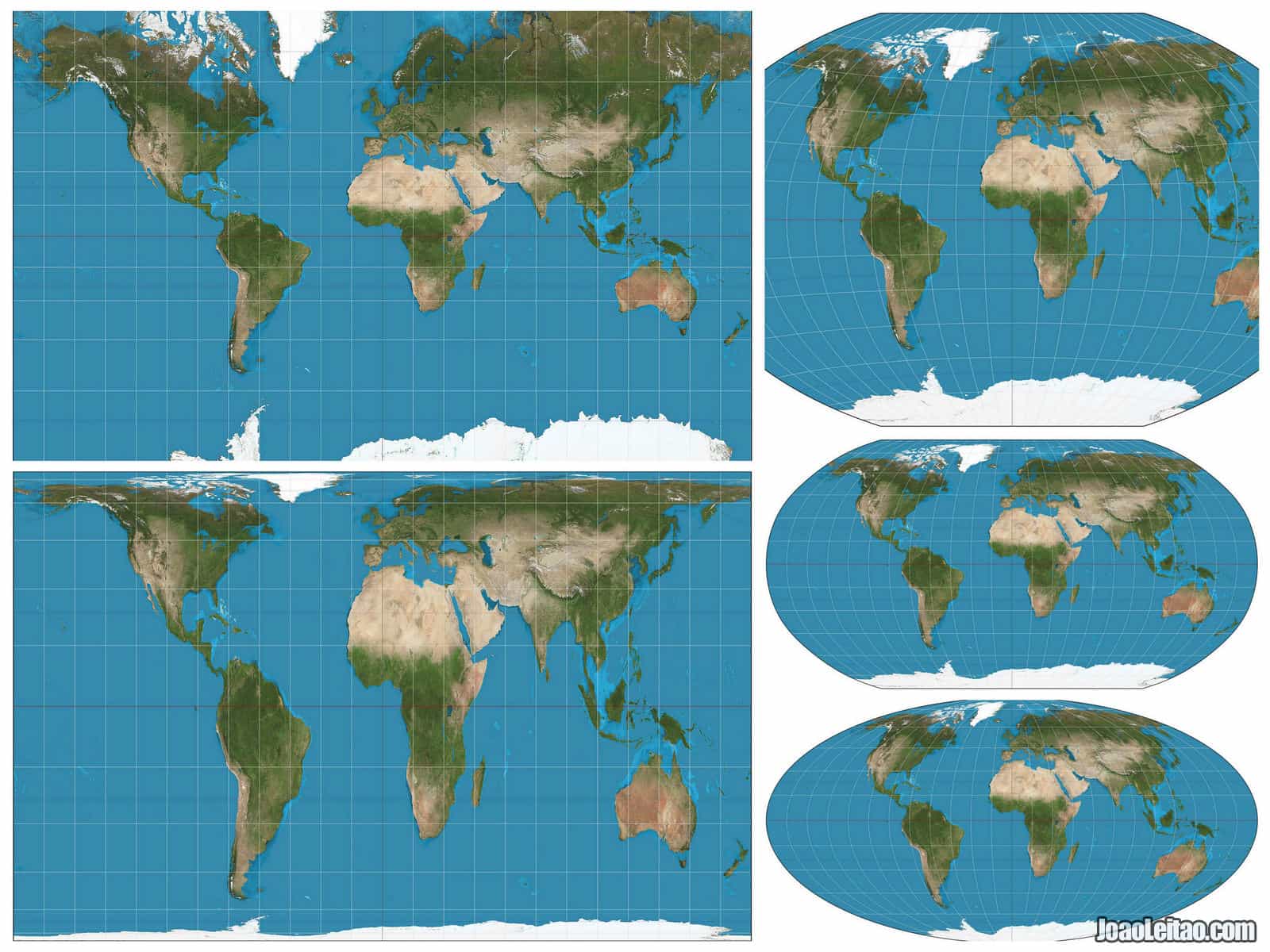
- Mercator Projection: Popularized for navigation, this projection preserves angles and shapes at the equator, but distorts areas significantly towards the poles, making Greenland appear larger than South America.
- Transverse Mercator Projection: This projection is widely used for topographic maps, as it preserves distances and shapes along a central meridian.
- Gall-Peters Projection: This projection emphasizes accurate area representation, showing continents in their true relative sizes, but distorts shapes, particularly near the poles.
2. Conic Projections:
- Albers Equal-Area Conic Projection: This projection preserves area, making it suitable for representing large landmasses, but distorts shapes and distances towards the edges of the map.
- Lambert Conformal Conic Projection: This projection maintains angles and shapes, making it ideal for mapping regions with a north-south orientation, but distorts distances and areas further from the central meridian.
3. Azimuthal Projections:
- Stereographic Projection: This projection preserves angles and shapes, making it useful for mapping polar regions. It distorts areas significantly towards the edges of the map.
- Orthographic Projection: This projection shows the Earth as it would appear from space, with a circular view centered on a specific point. It distorts distances and shapes towards the edges of the map.
4. Other Notable Projections:
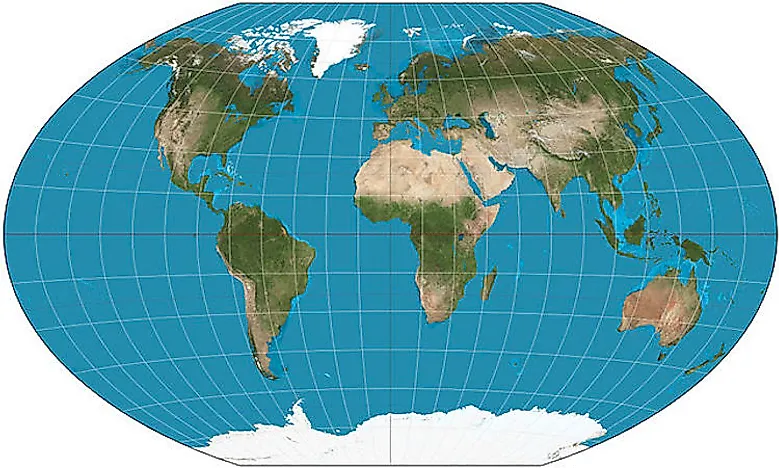
- Robinson Projection: This projection is a compromise between area and shape, aiming to minimize distortion across the map.
- Goode Homolosine Projection: This projection preserves areas, but distorts shapes, particularly near the poles, creating an interrupted projection with gaps between continents.
The Importance of Understanding Map Projections:
A map projections poster serves as a crucial tool for understanding the limitations and strengths of different projections. This knowledge is essential in various fields, including:
- Geography and Cartography: Choosing the appropriate projection for specific mapping purposes.
- Navigation: Using projections that preserve angles and distances for accurate navigation.
- Data Analysis: Interpreting data displayed on maps, understanding potential distortions in the representation.
- Education: Raising awareness about the complexities of representing the Earth on a flat surface.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Map Projections:
1. Why are there so many different map projections?
Different projections prioritize different properties, leading to a variety of choices depending on the intended use. Each projection has its strengths and weaknesses, making it suitable for specific purposes.
2. Which projection is the most accurate?
There is no single "most accurate" projection, as all projections introduce some degree of distortion. The accuracy depends on the specific property being preserved and the intended use of the map.
3. How can I choose the right projection for my needs?
Consider the purpose of the map, the area being mapped, and the properties that need to be preserved. For example, for mapping a global region, an equal-area projection might be suitable, while for navigation, a conformal projection is preferable.
4. Are there any projections that are completely distortion-free?
No, all projections introduce some degree of distortion. However, some projections minimize distortion in specific areas or for specific properties.
5. What is the difference between a map projection and a map?
A map projection is a mathematical formula that transforms the Earth’s surface onto a flat plane. A map is a visual representation of geographical information based on a specific projection.
Tips for Using a Map Projections Poster:
- Explore the different projections: Examine the various projections featured on the poster, noting their strengths and weaknesses.
- Compare and contrast: Compare the representations of the same region on different projections to understand how distortion varies.
- Consider the purpose: Think about the intended use of a map and choose a projection that best suits the purpose.
- Engage with the visual aids: Use the visual aids on the poster to understand the distortions introduced by different projections.
Conclusion:
Map projections are essential tools for representing the Earth’s surface on a flat plane. While they introduce distortions, understanding these distortions is crucial for accurate interpretation and analysis of geographical information. A map projections poster serves as a valuable resource for learning about the diverse world of map projections, their strengths, weaknesses, and applications. By understanding the complexities of map projections, we can navigate the world with greater accuracy and insight.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the World: A Guide to Map Projections. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!