Unraveling the Art of Map Projections: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unraveling the Art of Map Projections: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Art of Map Projections: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unraveling the Art of Map Projections: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unraveling the Art of Map Projections: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 The Challenge of Flattening the Globe
- 3.2 Navigating the Landscape of Map Projections
- 3.3 The Importance of Choosing the Right Projection
- 3.4 Demystifying Map Projections: Frequently Asked Questions
- 3.5 Tips for Understanding and Using Map Projections
- 3.6 Conclusion: Embracing the Art of Projection
- 4 Closure
Unraveling the Art of Map Projections: A Comprehensive Guide
![]()
The Earth, a sphere, is a complex three-dimensional object. Representing its intricate features on a two-dimensional surface, like a map, requires a transformation known as a map projection. This process, though seemingly simple, involves a series of mathematical calculations and choices that significantly influence the final representation of the Earth’s surface. Understanding the intricacies of map projections is crucial, as it allows us to decipher the inherent distortions and appreciate the unique characteristics of different map types.
The Challenge of Flattening the Globe
The fundamental challenge in creating a map lies in the impossibility of accurately representing a curved surface on a flat plane. Every attempt to flatten the Earth’s surface inevitably introduces distortions. These distortions manifest in various ways, affecting:
- Shape: The shapes of continents and countries can become elongated, compressed, or otherwise altered.
- Area: The relative sizes of landmasses can be exaggerated or minimized.
- Distance: The distances between locations can be misrepresented, leading to inaccuracies in travel calculations.
- Direction: The angles between geographic features, such as the direction of north, can be distorted.
Navigating the Landscape of Map Projections
To understand the different types of map projections, it is essential to consider the various properties they prioritize. Some projections aim to preserve area, while others focus on maintaining shape or direction. The choice of projection depends on the specific application and the desired emphasis.
Commonly Used Projections:
- Mercator Projection: This projection, popular for navigational purposes, preserves angles, ensuring that compass bearings remain accurate. However, it significantly distorts areas, particularly near the poles, making Greenland appear larger than South America, despite the latter’s significantly larger landmass.
- Lambert Conformal Conic Projection: This projection is commonly used for topographic maps and regional maps, as it minimizes distortion in areas near the standard parallels. It is often used for representing the contiguous United States.
- Equal-Area Projections: These projections, such as the Mollweide projection, prioritize preserving the relative areas of landmasses. However, they often distort shapes and directions.
- Azimuthal Projections: These projections, such as the Stereographic projection, preserve the direction from a central point. They are often used for representing polar regions.
Understanding the Trade-offs:
It is crucial to understand that no map projection can perfectly represent the Earth’s surface without introducing distortions. Choosing a projection involves weighing the trade-offs between preserving different properties. For instance, if accurate distances are paramount, a projection that preserves distances might be preferred, even if it distorts shapes or areas.
The Importance of Choosing the Right Projection
The choice of map projection has significant implications for various applications. For example:
- Navigation: Maps used for navigation, such as those found in ships or aircraft, rely on projections that preserve angles to ensure accurate compass readings.
- Geographic Research: Researchers studying global phenomena, such as climate change or population density, often utilize projections that preserve area to accurately represent the relative sizes of landmasses.
- Cartography: Mapmakers choose projections based on the specific needs of the map’s intended audience and purpose.
Demystifying Map Projections: Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Why are there so many different map projections?
A: The variety of map projections reflects the diverse needs and applications of maps. Each projection prioritizes different properties, making it suitable for specific purposes.
Q: Is there a "best" map projection?
A: No, there is no single "best" map projection. The optimal projection depends on the specific application and the desired emphasis on shape, area, distance, or direction.
Q: How can I identify the projection used on a map?
A: Most maps include a projection description or a scale bar that indicates the projection used. If not, consult the map’s accompanying documentation or the publisher’s website.
Q: Can I create my own map projection?
A: While creating a new map projection is possible, it requires advanced mathematical knowledge and specialized software. However, online tools and resources can help you explore and visualize different projections.
Tips for Understanding and Using Map Projections
- Be aware of the limitations of map projections: Every projection introduces distortions, so it is essential to understand the specific distortions associated with the projection used.
- Consider the purpose of the map: The choice of projection should be guided by the map’s intended use.
- Look for projection information: Always check for the projection description or scale bar on a map to understand its characteristics.
- Explore different projections: Experiment with various online tools and resources to visualize and compare different projections.
Conclusion: Embracing the Art of Projection
Map projections, though often taken for granted, represent a crucial aspect of understanding and interpreting geographic information. By understanding the principles behind these projections, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of representing the Earth’s surface on a flat plane. Recognizing the inherent distortions and the trade-offs involved in different projections allows us to critically evaluate maps and make informed decisions based on the specific needs of our applications. As we continue to explore and engage with geographic data, a comprehensive understanding of map projections remains essential for navigating the world, both literally and figuratively.

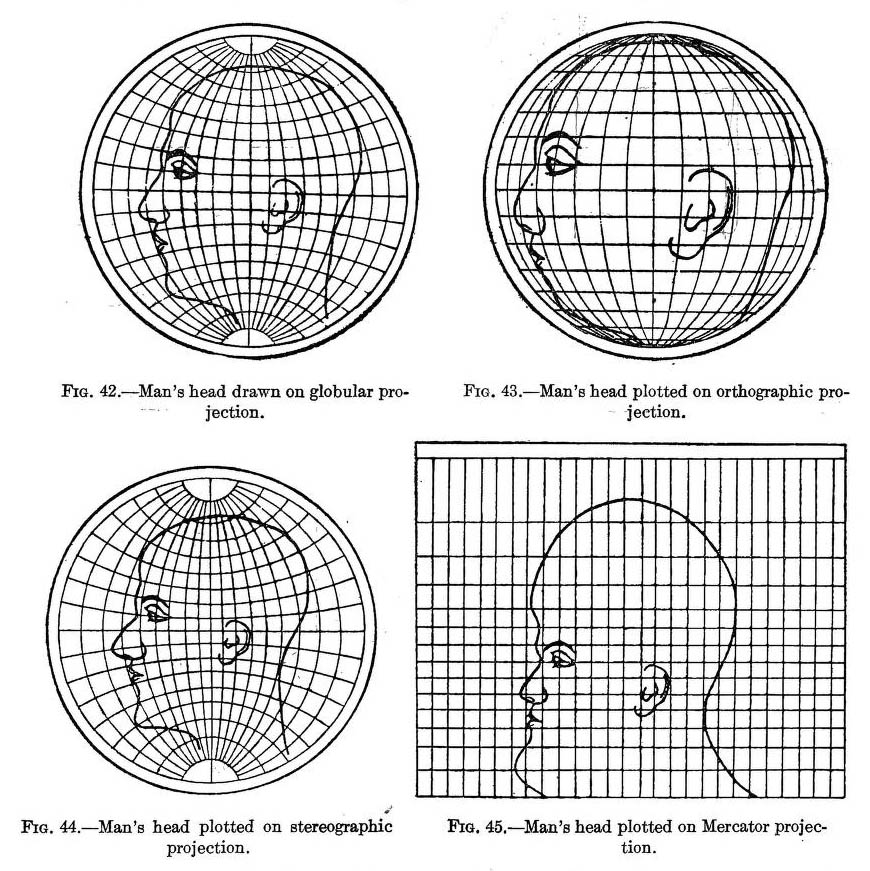

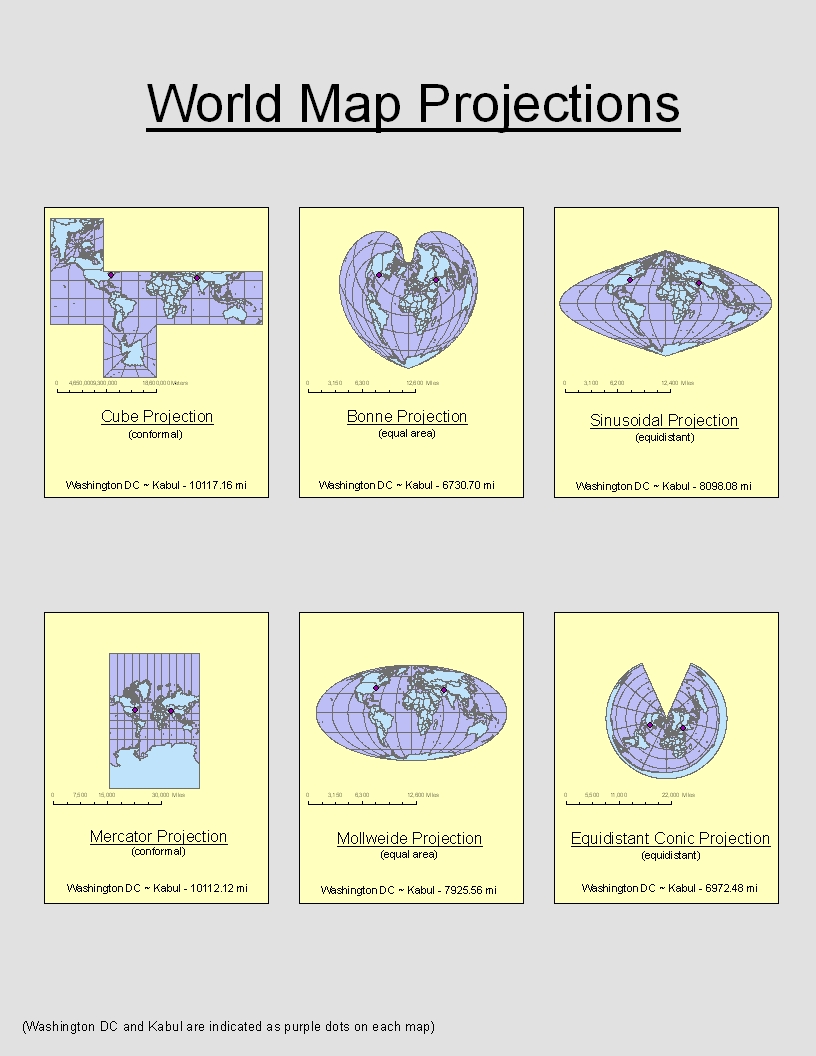

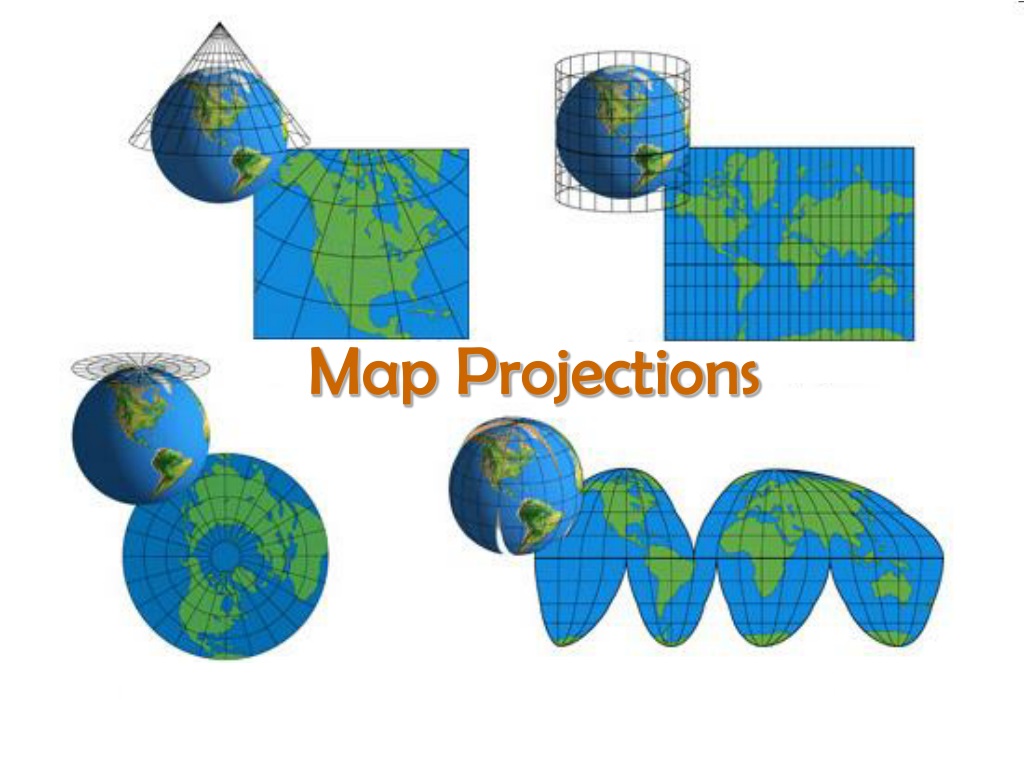


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Art of Map Projections: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!