Unlocking Spatial Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Radius Tools
Related Articles: Unlocking Spatial Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Radius Tools
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unlocking Spatial Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Radius Tools. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking Spatial Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Radius Tools
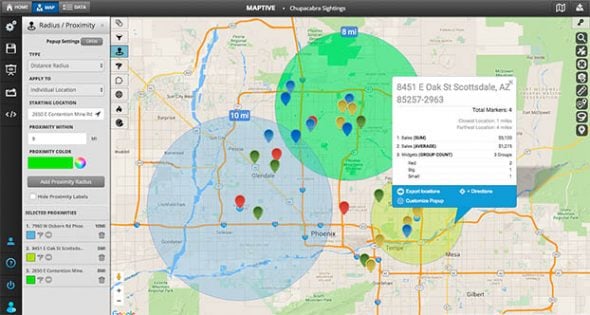
In a world increasingly reliant on location-based data, the ability to visualize and analyze spatial relationships is paramount. Map radius tools, often referred to as "circle drawing tools," have emerged as indispensable instruments for professionals across diverse fields, enabling them to understand, quantify, and leverage the power of proximity. This comprehensive guide delves into the functionality, benefits, and applications of map radius tools, offering a detailed understanding of their significance in the modern landscape of spatial analysis.
Understanding Map Radius Tools: The Essence of Proximity Analysis
At its core, a map radius tool empowers users to define circular areas of interest around a specific point on a map. This seemingly simple function unlocks a wealth of possibilities for spatial analysis, enabling users to:
- Determine the geographic scope of influence: By drawing a radius around a location, users can visualize the area potentially affected by a specific event, activity, or service. This is invaluable for businesses seeking to understand customer reach, for emergency responders assessing the impact of a disaster, or for researchers studying the influence of a particular phenomenon.
- Identify locations within a defined distance: Whether it’s finding restaurants within a 5-mile radius, locating potential customers within a 10-kilometer zone, or pinpointing businesses within a designated service area, map radius tools facilitate the identification of relevant locations based on their proximity to a central point.
- Analyze spatial relationships and patterns: By comparing radii drawn around different points, users can gain insights into the spatial distribution of data, identifying clusters, gaps, or overlaps. This is crucial for understanding market dynamics, identifying potential areas of growth, or assessing the effectiveness of a particular strategy.
Beyond the Circle: A Spectrum of Functionality
While the core functionality of a map radius tool centers around drawing circles, modern tools offer a wide array of features, expanding their capabilities and enhancing their usefulness:
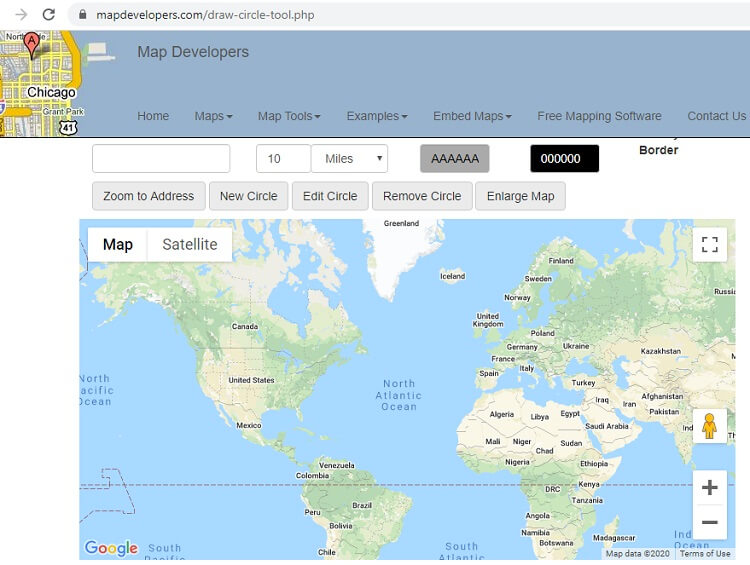
- Customizable radius settings: The ability to adjust the radius size allows for precise control over the area of interest, enabling users to refine their analysis based on specific needs and parameters.
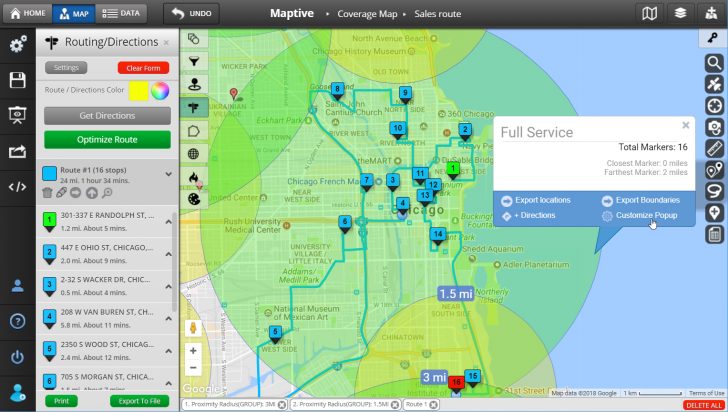
- Multiple radius drawing: Drawing multiple radii around different points allows for comparative analysis and the identification of overlapping or non-overlapping areas, providing valuable insights into spatial relationships and interactions.
- Integration with other map features: Many tools allow users to overlay radii with other map layers, such as roads, points of interest, or demographic data, enabling comprehensive spatial analysis and visualization.
- Data aggregation and analysis: Some tools offer advanced features for aggregating data within defined radii, allowing users to calculate statistics, generate reports, and gain deeper insights into the characteristics of the areas within their analysis.
Applications of Map Radius Tools: Unlocking Insights Across Disciplines
The versatility of map radius tools makes them indispensable for professionals in a wide range of fields, enabling them to tackle diverse challenges and gain valuable insights:
-
Business and Marketing:
- Market research and competitor analysis: Identifying potential customer bases and assessing competitor presence within specific geographic areas.
- Targeted advertising and campaign planning: Optimizing ad campaigns by focusing on areas with high concentrations of potential customers.
- Location optimization for businesses: Selecting optimal locations for new stores, offices, or distribution centers based on proximity to customers and resources.
-
Emergency Response and Disaster Management:
- Assessing the impact of natural disasters: Determining the extent of damage and identifying areas requiring immediate assistance.
- Planning evacuation routes: Defining safe zones and optimal evacuation paths based on distance and accessibility.
- Resource allocation and deployment: Optimizing the distribution of resources based on the affected areas and population density.
-
Real Estate and Property Management:
- Evaluating property value: Assessing the impact of proximity to amenities, transportation, and other factors on property value.
- Identifying potential buyers and sellers: Targeting potential clients based on their proximity to desired properties.
- Analyzing neighborhood trends and demographics: Understanding the characteristics of different neighborhoods and identifying areas with high growth potential.
-
Urban Planning and Development:
- Identifying areas for new development: Determining suitable locations for residential, commercial, or infrastructure development based on proximity to existing amenities and resources.
- Assessing the impact of infrastructure projects: Evaluating the potential impact of new roads, bridges, or public transportation on surrounding areas.
- Planning for sustainable development: Identifying areas with high environmental sensitivity and prioritizing development in areas with lower ecological impact.
-
Research and Academia:
- Analyzing spatial patterns and relationships: Identifying clusters, outliers, and trends in data based on geographic location.
- Conducting field studies and data collection: Selecting sampling locations based on proximity to specific features or phenomena.
- Developing and testing spatial models: Evaluating the accuracy and predictive power of models based on their ability to accurately capture spatial relationships.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries about Map Radius Tools
Q: What are the different types of map radius tools available?
A: Map radius tools are available in various forms, ranging from basic online tools to sophisticated software packages:
- Online map services: Many popular mapping websites, such as Google Maps, Bing Maps, and MapQuest, offer integrated radius drawing tools, enabling users to quickly define areas of interest within their browser.
- GIS software: Geographic Information System (GIS) software, such as ArcGIS, QGIS, and MapInfo, provides advanced capabilities for spatial analysis, including detailed radius drawing, data aggregation, and visualization.
- Specialized software packages: Several specialized software packages, tailored to specific industries or applications, incorporate map radius tools for tasks such as retail analysis, emergency response planning, or real estate management.
Q: What are the key considerations when choosing a map radius tool?
A: Selecting the most suitable tool depends on the specific needs and requirements of the user:
- Functionality: Consider the specific features and capabilities offered by the tool, such as radius customization, multiple radius drawing, data aggregation, and integration with other map features.
- Ease of use: Choose a tool that is intuitive and user-friendly, with a clear interface and straightforward functionalities.
- Data sources: Ensure the tool supports the required data sources, including geographic coordinates, address information, or other relevant spatial data.
- Cost: Determine the pricing model and cost-effectiveness of the tool based on your budget and usage requirements.
Q: How can I effectively use map radius tools for spatial analysis?
A: To maximize the effectiveness of map radius tools, consider the following tips:
- Define clear objectives: Clearly articulate the purpose and goals of your analysis, ensuring that the tool’s capabilities align with your objectives.
- Choose appropriate radius sizes: Select radius sizes that are relevant to your analysis and reflect the geographic scope of influence or the desired distance parameters.
- Utilize multiple radii: Drawing multiple radii around different points allows for comparative analysis and the identification of spatial relationships and patterns.
- Integrate with other map features: Overlay radii with other map layers, such as roads, points of interest, or demographic data, to gain comprehensive insights.
- Analyze and interpret results: Carefully interpret the results of your analysis, considering the limitations of the tool and the context of your data.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Proximity Analysis
Map radius tools have emerged as essential instruments for professionals across diverse fields, enabling them to unlock the power of proximity analysis and gain valuable insights into spatial relationships. By visualizing areas of interest, identifying locations within defined distances, and analyzing spatial patterns, these tools empower users to make informed decisions, optimize operations, and drive strategic initiatives. As our reliance on location-based data continues to grow, the importance of map radius tools will only increase, making them indispensable for navigating the complexities of our spatial world.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking Spatial Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Radius Tools. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!