Unraveling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projections Online
Related Articles: Unraveling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projections Online
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projections Online. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projections Online
![]()
The world is a sphere, yet we experience it on flat surfaces. This inherent conflict between three-dimensional reality and two-dimensional representation is the core challenge addressed by map projections. These mathematical transformations convert the Earth’s curved surface onto a plane, allowing us to visualize the globe in a manageable format.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Map Projections
The process of map projection involves several key components:
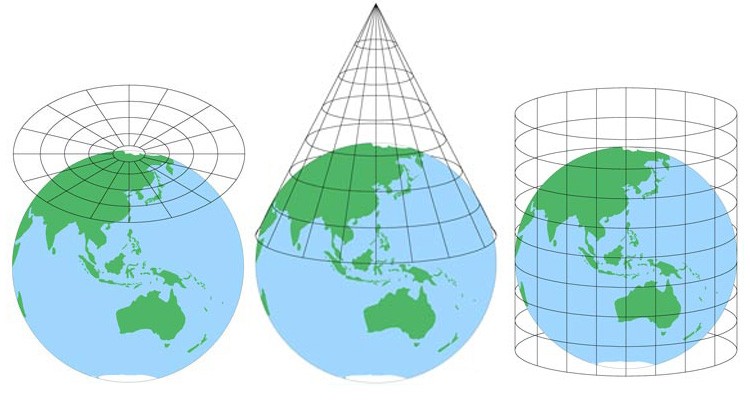
- The Globe: The Earth, with its complex spherical shape, serves as the starting point for projection.
- The Projection Surface: This can be a plane, a cylinder, or a cone, onto which the Earth’s features are transferred.
- The Projection Method: This defines the mathematical rules that govern how points on the globe are mapped onto the projection surface.
- The Distortion: No projection can perfectly represent the Earth without introducing some distortion. This distortion can affect shape, area, distance, or direction, depending on the chosen projection method.
Navigating the Diverse Landscape of Projections
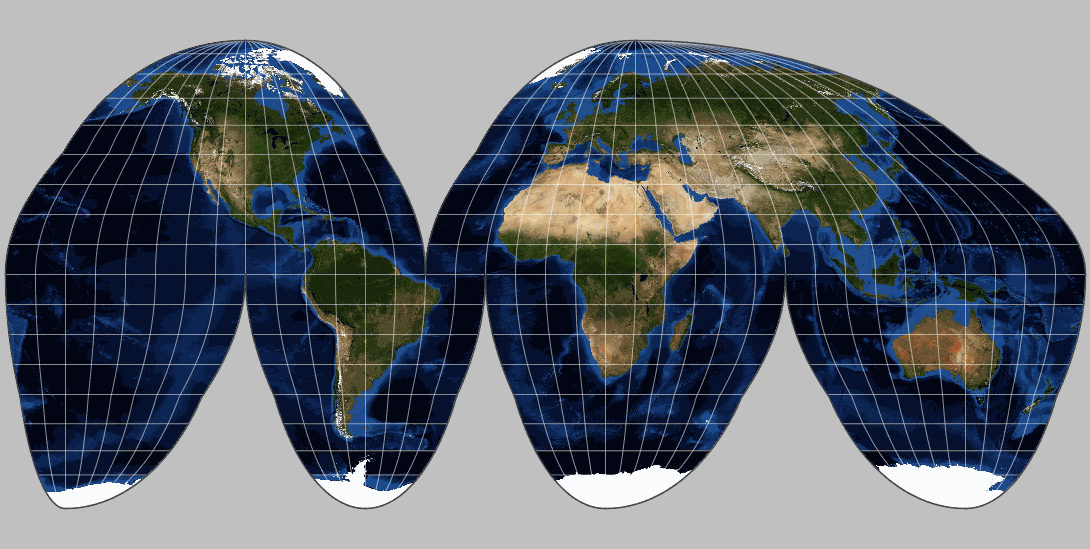
The world of map projections is rich and varied, with each projection offering a unique set of advantages and disadvantages. These projections are categorized based on their projection surface and the type of distortion they introduce:
-
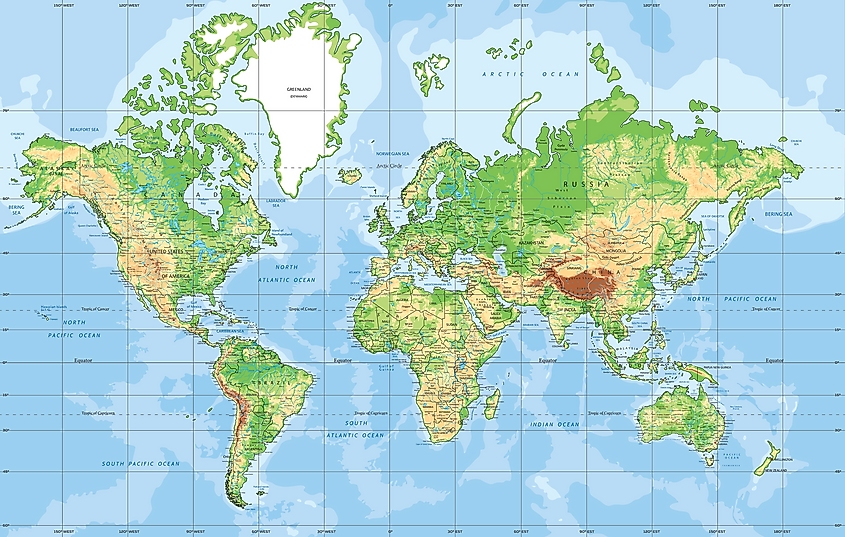
Cylindrical Projections: These projections wrap a cylinder around the globe, creating a rectangular map. Examples include the Mercator projection, known for its preservation of angles and use in navigation, and the Transverse Mercator projection, employed in large-scale mapping.
-
Conical Projections: These projections use a cone that intersects the globe at specific latitudes. Conical projections are often used for mapping mid-latitude regions, as they minimize distortion in those areas. The Lambert Conformal Conic projection is a prominent example.
-
Planar Projections: Also known as azimuthal projections, these projections use a plane that touches the globe at a single point. These are useful for mapping polar regions or specific areas of interest, such as a city or country. The Azimuthal Equidistant projection is a popular choice for this purpose.
The Power of Online Map Projections
The internet has revolutionized our access to and use of map projections. Online platforms offer a wealth of resources and tools, enabling users to:
- Explore a Wide Range of Projections: Numerous websites and mapping applications provide access to a vast library of projections, allowing users to compare and contrast different representations of the Earth.
- Customize Projections: Many online platforms allow users to adjust projection parameters, such as the central meridian, standard parallels, and distortion type, to tailor the projection to specific needs.
- Interact with Maps: Interactive maps online enable users to zoom in, pan around, and explore different areas of the globe with ease.
- Overlay Data: Online mapping tools allow users to overlay various datasets, such as population density, elevation, or climate data, onto projected maps, providing valuable insights and facilitating analysis.
The Importance of Understanding Distortion
While projections are essential for representing the Earth on flat surfaces, it’s crucial to understand their limitations. No projection can perfectly capture all aspects of the globe without introducing distortion. The type and extent of distortion vary depending on the chosen projection and the region being mapped.
Key Distortions and Their Implications:
- Shape Distortion: Some projections may distort the shapes of continents and countries, making them appear elongated or compressed.
- Area Distortion: Some projections may exaggerate or shrink the areas of landmasses, leading to misinterpretations of relative size.
- Distance Distortion: Projections can distort distances between points on the map, making them appear longer or shorter than they actually are.
- Direction Distortion: Some projections may distort the angles between lines on the map, affecting the accuracy of compass bearings.
Choosing the Right Projection for the Task
The selection of a suitable projection depends heavily on the intended use and the specific requirements of the map. Here are some key considerations:
- Purpose of the Map: Is the map intended for navigation, geographic analysis, or visualization?
- Area of Interest: What region of the Earth is being mapped?
- Level of Detail: How much detail is required on the map?
- Type of Distortion: What type of distortion is acceptable for the specific application?
FAQs about Map Projections Online
1. What is the best map projection for general use?
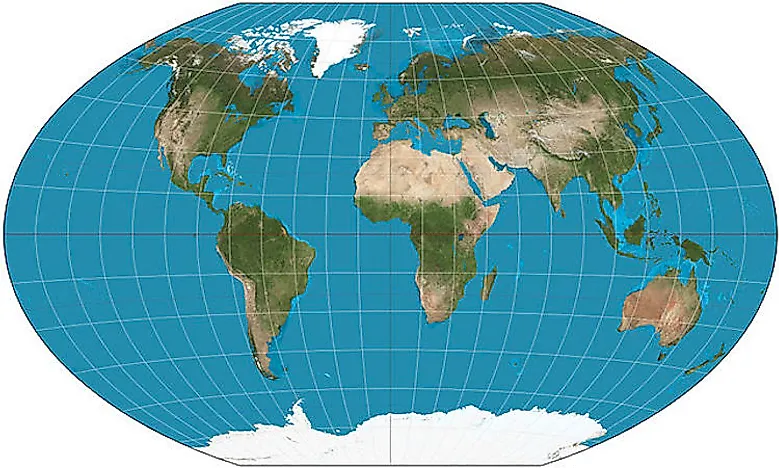
There is no single "best" projection for all purposes. The optimal projection depends on the specific application. For general-purpose maps, the Robinson projection is a good choice, as it minimizes distortion across the globe.
2. How can I find different map projections online?
Numerous websites and mapping applications offer access to a wide range of projections. Some popular options include:
- Google Maps: Allows users to switch between different projections, including the Mercator and Robinson projections.
- Mapbox: Provides a comprehensive library of projections, including custom options.
- ArcGIS Online: Offers a wide array of projections, including specialized projections for specific regions.
3. Are there any free online tools for creating maps with different projections?
Yes, several free online tools allow users to create maps using different projections. Some popular options include:
- Proj4js: A JavaScript library that enables users to work with projections in web applications.
- Leaflet: A JavaScript library for interactive maps, allowing users to choose from a variety of projections.
- OpenLayers: An open-source JavaScript library for creating interactive maps with support for various projections.
4. What is the difference between a Mercator projection and a Robinson projection?
The Mercator projection is a cylindrical projection that preserves angles, making it ideal for navigation. However, it distorts areas, particularly near the poles. The Robinson projection is a compromise projection that minimizes distortion across the globe, but it does not preserve angles or areas.
5. How can I understand the distortion in a map projection?
Many online map projection tools provide visual indicators of distortion. These indicators can be in the form of grids, color gradients, or other graphical representations. By examining these indicators, users can gain a better understanding of the distortions present in a particular projection.
Tips for Using Map Projections Online
- Be Aware of Distortion: Remember that all map projections introduce some form of distortion. Consider the type and extent of distortion when interpreting map information.
- Choose the Right Projection: Select a projection that is appropriate for the intended purpose and the region being mapped.
- Explore Different Projections: Experiment with various projections to see how they affect the visual representation of the Earth.
- Use Online Tools Effectively: Take advantage of the features and capabilities offered by online map projection tools to enhance your understanding and analysis.
Conclusion
Map projections are essential tools for visualizing and understanding the Earth’s complex surface. Online platforms have made these tools more accessible than ever before, enabling users to explore a wide range of projections, customize maps, and interact with geographic data in new ways. By understanding the principles of map projections and their limitations, users can make informed decisions about the appropriate projection for their needs and interpret map information with greater accuracy and insight.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projections Online. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!