Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projection Viewers
Related Articles: Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projection Viewers
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projection Viewers. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projection Viewers
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projection Viewers
- 3.1 What are Map Projection Viewers?
- 3.2 The Importance of Understanding Map Projections
- 3.3 A Closer Look at Different Map Projections
- 3.4 Using Map Projection Viewers for Informed Decision-Making
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.6 Tips for Using Map Projection Viewers Effectively
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projection Viewers
![]()
The Earth, a sphere suspended in space, presents a unique challenge to cartographers: how to represent its three-dimensional surface on a two-dimensional map. This challenge is addressed by map projections, mathematical transformations that flatten the globe onto a plane. However, this process inevitably introduces distortions, affecting the accurate representation of shapes, areas, distances, and directions. This is where map projection viewers come into play, offering a powerful tool for understanding and visualizing these distortions.
What are Map Projection Viewers?
Map projection viewers are interactive software applications that allow users to explore and compare different map projections. They provide a visual representation of how various projections distort the Earth’s surface, enabling users to analyze their suitability for specific applications. These viewers typically feature a user-friendly interface, allowing users to:
- Select and visualize various map projections: Users can choose from a wide range of projections, including cylindrical, conical, azimuthal, and others, each with its unique characteristics and distortions.
- Customize map settings: Users can adjust parameters like the projection type, center point, scale, and other settings to fine-tune the visualization.
- Compare projections side-by-side: This feature allows users to visually compare the distortions introduced by different projections, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses.
- Overlay data: Users can overlay geographical data, such as country boundaries, elevation, population density, or other relevant information, onto the projected map.
- Generate static images or interactive maps: Users can export their visualizations in various formats, including images, PDF files, or interactive web maps.
The Importance of Understanding Map Projections
The choice of map projection is crucial for accurately representing spatial data and conveying information effectively. Understanding the inherent distortions associated with each projection is essential for:
- Accurate distance measurement: Some projections preserve distances along specific lines, while others distort them significantly. This is particularly important for applications like navigation, travel planning, and resource management.
- Preserving area relationships: Certain projections maintain the accurate representation of areas, crucial for applications like population density mapping, resource distribution analysis, and environmental studies.
- Maintaining shape fidelity: Some projections prioritize accurate shape representation, essential for applications like geological mapping, land surveying, and urban planning.
- Understanding directional relationships: Projections can distort directions, leading to misinterpretations in applications like navigation, weather forecasting, and military operations.
By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of different projections, users can choose the most appropriate one for their specific needs, ensuring accurate data representation and informed decision-making.
A Closer Look at Different Map Projections
Map projections are broadly classified into three main categories:
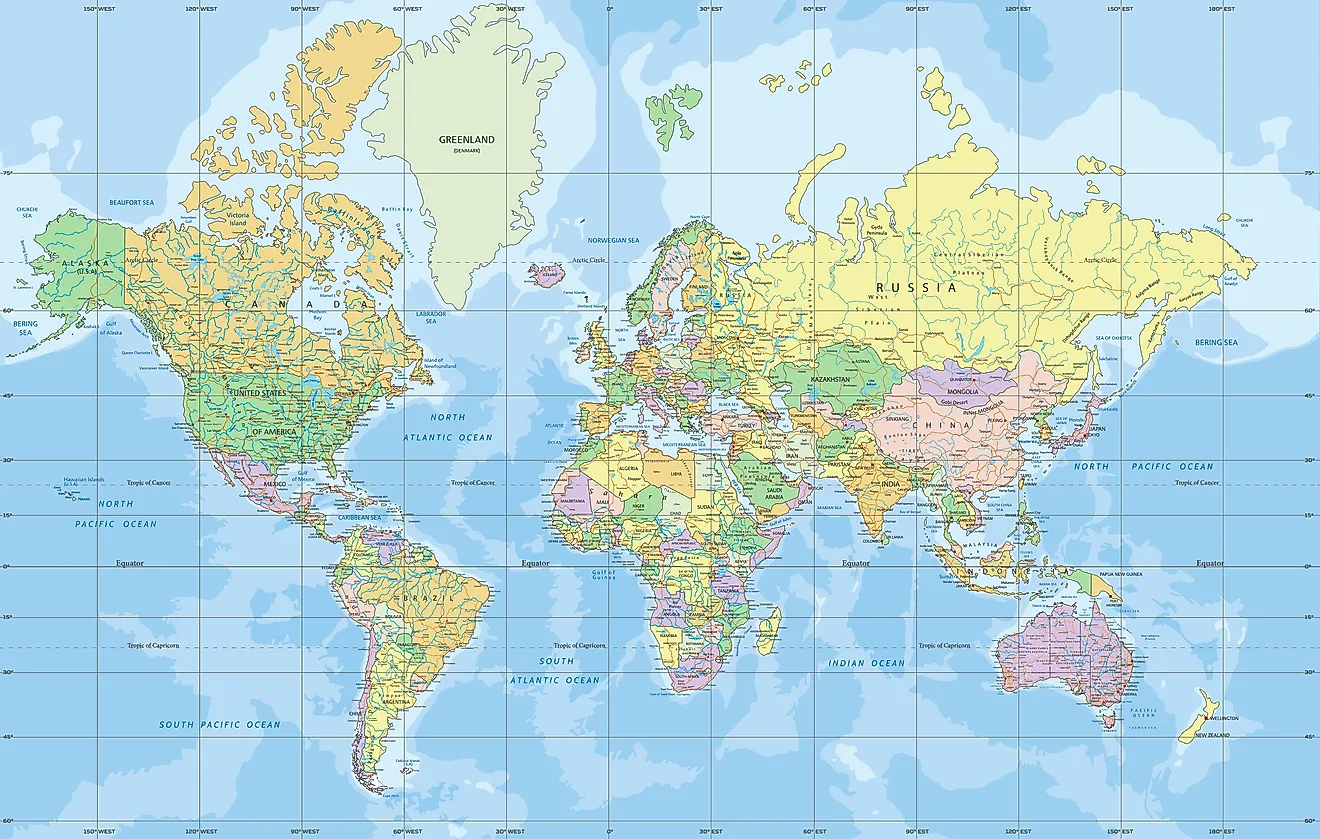
1. Cylindrical Projections: These projections imagine the Earth wrapped in a cylinder, with the map then unrolled. Examples include the Mercator projection, widely used for navigation due to its preservation of straight lines representing true directions, and the Transverse Mercator projection, often employed for large-scale mapping.
2. Conical Projections: These projections imagine a cone placed over the Earth, with the map then unrolled. Examples include the Lambert Conformal Conic projection, commonly used for regional mapping, and the Albers Equal-Area Conic projection, preserving area relationships.
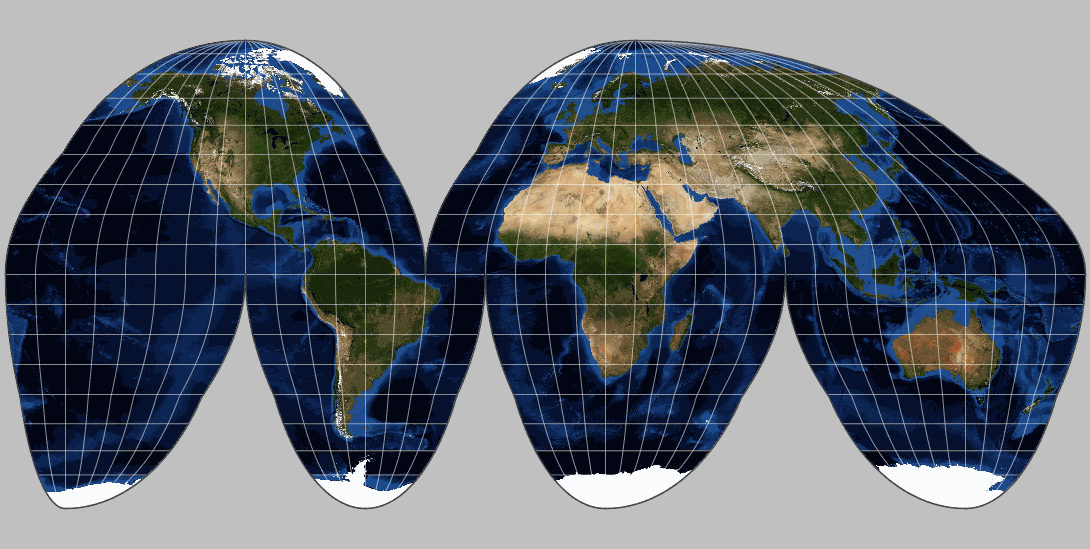
3. Azimuthal Projections: These projections imagine a plane touching the Earth at a specific point, with the map then projected onto the plane. Examples include the Stereographic projection, preserving angles and used for navigation, and the Orthographic projection, creating a realistic view of the Earth from a specific point in space.
Each projection type has its unique properties and distortions. Cylindrical projections, for instance, tend to exaggerate areas near the poles, while conical projections are generally more accurate for mid-latitude regions. Azimuthal projections excel at representing polar regions but introduce significant distortions at the equator.
Using Map Projection Viewers for Informed Decision-Making
Map projection viewers empower users to make informed decisions by providing a platform for:
- Visualizing and analyzing spatial data: Users can visualize and analyze geographical data, such as population distribution, climate patterns, or resource availability, in various projections, revealing insights into spatial relationships and trends.
- Comparing different projections for specific applications: By comparing projections side-by-side, users can identify the most suitable one for their specific needs, ensuring accurate data representation and effective communication.
- Understanding the limitations of different projections: Users can gain a deeper understanding of the inherent distortions associated with various projections, enabling them to interpret data critically and avoid misinterpretations.
- Communicating spatial information effectively: By using appropriate projections and visualizations, users can effectively communicate spatial information to diverse audiences, ensuring clarity and understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Why is it important to use a map projection viewer?
A: Map projection viewers allow users to visualize and understand the distortions inherent in different map projections, enabling them to choose the most appropriate projection for their specific needs and ensure accurate data representation.
Q: What are the different types of map projections available in viewers?
A: Map projection viewers typically offer a wide range of projections, including cylindrical, conical, azimuthal, and others, each with its unique characteristics and distortions.
Q: How can I use a map projection viewer to compare different projections?
A: Most viewers allow users to select and visualize multiple projections simultaneously, enabling side-by-side comparisons to highlight their strengths and weaknesses.
Q: Can I overlay data onto a projected map using a viewer?
A: Many viewers allow users to overlay geographical data, such as country boundaries, elevation, population density, or other relevant information, onto the projected map.
Q: What are some common applications of map projection viewers?
A: Map projection viewers are used in various fields, including geography, cartography, navigation, environmental studies, urban planning, and resource management.
Tips for Using Map Projection Viewers Effectively
- Start with a basic understanding of map projections: Familiarize yourself with the different types of projections and their inherent distortions.
- Explore different projections and their properties: Experiment with various projections to understand their strengths and weaknesses.
- Consider the specific application: Choose a projection that best suits your specific needs, considering factors like distance preservation, area accuracy, shape fidelity, and directionality.
- Overlay relevant data: Use the viewer to overlay geographical data onto the projected map to gain deeper insights into spatial relationships.
- Compare different projections side-by-side: Visualize and compare multiple projections simultaneously to identify the most suitable one for your application.
Conclusion
Map projection viewers play a vital role in understanding and visualizing the complexities of representing the Earth’s surface on a flat map. By offering a platform for exploring different projections, their distortions, and their suitability for specific applications, these viewers empower users to make informed decisions, ensuring accurate data representation and effective communication of spatial information. As technology continues to advance, map projection viewers will likely become even more sophisticated, offering users even greater insights into the intricate world of map projections and their impact on our understanding of the world around us.

![]()



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projection Viewers. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!