Unveiling the Power of Python’s map Function: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Python’s map Function: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Python’s map Function: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Python’s map Function: A Comprehensive Guide
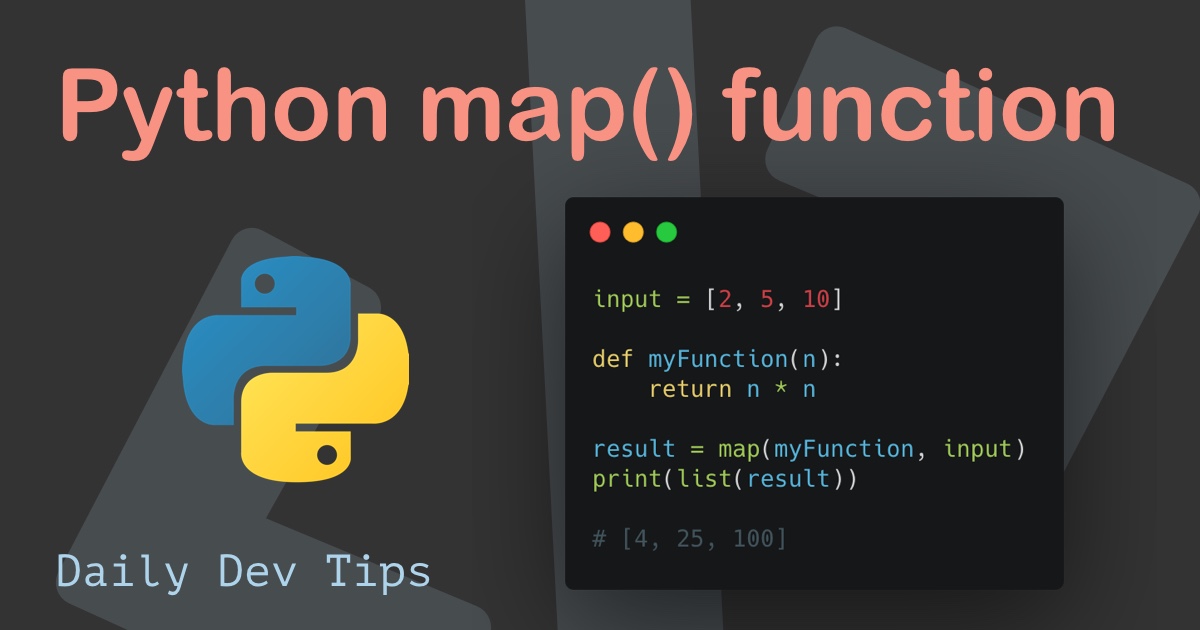
The map function in Python is a powerful tool for efficiently applying a given function to each element of an iterable, such as a list, tuple, or string. This concise and elegant function significantly streamlines code, enhances readability, and offers a more efficient approach to processing data.
Understanding the Essence of map
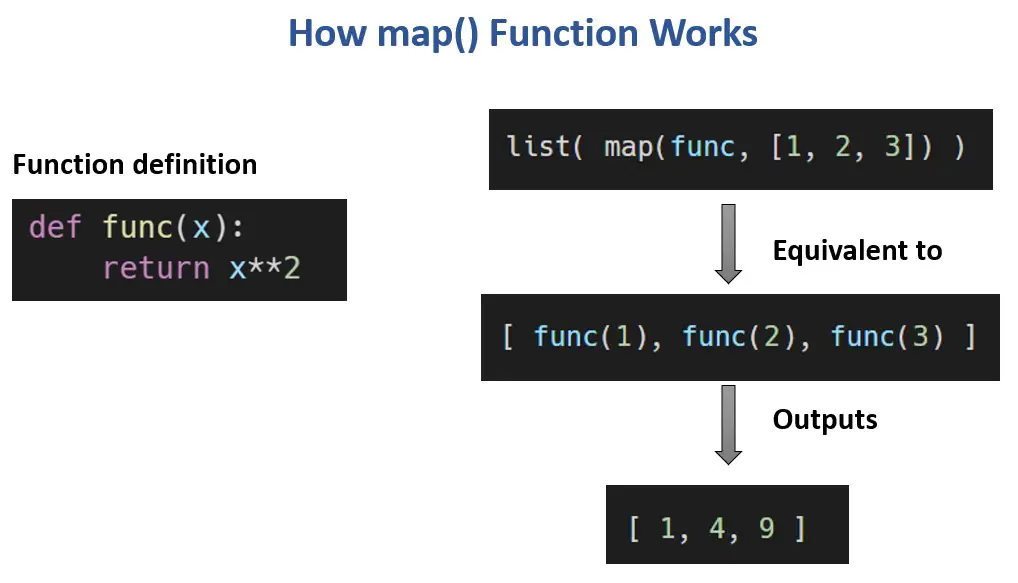
At its core, map operates as a higher-order function, meaning it takes another function as an argument. It then applies this function to every element within the provided iterable, generating a new iterable containing the transformed results.
Syntax and Functionality
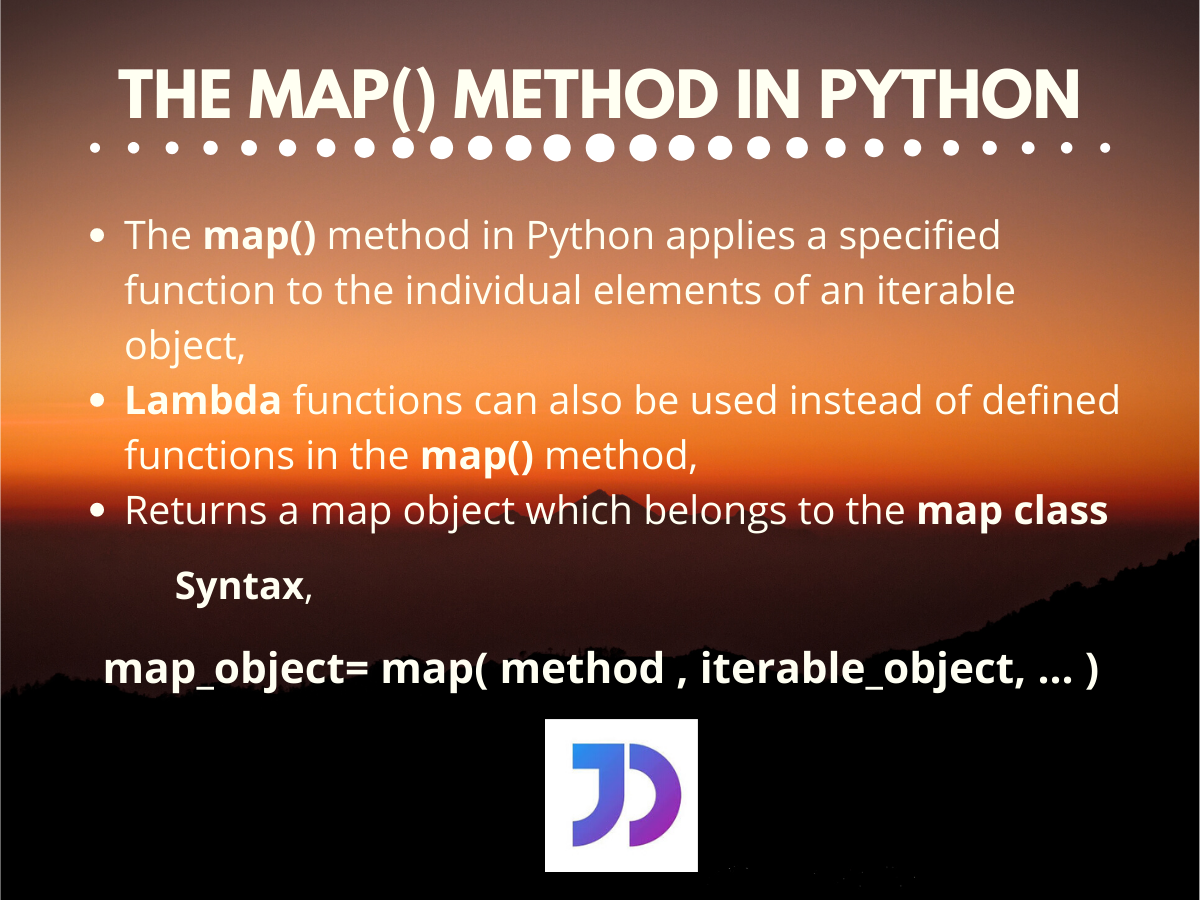
The syntax of the map function is straightforward:
map(function, iterable)-
function: The function to be applied to each element of the iterable. -
iterable: The sequence of elements to be processed.
Illustrative Examples
Let’s delve into practical examples to understand the versatility of map.
1. Squaring Numbers in a List:
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
def square(x):
return x * x
squared_numbers = map(square, numbers)
print(list(squared_numbers)) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]In this example, the square function multiplies each element of the numbers list by itself, producing a new list containing the squared values.
2. Converting Strings to Uppercase:
names = ["john", "jane", "peter", "mary"]
def to_uppercase(name):
return name.upper()
uppercase_names = map(to_uppercase, names)
print(list(uppercase_names)) # Output: ['JOHN', 'JANE', 'PETER', 'MARY']Here, the to_uppercase function converts each name in the names list to uppercase.
3. Applying Multiple Functions:
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
def square(x):
return x * x
def cube(x):
return x * x * x
squared_and_cubed = map(lambda x: (square(x), cube(x)), numbers)
print(list(squared_and_cubed)) # Output: [(1, 1), (4, 8), (9, 27), (16, 64), (25, 125)]This example demonstrates applying multiple functions simultaneously using a lambda function. It squares and cubes each number in the numbers list, generating a list of tuples containing the results.
Advantages of Using map
-
Conciseness and Readability: The
mapfunction offers a concise and elegant way to express the application of a function to multiple elements, enhancing code readability. -
Efficiency:
mapleverages Python’s built-in iteration mechanisms, often leading to improved performance compared to manually looping through elements. -
Functional Programming Paradigm:
mapaligns with the functional programming paradigm, promoting code that is more modular, reusable, and easier to test.
Beyond Basic Usage: Exploring Lambda Functions and Multiple Iterables
-
Lambda Functions:
mapseamlessly integrates with lambda functions, providing a concise way to define anonymous functions within themapcall.
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
doubled_numbers = map(lambda x: x * 2, numbers)
print(list(doubled_numbers)) # Output: [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]-
Multiple Iterables:
mapcan handle multiple iterables, applying the function to corresponding elements from each iterable.
numbers1 = [1, 2, 3]
numbers2 = [4, 5, 6]
def add(x, y):
return x + y
sums = map(add, numbers1, numbers2)
print(list(sums)) # Output: [5, 7, 9]Addressing Common Concerns
1. Understanding the Output of map:
The map function returns an iterator, not a list. To access the results, you need to explicitly convert the iterator to a list using list(map(...)).
2. Handling Iterables of Different Lengths:
When using multiple iterables, map stops processing once the shortest iterable is exhausted.
3. Choosing Between map and List Comprehensions:
Both map and list comprehensions offer similar functionality, but list comprehensions often provide a more concise and readable solution. However, map can be more efficient for complex functions or when working with multiple iterables.
FAQs
Q: When is it beneficial to use map instead of a loop?
A: map is generally preferred over loops when:
- You need to apply a function to each element of an iterable.
- The function is simple and concise.
- You value code readability and conciseness.
Q: Can map be used with nested iterables?
A: While map itself doesn’t directly handle nested iterables, you can use nested map calls or list comprehensions to achieve the desired result.
Q: How does map handle errors?
A: If the function applied by map raises an exception, the exception will be propagated, potentially halting the entire process.
Tips
-
Prioritize Readability: Use
mapwhen it enhances code readability and clarity. -
Consider Performance: For complex functions or large datasets,
mapmight offer performance advantages over loops. -
Explore Lambda Functions: Lambda functions can provide a concise and elegant way to define functions within the
mapcall. -
Embrace the Functional Paradigm:
mapaligns with the functional programming approach, promoting modularity and reusability.
Conclusion
The map function in Python is a valuable tool for streamlining code and enhancing efficiency. It offers a concise and elegant way to apply functions to iterables, promoting code readability and facilitating functional programming principles. By understanding the core principles and advantages of map, developers can leverage its power to write more efficient and expressive Python code.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Python’s map Function: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!