Unlocking Efficiency: The Power of the Python Map Function
Related Articles: Unlocking Efficiency: The Power of the Python Map Function
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unlocking Efficiency: The Power of the Python Map Function. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking Efficiency: The Power of the Python Map Function
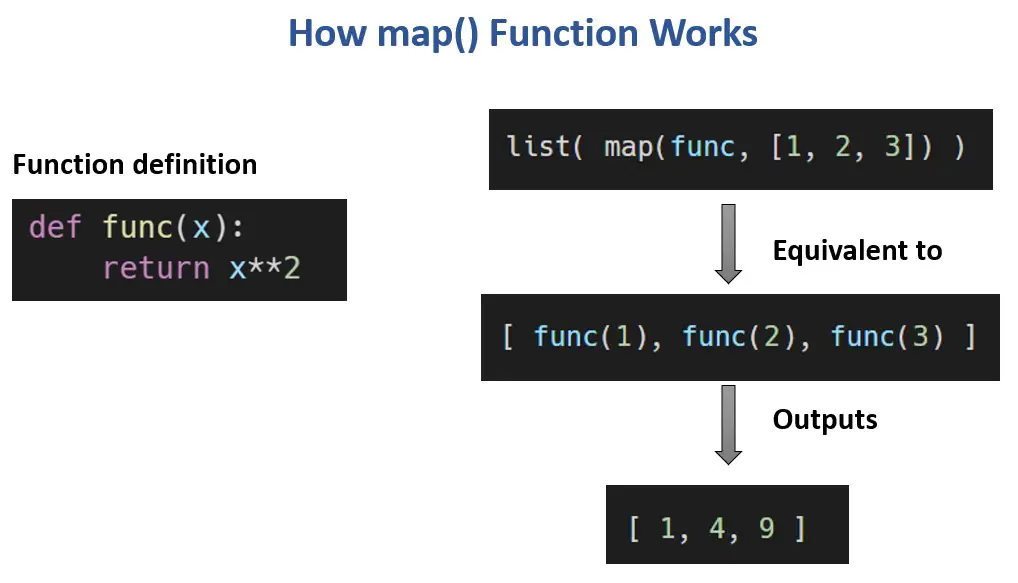
In the realm of programming, efficiency is paramount. Python, known for its readability and versatility, offers a plethora of tools to streamline code and enhance performance. Among these tools, the map function stands out as a powerful mechanism for applying functions to iterable objects in a concise and elegant manner.
The map function in Python acts as a bridge between functions and iterables, enabling the application of a function to each element of an iterable, such as a list, tuple, or string, without the need for explicit looping. This streamlined approach not only simplifies code but also enhances its efficiency and readability.
Understanding the Mechanics
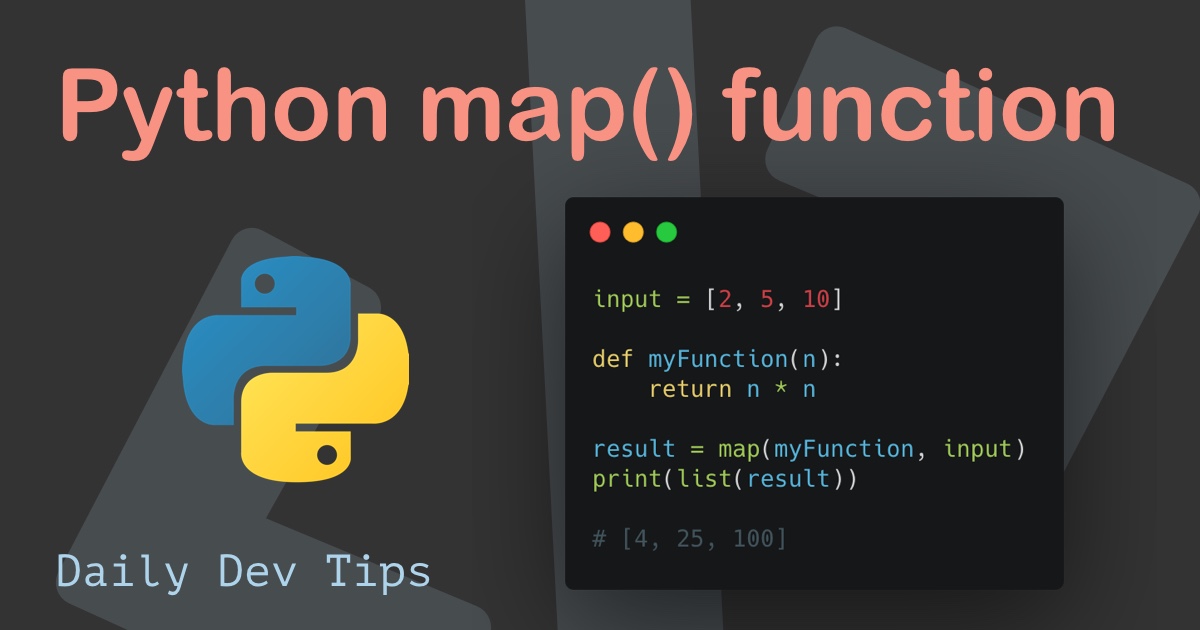
At its core, the map function takes two arguments: a function and an iterable. It iterates through each element of the iterable, applies the provided function to it, and returns a map object containing the transformed elements. This map object can be readily converted to a list, tuple, or other desired iterable structure using functions like list(), tuple(), or set().
Benefits of Employing the map Function
The map function offers a compelling suite of advantages, making it an indispensable tool in the Python programmer’s arsenal:
-
Conciseness and Readability: The
mapfunction allows for concise and expressive code, replacing verbose loops with a single, elegant line. This clarity enhances code maintainability and comprehension. -
Enhanced Efficiency: By eliminating the need for explicit loops, the
mapfunction often leads to improved performance, particularly when dealing with large datasets. This optimization is achieved by leveraging the underlying C implementation of themapfunction, resulting in faster execution times. -
Functional Programming Paradigm: The
mapfunction aligns seamlessly with the principles of functional programming, promoting code reusability, modularity, and immutability. This approach fosters a cleaner and more maintainable codebase. -
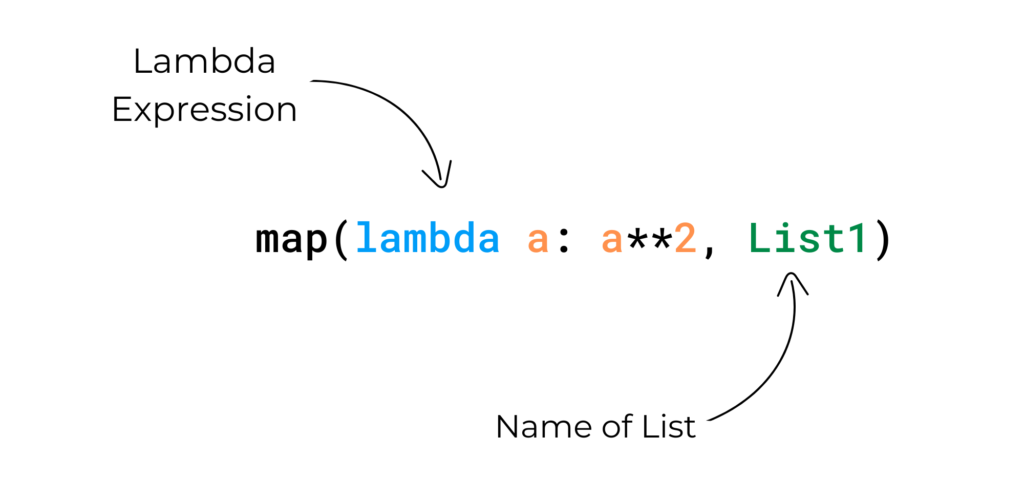
Flexibility and Adaptability: The
mapfunction is remarkably versatile. It can be used with any function that accepts a single argument, including built-in functions, user-defined functions, and lambda functions. This flexibility allows for a wide range of applications.
Illustrative Examples
To solidify the understanding of the map function’s capabilities, let’s explore some practical examples:
-
Squaring Elements of a List:
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] squared_numbers = list(map(lambda x: x**2, numbers)) print(squared_numbers) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]This example demonstrates how to square each element in a list using a lambda function within the
mapfunction. -
Converting Strings to Uppercase:
names = ["john", "jane", "peter"] uppercase_names = list(map(str.upper, names)) print(uppercase_names) # Output: ['JOHN', 'JANE', 'PETER']Here, the
mapfunction applies thestr.uppermethod to each string in the list, resulting in a list of uppercase strings. -
Applying Multiple Functions:
def square(x): return x**2 def cube(x): return x**3 numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] squared_cubed = list(map(lambda x: (square(x), cube(x)), numbers)) print(squared_cubed) # Output: [(1, 1), (4, 8), (9, 27), (16, 64), (25, 125)]This example showcases the ability to apply multiple functions to each element using a lambda function within the
mapfunction.
Addressing Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why use the map function instead of a loop?
The map function offers several advantages over explicit loops:
- Conciseness: It provides a more compact and readable way to apply functions to iterable objects.
- Efficiency: It often performs faster due to its underlying C implementation.
- Functional Programming: It aligns with the functional programming paradigm, promoting code reusability and modularity.
2. Can the map function be used with multiple iterables?
Yes, the map function can accept multiple iterables as arguments. In this case, the function applied will receive one element from each iterable on each iteration. The resulting map object will contain tuples, each tuple comprising elements from the corresponding iterables.
3. Is the map function always the best choice?
While the map function is a powerful tool, it’s not always the optimal solution. For simple operations or scenarios where code clarity is paramount, a loop might be a better approach. However, for more complex transformations or when efficiency is a primary concern, the map function often shines.
4. How can I handle errors during the mapping process?
The map function itself doesn’t provide error handling mechanisms. To handle errors, you can either use a try...except block within the function applied by map or use a list comprehension with a conditional statement to filter out elements that cause errors.
Tips for Effective map Function Usage
- Choose the right function: Select a function that aligns with the desired transformation for the elements of the iterable.
-
Consider readability: While the
mapfunction can be concise, prioritize readability and maintainability. - Handle potential errors: Implement error handling mechanisms to prevent unexpected program termination.
-
Utilize lambda functions: Lambda functions are often ideal for simple functions applied within the
mapfunction.
Conclusion
The map function in Python empowers programmers to apply functions to iterables in a highly efficient and elegant manner. Its conciseness, readability, and alignment with functional programming principles make it a valuable tool for enhancing code quality and performance. By understanding its mechanics and benefits, programmers can leverage the map function to streamline their code, improve efficiency, and unlock the full potential of Python’s expressive capabilities.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking Efficiency: The Power of the Python Map Function. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!