Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projections
Related Articles: Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projections
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projections. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projections
![]()
The Earth, a sphere teeming with life and history, presents a challenge for cartographers: how to accurately depict its three-dimensional surface on a two-dimensional plane. This seemingly impossible task is tackled through the art and science of map projections. These ingenious transformations allow us to represent our planet’s complex geography, facilitating navigation, analysis, and understanding of the world around us.
A Journey from Sphere to Plane:
Imagine trying to flatten a perfectly round orange peel without tearing or stretching it. This is analogous to the challenge faced when projecting a sphere onto a flat surface. Map projections, by their very nature, involve distortions. They are not perfect replicas but rather representations that prioritize certain aspects of the Earth’s surface at the expense of others. This trade-off between accuracy and practicality is the essence of map projections.
The Fundamentals of Projections:
At the heart of every map projection lies a mathematical formula that governs the transformation of spherical coordinates (longitude and latitude) to planar coordinates (x and y). This formula determines the projection’s characteristics, including its:
- Shape: Projections can preserve shapes locally or globally, leading to different types like cylindrical, conic, and azimuthal.
- Area: Some projections maintain accurate area ratios, while others prioritize shape or distance.
- Distance: Projections can accurately depict distances along specific lines or across the entire map.
Common Map Projections and their Applications:
The selection of a map projection is not arbitrary. It is determined by the specific purpose for which the map is intended. Different projections excel in different areas, showcasing the inherent trade-offs between accuracy and specific needs.
1. Cylindrical Projections:
- Mercator Projection: This projection, popular for navigation, preserves angles and shapes locally but distorts areas significantly towards the poles. This leads to an exaggerated depiction of landmasses near the poles.
- Transverse Mercator Projection: A variation of the Mercator projection, this projection is used for large-scale maps and is particularly useful for mapping countries with a predominantly north-south orientation.
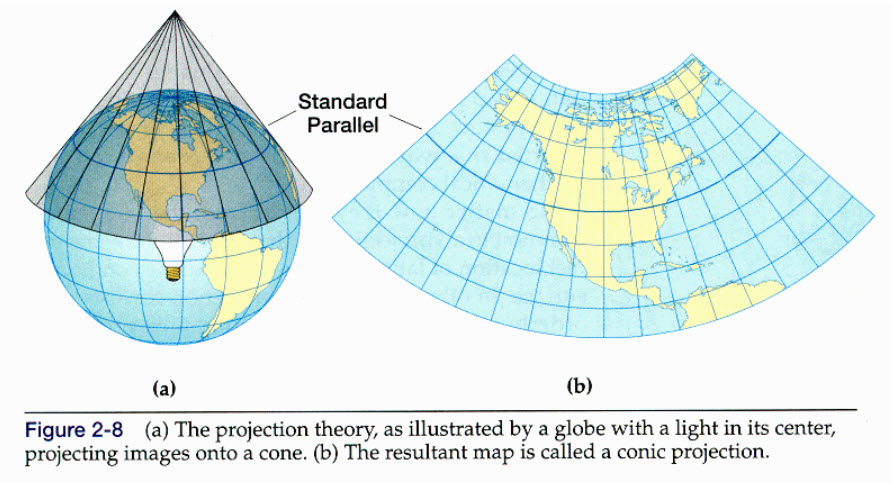
2. Conic Projections:
- Albers Equal-Area Conic Projection: This projection preserves area, making it ideal for thematic maps that depict spatial distribution of data. It is commonly used for mapping large regions like continents.
- Lambert Conformal Conic Projection: This projection preserves shapes locally, making it suitable for maps focusing on regional details. It is commonly used for mapping states and smaller geographic areas.
3. Azimuthal Projections:
- Stereographic Projection: This projection preserves angles and shapes locally, offering a clear view of a specific area. It is commonly used for mapping polar regions.
- Orthographic Projection: This projection depicts the Earth as it would appear from a point in space, preserving the relative sizes of landmasses. It is commonly used for creating world maps.
Beyond the Basics: Understanding the Distortions:
While map projections strive to preserve certain aspects of the Earth, they inevitably introduce distortions. These distortions are not random but follow predictable patterns based on the chosen projection.
- Area Distortion: Some projections, like the Mercator projection, significantly exaggerate the areas of landmasses near the poles. This can lead to misinterpretations of the relative sizes of countries.
- Shape Distortion: While some projections preserve shapes locally, they can distort the overall shape of continents or oceans. This can be particularly noticeable in projections that prioritize area preservation.
- Distance Distortion: Not all projections can accurately represent distances across the entire map. Some projections may accurately depict distances along specific lines, while others may distort distances in all directions.
The Importance of Map Projections:
Despite their limitations, map projections play a crucial role in our understanding of the world. They are essential for:
- Navigation: Projections like the Mercator projection are crucial for seafaring and air travel, providing accurate directions and distances.
- Spatial Analysis: Projections allow us to analyze spatial data, such as population density, climate patterns, and resource distribution, providing insights into global trends and patterns.
- Communication: Maps serve as a powerful tool for communicating geographic information, enabling us to visualize and understand complex relationships between different locations and phenomena.
Navigating the World of Projections:
Choosing the right map projection is crucial for conveying accurate information and avoiding misinterpretations. Here are some tips to guide your selection:
- Consider the intended use of the map: Determine the primary purpose of the map, whether it is for navigation, spatial analysis, or communication.
- Understand the inherent distortions: Be aware of the limitations of different projections and choose one that minimizes distortions for the intended purpose.
- Consult with experts: If you are unsure about the best projection for your needs, consult with cartographers or GIS specialists.
Conclusion:
Map projections are not merely tools for representing the Earth; they are powerful instruments for understanding our planet and its complexities. By understanding the principles of map projections and the inherent trade-offs involved, we can navigate the world of cartography with greater awareness and precision. From navigating the oceans to analyzing global trends, map projections continue to shape our understanding of the world around us.
FAQs:
Q: What is the most accurate map projection?
A: There is no single "most accurate" map projection. Accuracy depends on the specific aspect of the Earth you are trying to represent. Each projection has its strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice depends on the intended use of the map.
Q: Why are map projections distorted?
A: Distortions are unavoidable when projecting a sphere onto a flat surface. The Earth’s curved surface cannot be perfectly flattened without stretching or tearing.
Q: How do I choose the right map projection for my needs?
A: Consider the purpose of your map, the geographic area you are mapping, and the specific aspects of the Earth you want to emphasize. Consult with experts or research different projections to find the best fit.
Q: Are there any map projections that are completely distortion-free?
A: No, all map projections introduce some form of distortion. However, some projections minimize distortions in certain areas, such as shape, area, or distance.
Q: What is the difference between a Mercator projection and a Robinson projection?
A: The Mercator projection is a cylindrical projection that preserves angles and shapes locally but distorts areas significantly towards the poles. The Robinson projection is a compromise projection that attempts to minimize distortions in area, shape, and distance but does not perfectly preserve any of them.
Q: How are map projections used in everyday life?
A: Map projections are used in a wide range of applications, including navigation, weather forecasting, resource management, and geographic information systems. They are essential for understanding the world around us and making informed decisions.
![]()
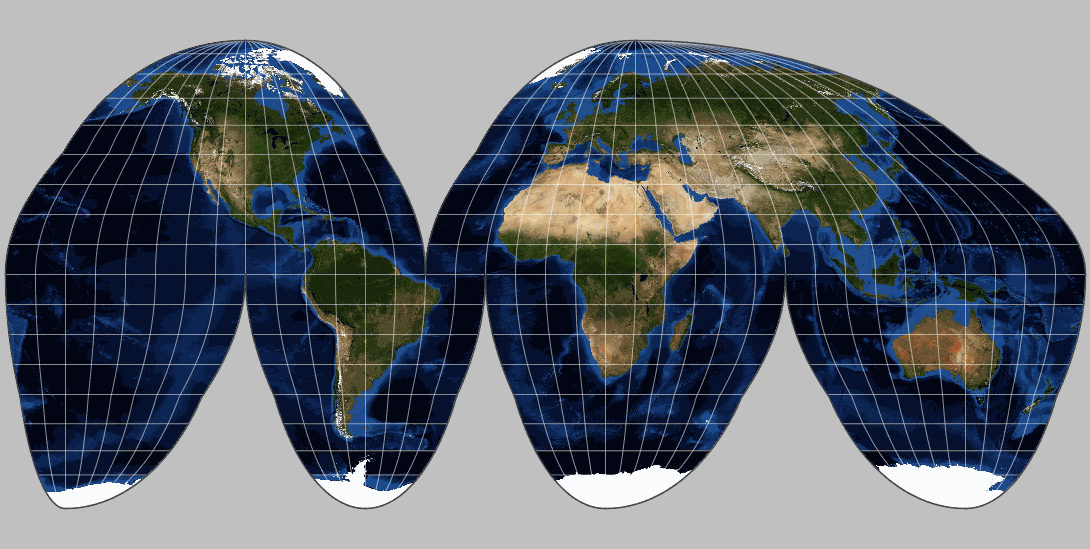


![50 Map Projections Types: A Visual Reference Guide [BIG LIST]](https://i.pinimg.com/736x/92/c0/c3/92c0c3a32f48481ca33ef54d5862f5a5.jpg)
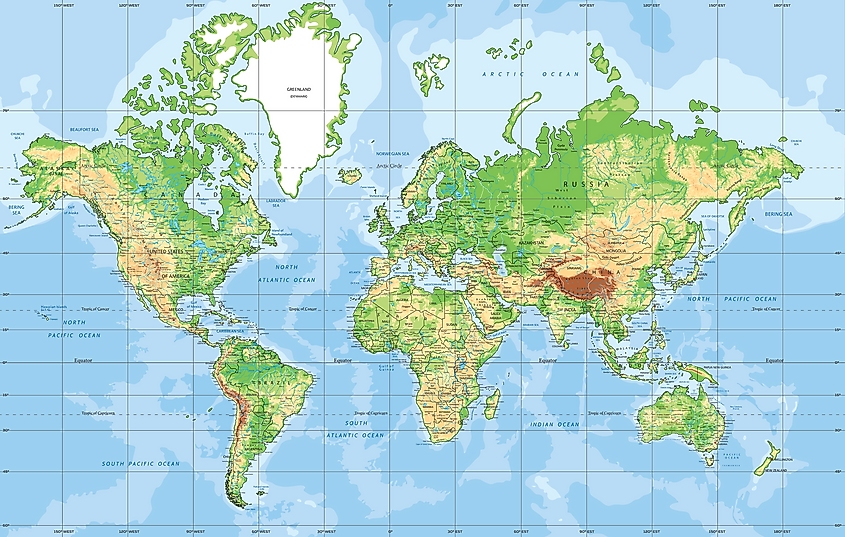
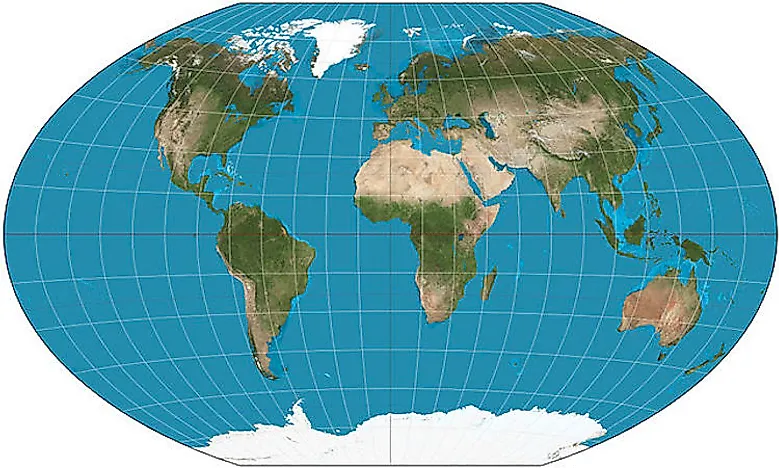
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projections. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!