Unlocking the Power of Python’s map Function: Transforming Data with Elegance
Related Articles: Unlocking the Power of Python’s map Function: Transforming Data with Elegance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Power of Python’s map Function: Transforming Data with Elegance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unlocking the Power of Python’s map Function: Transforming Data with Elegance
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unlocking the Power of Python’s map Function: Transforming Data with Elegance
- 3.1 Understanding the Fundamentals of map
- 3.2 The Advantages of map
- 3.3 Beyond Basic Transformations: Advanced Applications
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions
- 3.5 Tips for Effective map Usage
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unlocking the Power of Python’s map Function: Transforming Data with Elegance

The map function in Python is a powerful tool for applying transformations to data in a concise and efficient manner. It allows developers to apply a specific function to each element of an iterable, such as a list, tuple, or string, generating a new iterable containing the transformed results. This ability to streamline data manipulation makes map a fundamental component of any Python developer’s toolkit.
Understanding the Fundamentals of map
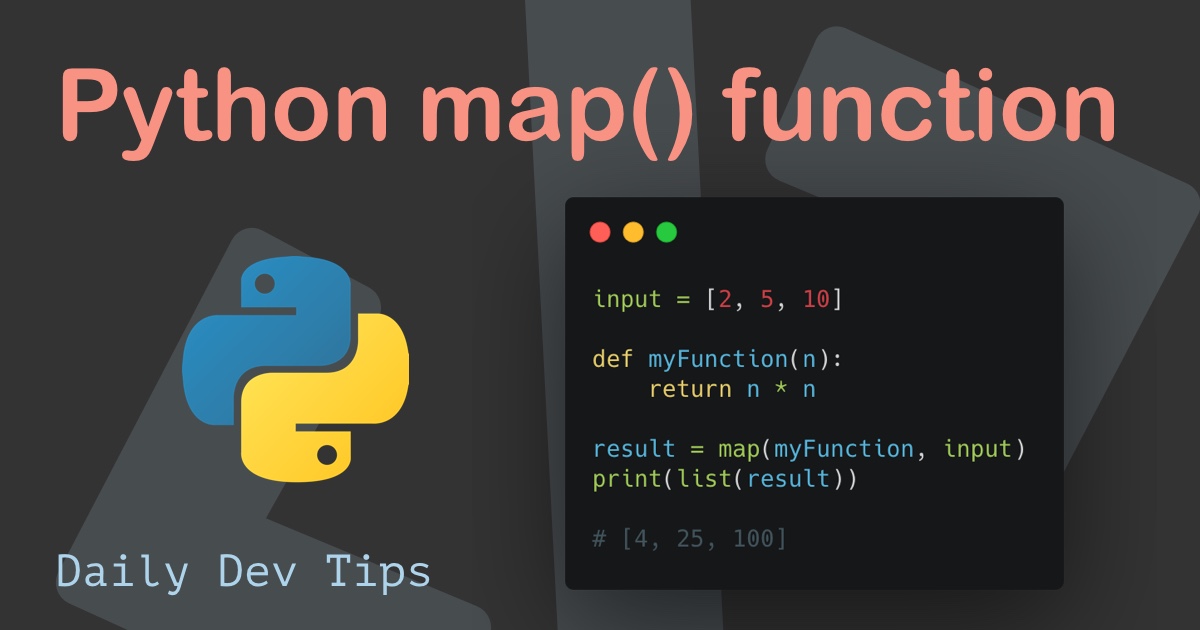
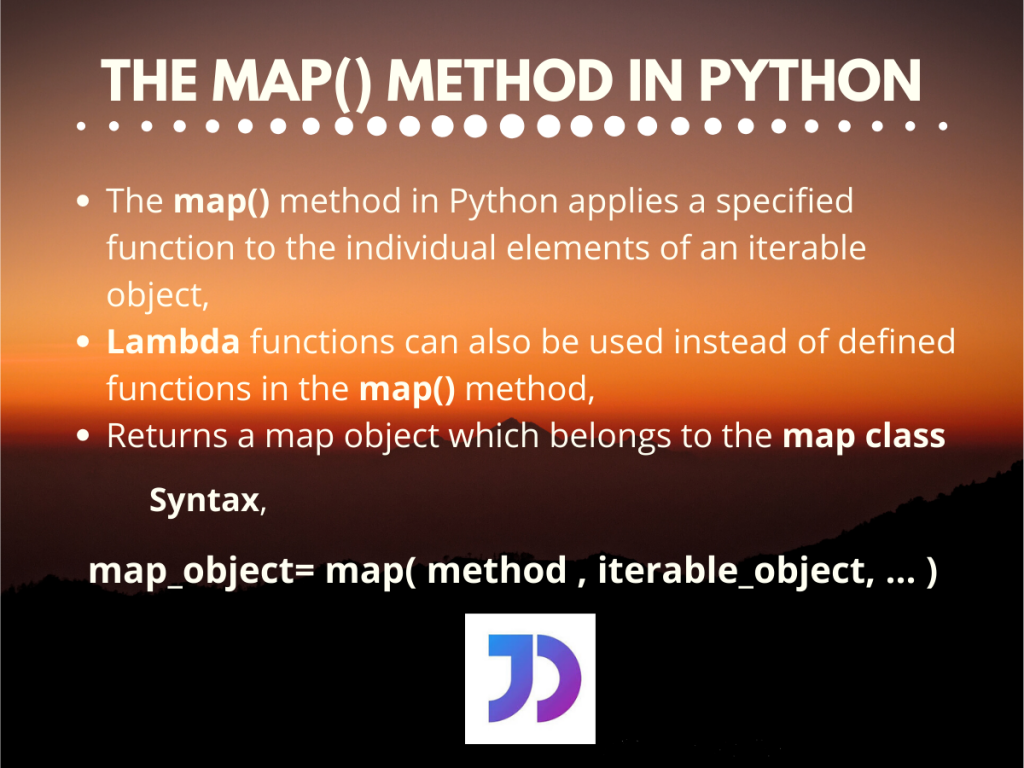
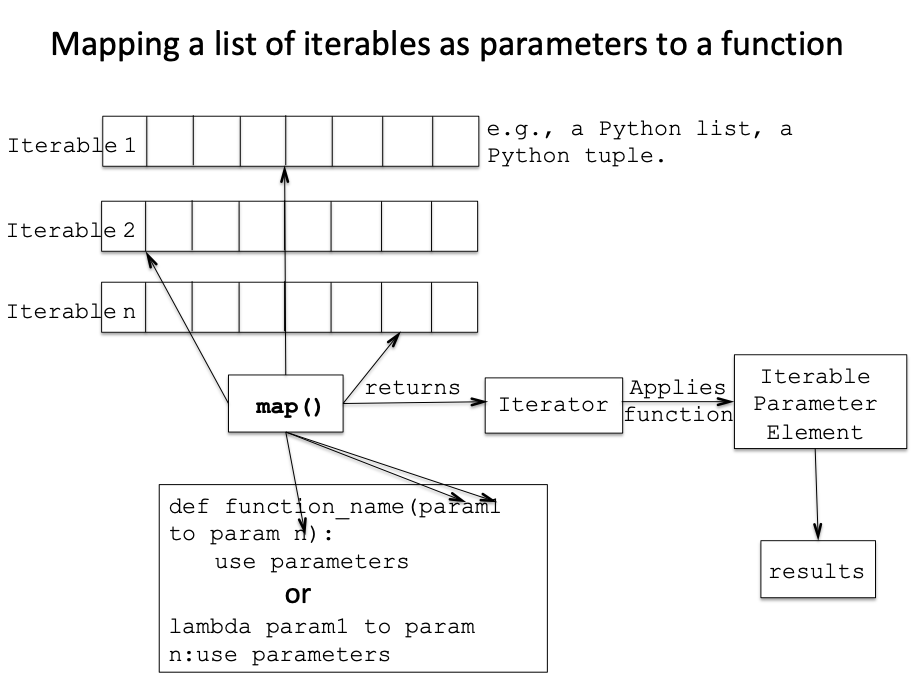
At its core, map operates by taking two arguments: a function and an iterable. The function is applied to each element of the iterable, and the resulting values are collected into a new iterable. This new iterable can then be converted into a list, tuple, or other desired data structure.
Example:
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
def square(x):
return x**2
squared_numbers = list(map(square, numbers))
print(squared_numbers) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]In this example, the square function squares each element of the numbers list. map applies this function to each element, generating a new iterable containing the squared values. The list constructor then converts this iterable into a list.
The Advantages of map
-
Conciseness:
mapprovides a succinct way to express data transformations. The code becomes more readable and easier to understand compared to using explicit loops. -
Efficiency:
mapleverages Python’s internal optimization for iterators, making it potentially faster than manual looping, especially for large datasets. -
Flexibility:
mapaccepts any callable function as its first argument, allowing for a wide range of transformations. This includes built-in functions, user-defined functions, lambda expressions, and even functions within classes. -
Immutability:
mapdoes not modify the original iterable. It returns a new iterable with the transformed values, preserving the integrity of the original data.
Beyond Basic Transformations: Advanced Applications
The true power of map extends beyond simple element-wise transformations. It can be used to:
-
Combine Operations: Multiple functions can be chained using
mapto perform complex data manipulations. For instance, you can first square each element and then take the square root, all within a singlemapcall. -
Apply Functions with Multiple Arguments:
mapcan be used with functions that accept multiple arguments by providing multiple iterables as additional arguments. The function will be applied to corresponding elements from each iterable. -
Process Data from Multiple Sources:
mapcan be used to process data from multiple sources simultaneously, such as reading data from files or network connections. -
Create Custom Iterators:
mapcan be used to create custom iterators that generate values on demand, improving memory efficiency for large datasets.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What if I need to apply different functions to different elements of the iterable?
A: While map applies the same function to all elements, you can achieve conditional transformations by using a lambda function within map. This lambda function can check conditions and apply different functions accordingly.
Q2: Can map be used with nested iterables like lists of lists?
A: Yes, map can be used with nested iterables. However, it will apply the function to the outermost elements. To apply the function to inner elements, you can use nested map calls or a combination of map and other techniques like list comprehensions.
Q3: Is map always faster than loops?
A: While map often offers performance advantages, it’s not a guarantee. For very simple transformations, the overhead of creating an iterator and applying the function might outweigh the benefits of map. In such cases, a simple loop might be more efficient.
Q4: What if I need to modify the original iterable instead of creating a new one?
A: map itself does not modify the original iterable. For in-place modifications, you can use techniques like list comprehensions or loops with indexing.
Tips for Effective map Usage
-
Choose the Right Function: Select a function that accurately reflects the desired transformation and ensures clarity in your code.
-
Prioritize Readability: While
mapoffers conciseness, prioritize readability over brevity. If the transformation logic becomes complex, consider using a dedicated function to improve code clarity. -
Understand Performance Implications: Be mindful of the potential overhead associated with
mapfor simple transformations. Consider whether a loop might be more efficient in such scenarios. -
Embrace Functional Programming:
mapis a core concept in functional programming. Explore other functional techniques likefilter,reduce, andlambdafunctions to enhance your data manipulation skills.
Conclusion
The map function in Python is a powerful tool for transforming data efficiently and elegantly. It enables developers to apply functions to iterables in a concise manner, promoting code readability and potential performance gains. By understanding its capabilities and utilizing it effectively, developers can streamline data manipulation tasks and unlock the full potential of this versatile function.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Power of Python’s map Function: Transforming Data with Elegance. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!