Unveiling the Power of Map Radius Plotters: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Spatial Relationships
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Map Radius Plotters: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Spatial Relationships
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Map Radius Plotters: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Spatial Relationships. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Map Radius Plotters: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Spatial Relationships
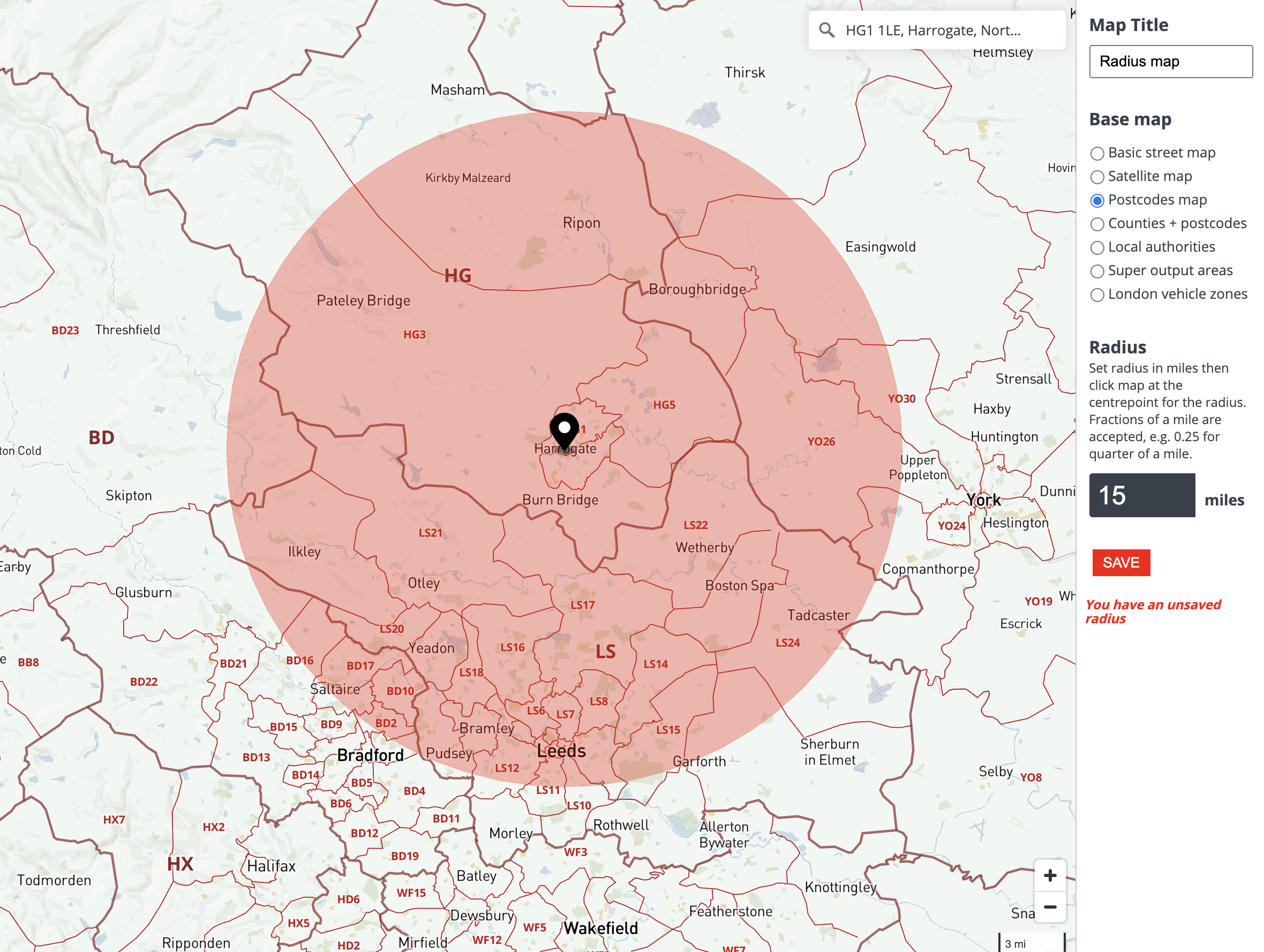
In the realm of spatial analysis and data visualization, the ability to understand and represent the geographical scope of phenomena is paramount. Map radius plotters emerge as powerful tools in this domain, enabling users to visually depict areas of influence, proximity, and service coverage with precision. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of map radius plotters, delving into their functionality, applications, benefits, and limitations.
Understanding Map Radius Plotters: A Visual Representation of Spatial Influence
A map radius plotter, also known as a circle drawing tool, is a software or online application designed to create circles or radius-based areas on maps. These circles represent a specific distance or range from a central point, often referred to as the "origin" or "focal point." The user defines the radius, typically in units of distance such as miles, kilometers, or meters, and the plotter generates a circle encompassing all locations within that specified distance from the origin.
The Essence of Map Radius Plotters: A Bridge Between Data and Visualization
The core strength of map radius plotters lies in their ability to transform raw data into visually compelling insights. By overlaying circles on existing maps, these tools provide a clear and intuitive representation of spatial relationships. This visualization process is particularly valuable for:
- Defining Service Areas: Businesses can utilize map radius plotters to define their service areas, showcasing the geographical reach of their operations. This facilitates customer acquisition, marketing campaigns, and logistics planning.
- Analyzing Proximity: Determining the proximity of points of interest, such as schools, hospitals, or retail outlets, to residential areas or specific demographics can be achieved through map radius plotters. This information is crucial for urban planning, community development, and market research.
- Assessing Impact Zones: In emergency management, environmental studies, or disaster planning, map radius plotters aid in visualizing the potential impact zone of events like natural disasters, industrial accidents, or disease outbreaks. This assists in preparedness and response efforts.
- Visualizing Geographic Coverage: Researchers, analysts, and marketers can use map radius plotters to visualize the coverage of surveys, data collection efforts, or marketing campaigns, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of geographic reach and potential biases.
A Deeper Dive into Functionality: Key Features and Capabilities
Beyond the basic function of drawing circles, modern map radius plotters offer a range of advanced features, enhancing their versatility and analytical power:
- Customizable Radius: Users can adjust the radius of the circles dynamically, enabling exploration of different spatial scales and impact zones.
- Multiple Origins: The ability to plot multiple circles from different origins allows for comparative analysis of service areas, proximity, or impact zones.
- Polygon Generation: Some map radius plotters can create polygons from the plotted circles, facilitating further analysis and calculations.
- Data Integration: Integration with external data sources allows for the overlay of demographic information, property data, or other relevant spatial data on the map, enriching the visualization.
- Interactive Visualization: Interactive map radius plotters enable users to zoom, pan, and manipulate the map, providing a dynamic and user-friendly experience.
- Export Options: The ability to export the generated maps in various formats (e.g., PNG, PDF, SVG) facilitates sharing and integration into reports and presentations.
Beyond Visualization: Applications Across Diverse Fields
The versatility of map radius plotters extends beyond visual representation, finding applications in a wide range of fields:
- Business and Marketing: Identifying potential customers, optimizing delivery routes, analyzing market penetration, and targeting specific demographics.
- Real Estate: Evaluating property values based on proximity to amenities, assessing market competition, and identifying optimal locations for new developments.
- Urban Planning: Planning public transportation systems, optimizing resource allocation, and assessing the impact of infrastructure projects.
- Emergency Management: Defining evacuation zones, identifying vulnerable areas, and coordinating rescue efforts.
- Environmental Studies: Mapping pollution dispersal zones, assessing the impact of environmental hazards, and monitoring wildlife populations.
- Healthcare: Analyzing the distribution of healthcare facilities, identifying underserved areas, and planning outreach programs.
- Education: Mapping school districts, assessing access to education, and planning school bus routes.
Benefits and Limitations: A Balanced Perspective
While map radius plotters offer significant advantages, it is essential to acknowledge their limitations:
Benefits:
- Enhanced Spatial Understanding: Map radius plotters provide a clear and intuitive visualization of spatial relationships, aiding in decision-making and communication.
- Simplified Analysis: The ability to visually represent data on maps simplifies complex spatial analysis, making it accessible to a wider audience.
- Improved Efficiency: Map radius plotters streamline tasks such as service area definition, proximity analysis, and impact zone assessment, saving time and resources.
- Data-Driven Insights: The visualization of spatial data enables users to draw data-driven conclusions and make informed decisions.
Limitations:
- Simplified Representation: Map radius plotters present a simplified view of reality, potentially neglecting complexities and nuances of the spatial landscape.
- Accuracy Dependence: The accuracy of the plotted circles depends on the underlying map data and the chosen radius unit, requiring careful consideration of data sources and limitations.
- Limited Analytical Capabilities: While map radius plotters provide visual insights, they are not substitutes for advanced spatial analysis tools capable of complex calculations and modeling.
Navigating the Landscape: Choosing the Right Map Radius Plotter
The abundance of available map radius plotters necessitates a thoughtful selection process:
- Functionality: Consider the specific features and capabilities required for the intended application, such as customizable radii, polygon generation, and data integration.
- Ease of Use: Choose a plotter with a user-friendly interface and intuitive navigation, facilitating seamless operation and data analysis.
- Data Sources: Ensure compatibility with the desired map data sources, including Google Maps, OpenStreetMap, or proprietary datasets.
- Pricing: Evaluate the pricing model, considering options such as free trials, subscription plans, or one-time purchase.
- Support: Assess the availability of technical support, documentation, and online resources for troubleshooting and guidance.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
Q: Are map radius plotters suitable for all types of spatial analysis?
A: While map radius plotters excel in visualizing proximity and coverage, they are not suitable for all types of spatial analysis. For complex calculations, modeling, and advanced spatial analysis, dedicated GIS software is recommended.
Q: What are the key factors to consider when choosing a radius unit for plotting circles?
A: The choice of radius unit depends on the context and the intended application. For local analysis, units like meters or kilometers may be suitable, while for regional or global analysis, miles or kilometers are preferred.
Q: Can map radius plotters be used for marketing and customer segmentation?
A: Yes, map radius plotters can be valuable tools for marketing and customer segmentation. By visualizing service areas and proximity to target demographics, businesses can tailor marketing campaigns and optimize customer acquisition efforts.
Q: Are there any limitations to the accuracy of map radius plotters?
A: The accuracy of plotted circles depends on the quality of the underlying map data and the chosen radius unit. Factors like terrain variations, map projections, and data resolution can influence the accuracy of the visualization.
Tips for Effective Use of Map Radius Plotters:
- Define a Clear Objective: Establish a specific goal for using the map radius plotter, whether it’s defining service areas, analyzing proximity, or visualizing impact zones.
- Choose the Right Data Sources: Select accurate and relevant map data sources that align with the intended application and geographical scope.
- Optimize Radius Settings: Experiment with different radii to explore various spatial scales and identify the most informative settings.
- Overlay Relevant Data: Integrate demographic information, property data, or other relevant spatial data to enrich the visualization and draw deeper insights.
- Interpret Results with Caution: Remember that map radius plotters provide a simplified representation of reality, and the results should be interpreted with caution and considered in the context of other relevant data.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Spatial Understanding
Map radius plotters emerge as essential tools for visualising spatial relationships and gaining insights from geographical data. Their ability to represent areas of influence, proximity, and coverage on maps facilitates informed decision-making, improved planning, and enhanced communication across diverse fields. By embracing the power of visualization, map radius plotters empower users to navigate the complexities of the spatial world, unlocking a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of places and phenomena.
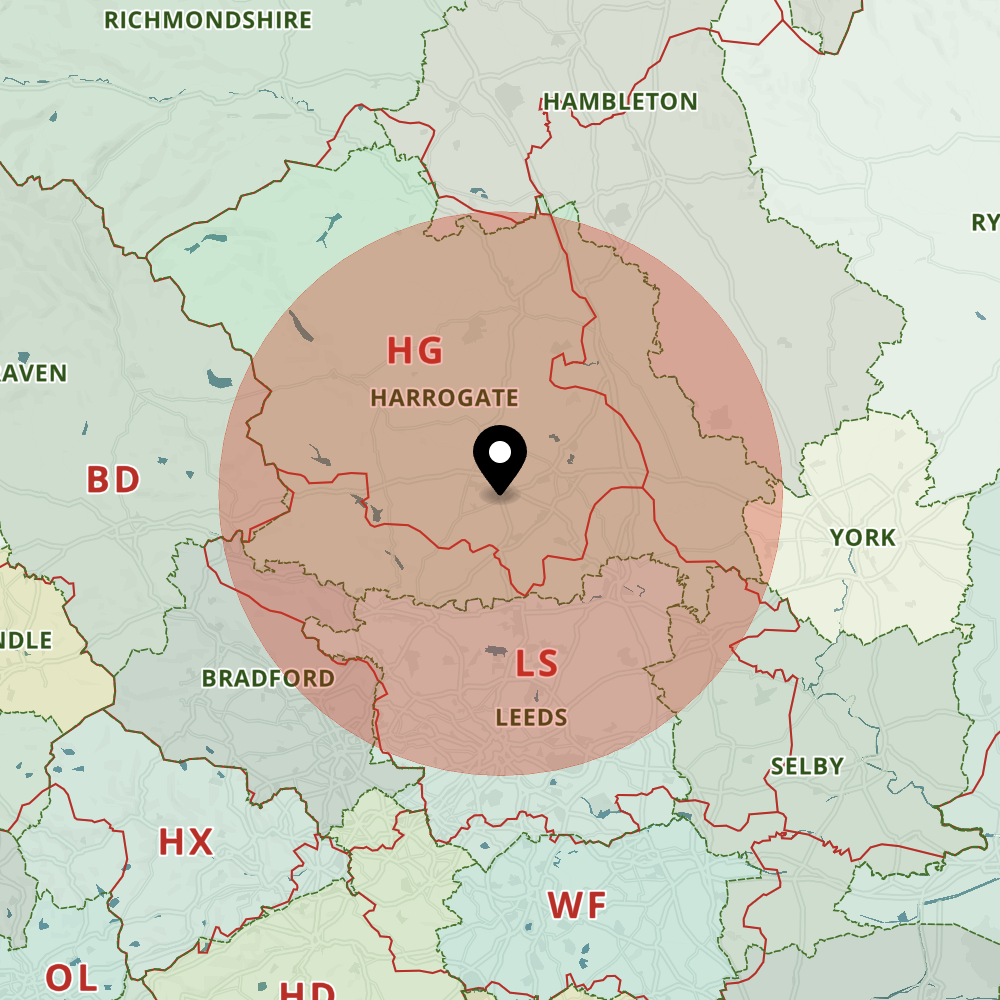




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Map Radius Plotters: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Spatial Relationships. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!