Unlocking Spatial Insights: Exploring the Power of Map Radius Drawers
Related Articles: Unlocking Spatial Insights: Exploring the Power of Map Radius Drawers
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unlocking Spatial Insights: Exploring the Power of Map Radius Drawers. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking Spatial Insights: Exploring the Power of Map Radius Drawers

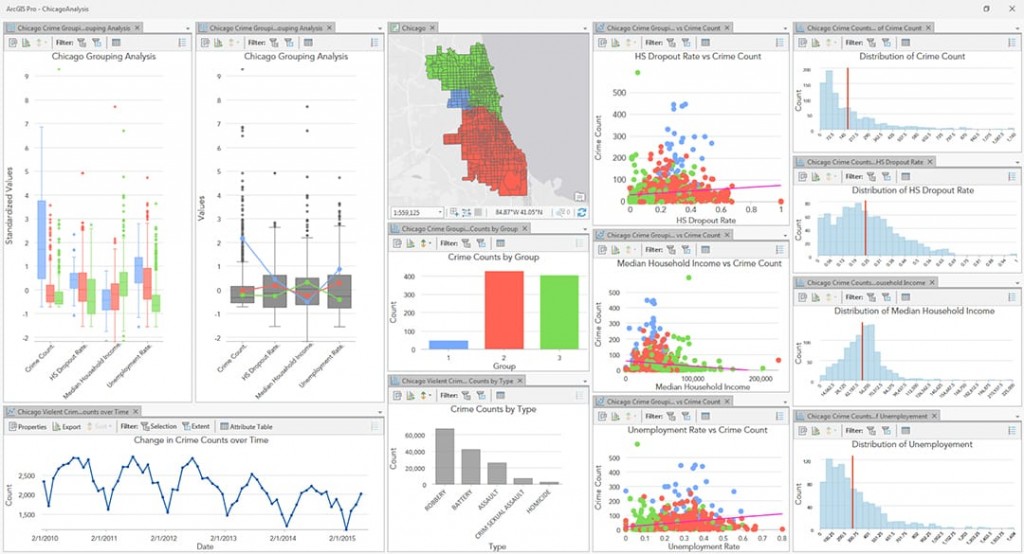
In the realm of geographic information systems (GIS) and spatial analysis, the ability to visualize and analyze data within defined geographic boundaries is paramount. This is where the concept of a "map radius drawer" emerges as a powerful tool, enabling users to define and manipulate circular areas of interest on maps. This article delves into the intricacies of map radius drawers, exploring their functionality, applications, and significance in various fields.
Understanding the Core Functionality
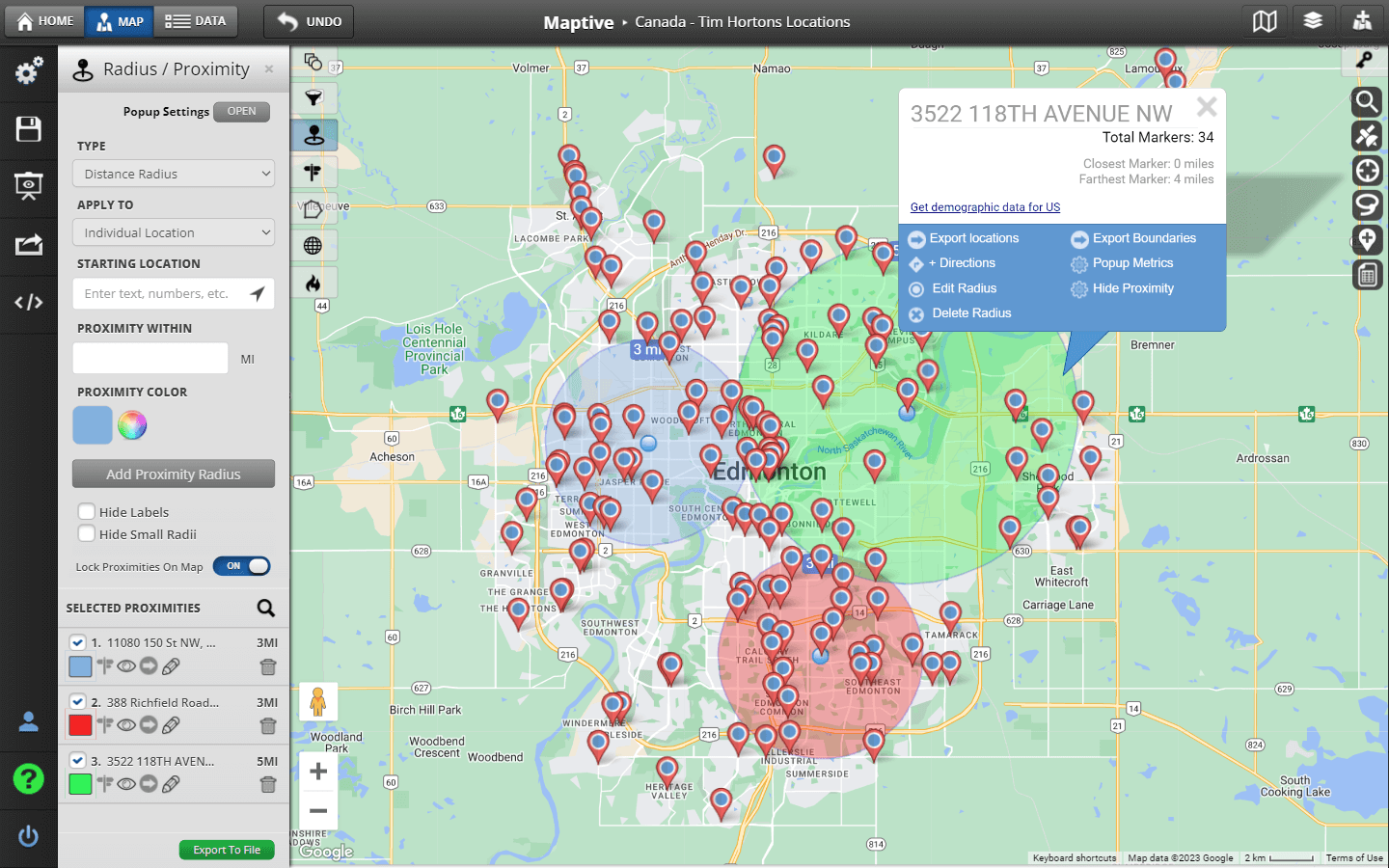
A map radius drawer, often implemented as an interactive feature within GIS software, allows users to draw circles of varying radii on a map. These circles represent a specific distance from a chosen point of origin, effectively creating a visual representation of an area within a designated radius. This simple yet powerful functionality unlocks a range of possibilities for spatial analysis and visualization.
Key Components and Operations
A typical map radius drawer consists of the following components:
- Origin Point: The starting point from which the radius is calculated. This can be a specific location, an address, or a point of interest.
- Radius Input: A field or slider that allows users to define the radius of the circle. The unit of measurement can be kilometers, miles, or any other relevant unit.
- Drawing Mechanism: The method used to create the circle on the map. This can involve clicking and dragging the mouse or using a pre-defined radius value.
- Visualization: The circle is displayed on the map, often with a distinct color or pattern to differentiate it from other map features.
Applications: A Spectrum of Possibilities
The applications of map radius drawers extend far beyond basic map visualization. They are employed across diverse fields, each leveraging their unique capabilities to address specific challenges.
1. Business and Marketing:
- Market Analysis: Identifying potential customers within a defined radius of a business location.
- Targeted Advertising: Delivering promotional messages to individuals residing within specific geographic zones.
- Franchise Location: Evaluating potential locations for new business outlets based on proximity to existing customers or competitors.
2. Emergency Response and Disaster Management:
- Evacuation Zones: Defining areas requiring immediate evacuation during natural disasters or emergencies.
- Resource Allocation: Determining the optimal distribution of emergency services based on proximity to affected areas.
- Incident Analysis: Mapping the impact radius of an incident, such as a chemical spill or a wildfire.
3. Environmental Monitoring and Management:
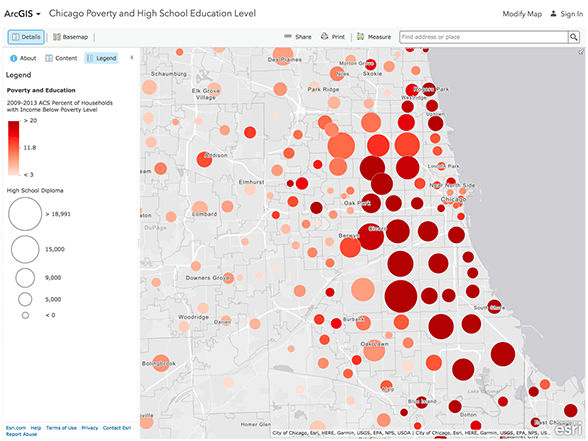
- Pollution Monitoring: Identifying areas with elevated pollution levels within a specific radius of a source.
- Wildlife Conservation: Defining protected areas around critical habitats or endangered species.
- Climate Change Analysis: Mapping the potential impact of rising sea levels or extreme weather events on vulnerable coastal regions.
4. Urban Planning and Development:
- Infrastructure Planning: Determining the service area of new infrastructure projects, such as hospitals or schools.
- Traffic Management: Identifying areas prone to congestion within a certain radius of major intersections.
- Urban Renewal: Mapping the impact of redevelopment projects on surrounding neighborhoods.
5. Healthcare and Public Health:
- Disease Surveillance: Tracking the spread of infectious diseases within a specified radius of confirmed cases.
- Healthcare Access: Identifying areas with limited access to healthcare facilities based on distance.
- Public Health Campaigns: Targeting specific geographic areas for public health interventions.
Beyond Basic Functionality: Advanced Features
Modern GIS software often incorporates advanced features that enhance the capabilities of map radius drawers, providing greater flexibility and analytical power:
- Multiple Radii: The ability to draw multiple circles with different radii from a single origin point.
- Customizable Shapes: Drawing ellipses, polygons, or other irregular shapes instead of just circles.
- Buffering: Creating a buffer zone around the circle, expanding or contracting the area of interest.
- Overlay Analysis: Combining multiple radius drawers to analyze spatial relationships between different areas of interest.
- Data Integration: Linking radius drawers to specific data layers, allowing for the analysis of population density, demographics, or other relevant information within the defined areas.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
Q: How accurate are map radius drawers in real-world scenarios?
A: The accuracy of a map radius drawer depends on the underlying map projection and the chosen unit of measurement. While geographic distances are generally accurate, factors like terrain variations or complex urban environments can introduce minor inaccuracies.
Q: Can map radius drawers be used for dynamic analysis?
A: Some GIS software allows for dynamic radius adjustments, enabling users to interactively explore the impact of different radii on spatial relationships. This is particularly useful for analyzing data trends and identifying optimal parameters.
Q: Are there any limitations to using map radius drawers?
A: While powerful, map radius drawers have certain limitations. They are primarily focused on circular areas, and analyzing complex spatial relationships might require additional tools or advanced techniques.
Tips for Effective Use
- Clear Objectives: Define specific goals and questions that the radius drawer analysis aims to address.
- Appropriate Radius: Choose a radius that aligns with the scale and scope of the analysis.
- Data Quality: Ensure the accuracy and relevance of the data used in conjunction with the radius drawer.
- Visualization: Employ clear and informative map symbols and legends to communicate the results effectively.
- Contextualization: Consider the broader geographic context and potential biases when interpreting results.
Conclusion: Empowering Spatial Understanding
Map radius drawers are indispensable tools in the GIS toolkit, facilitating spatial analysis and visualization across various disciplines. Their ability to define and manipulate circular areas of interest unlocks a wealth of insights, empowering users to understand spatial relationships, make informed decisions, and address complex challenges. As technology continues to evolve, map radius drawers are likely to become even more sophisticated, offering enhanced functionalities and a deeper understanding of the spatial world around us.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking Spatial Insights: Exploring the Power of Map Radius Drawers. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
