Unlocking Geographic Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Radius Map Tools
Related Articles: Unlocking Geographic Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Radius Map Tools
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unlocking Geographic Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Radius Map Tools. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking Geographic Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Radius Map Tools
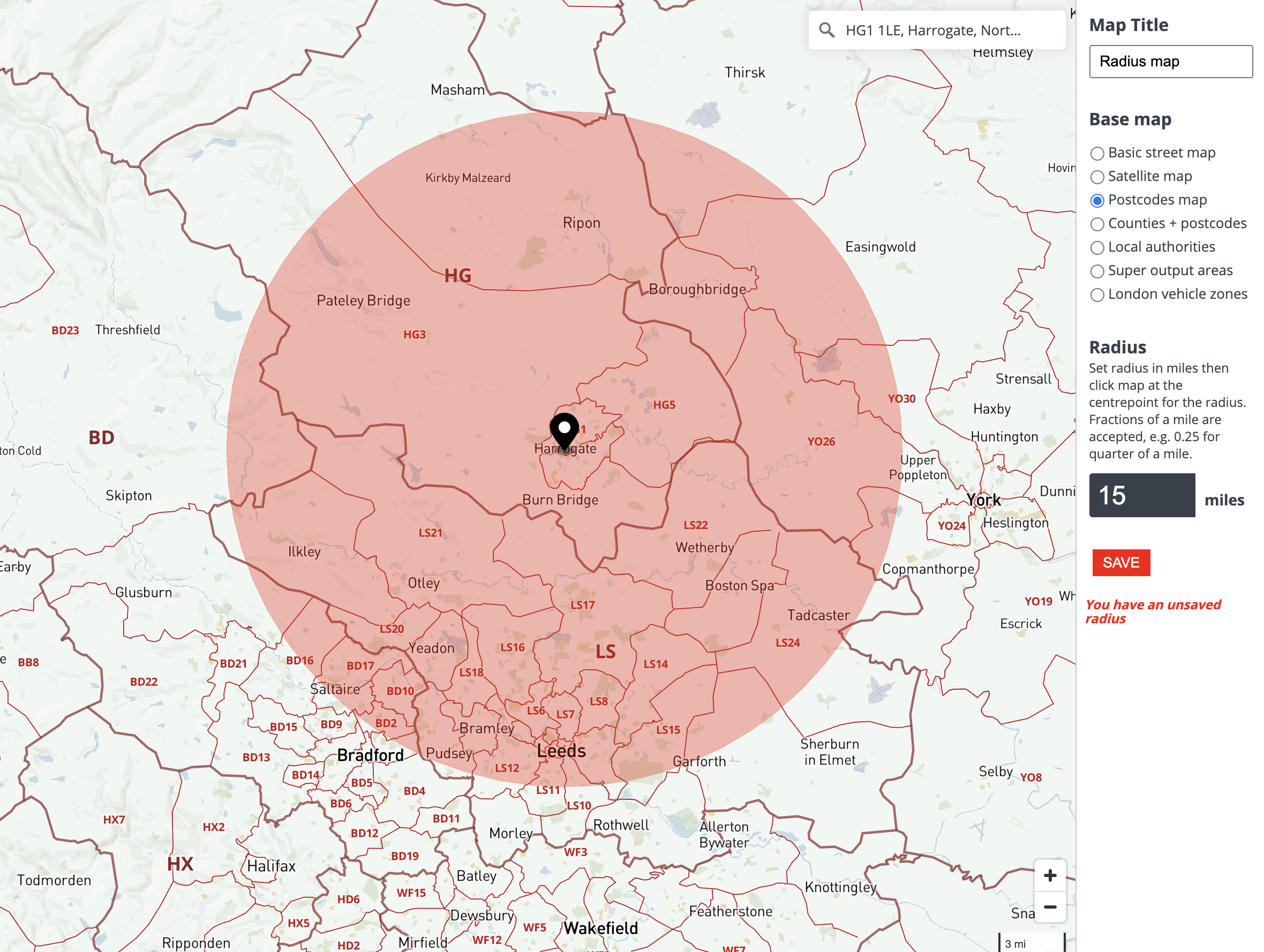
In the digital age, where data reigns supreme, understanding geographic relationships is paramount. Businesses, researchers, and individuals alike rely on spatial analysis to gain meaningful insights from data that is inherently tied to location. Enter the radius map tool, a powerful instrument for visualizing and analyzing data within defined geographical areas. This guide delves into the intricacies of radius map tools, exploring their functionalities, applications, and the profound impact they have on various domains.
Understanding the Essence of Radius Map Tools
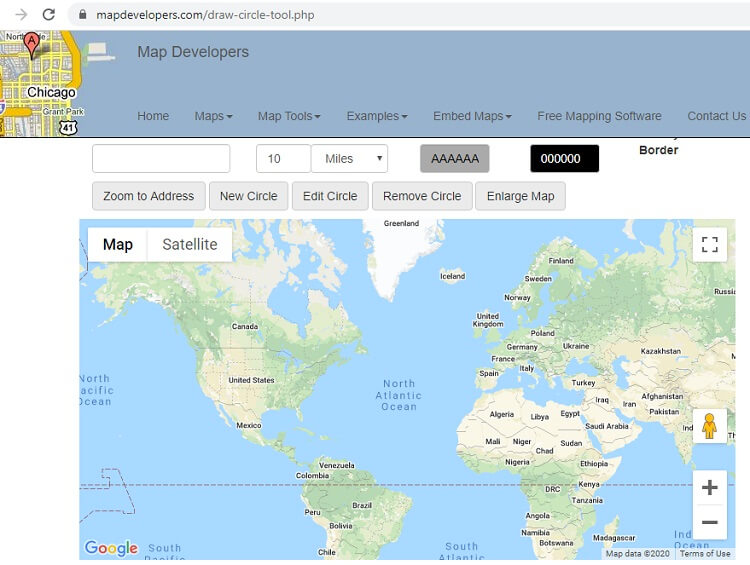
At its core, a radius map tool facilitates the creation of circles, or "buffers," around a designated point on a map. These circles represent a specific distance, allowing users to visualize and analyze data within that defined radius. This simple yet powerful concept unlocks a wealth of possibilities for understanding spatial relationships and patterns.
Key Components of a Radius Map Tool
A robust radius map tool typically encompasses the following features:
- Map Interface: A user-friendly interface with interactive maps that allow for seamless navigation and exploration.
- Point Selection: The ability to select specific points on the map, which serve as the center of the radius.
- Radius Definition: Tools to define the desired radius, often measured in units like kilometers, miles, or meters.
- Data Overlay: The capability to overlay various datasets onto the map, enabling the visualization of relationships between spatial data and the defined radius.
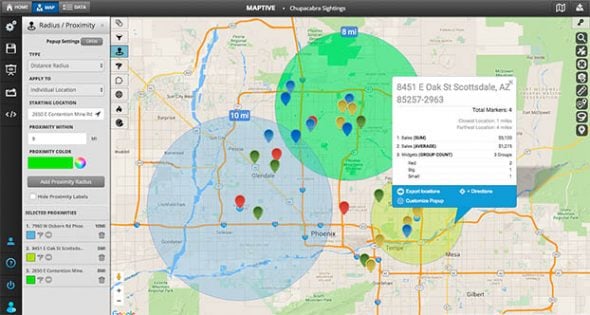
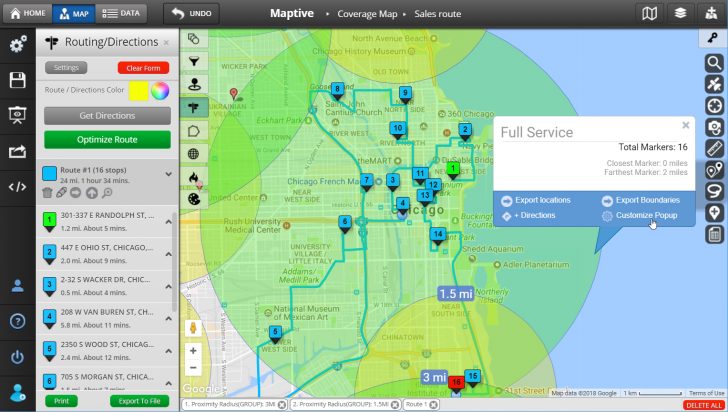
- Data Visualization: A range of visualization options, including heatmaps, markers, and thematic maps, to effectively communicate insights.
- Data Analysis: Tools for analyzing data within the radius, such as calculating population density, identifying nearby points of interest, or analyzing demographic trends.
Applications Across Diverse Domains
The versatility of radius map tools transcends boundaries, finding application in a multitude of fields:
- Business and Marketing: Businesses leverage radius maps to identify potential customers, target advertising campaigns, and analyze market competition within specific geographic areas.
- Real Estate: Real estate professionals utilize radius maps to assess property values, analyze neighborhood demographics, and identify potential buyers or sellers within a defined radius.
- Healthcare: Hospitals and healthcare providers use radius maps to optimize patient access, analyze service utilization patterns, and identify areas with underserved populations.
- Education: Schools and universities employ radius maps to assess student catchment areas, analyze school performance, and identify potential partnerships within a specific geographic scope.
- Urban Planning: Urban planners rely on radius maps to analyze traffic patterns, assess infrastructure needs, and plan for future development within defined areas.
- Environmental Studies: Environmental researchers utilize radius maps to analyze pollution levels, identify sensitive ecosystems, and understand the impact of human activities on specific geographic areas.
Benefits of Employing Radius Map Tools
The adoption of radius map tools unlocks several key benefits:
- Enhanced Spatial Understanding: By visualizing data within a defined radius, users gain a deeper understanding of spatial relationships and patterns that might otherwise be overlooked.
- Targeted Data Analysis: Radius maps enable focused analysis of data within specific geographic areas, leading to more accurate and relevant insights.
- Improved Decision-Making: By visualizing and analyzing data within a defined radius, stakeholders can make more informed decisions based on a clear understanding of the geographic context.
- Increased Efficiency: Radius map tools streamline the process of analyzing spatial data, saving time and effort compared to manual methods.
- Effective Communication: The visual representation of data within a radius facilitates effective communication of insights to diverse audiences.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What types of data can be used with radius map tools?
Radius map tools can accommodate various data types, including:
- Point Data: Locations represented by individual points, such as businesses, schools, or hospitals.
- Polygon Data: Areas defined by boundaries, such as neighborhoods, cities, or counties.
- Line Data: Linear features, such as roads, rivers, or pipelines.
2. How accurate are radius maps?
The accuracy of radius maps depends on the quality of the underlying data and the chosen projection system. It’s essential to use reliable data sources and consider the potential for distortion caused by map projections.
3. What are some limitations of radius map tools?
While powerful, radius map tools do have limitations:
- Oversimplification: The circular shape of the radius may not accurately represent complex geographic features or real-world boundaries.
- Data Availability: The availability of accurate and relevant data can be a limiting factor in the effectiveness of radius map analysis.
- Data Interpretation: Care must be taken to interpret data within the radius contextually, avoiding overgeneralization or misinterpretation.
Tips for Effective Radius Map Usage
- Define Clear Objectives: Establish clear goals for the analysis to ensure the radius map tool effectively addresses the specific needs.
- Select Appropriate Data: Choose data sources that are relevant, accurate, and consistent with the objectives of the analysis.
- Experiment with Radius Sizes: Explore different radius sizes to understand their impact on the results and identify the most meaningful scale for the analysis.
- Consider Geographic Context: Account for the specific geographic context and potential limitations of the circular radius shape.
- Visualize Data Effectively: Utilize a range of visualization options to communicate insights clearly and effectively to diverse audiences.
Conclusion
Radius map tools are invaluable instruments for unlocking geographic insights and understanding spatial relationships. By visualizing and analyzing data within defined areas, these tools empower businesses, researchers, and individuals to make informed decisions, optimize operations, and gain a deeper understanding of the world around them. As technology continues to advance, radius map tools are poised to play an even more prominent role in shaping our understanding of the spatial dimension of data, driving innovation and progress across diverse fields.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking Geographic Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Radius Map Tools. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!