Understanding the World Through Regional Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the World Through Regional Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the World Through Regional Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the World Through Regional Maps: A Comprehensive Guide

The world map, a familiar visual representation of our planet, often appears as a single, unified entity. However, a deeper understanding of the world emerges when we delve into its regional divisions. These regional maps, by dissecting the globe into distinct geographical units, provide a nuanced perspective on diverse cultures, landscapes, economies, and geopolitical dynamics. This article explores the significance of world map regions, examining their classifications, key characteristics, and the benefits they offer in navigating a complex global landscape.
Classifying the World: Different Regional Frameworks
The division of the world into regions is not a fixed or universally agreed upon system. Instead, various frameworks exist, each emphasizing different aspects of the world’s interconnectedness. Some common regional classifications include:
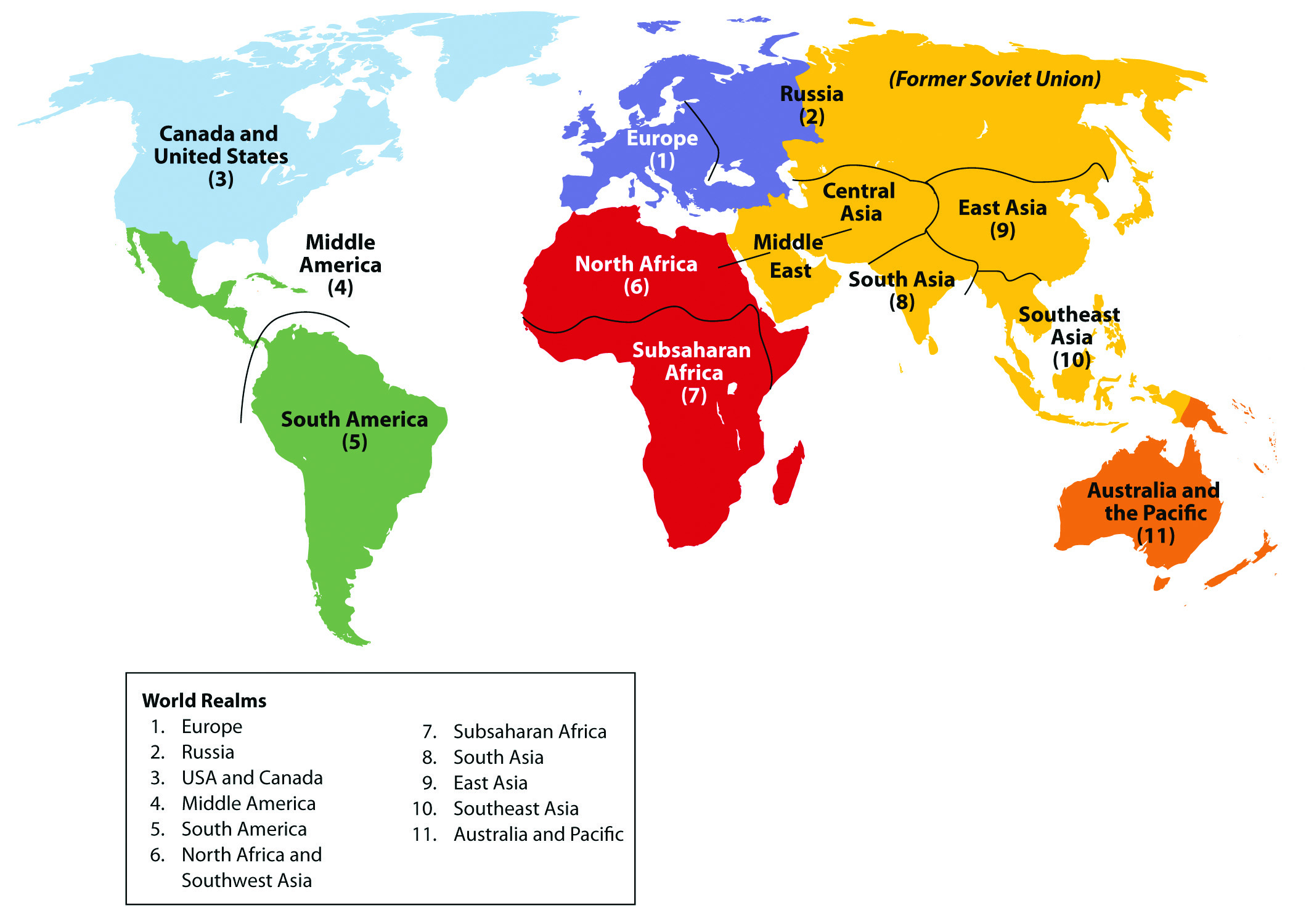
1. Continental Divisions: This is perhaps the most basic and widely recognized framework. It divides the world into seven continents: Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Europe, Australia, and Antarctica. This classification primarily focuses on geographical boundaries and landmasses, offering a general overview of the world’s major land areas.
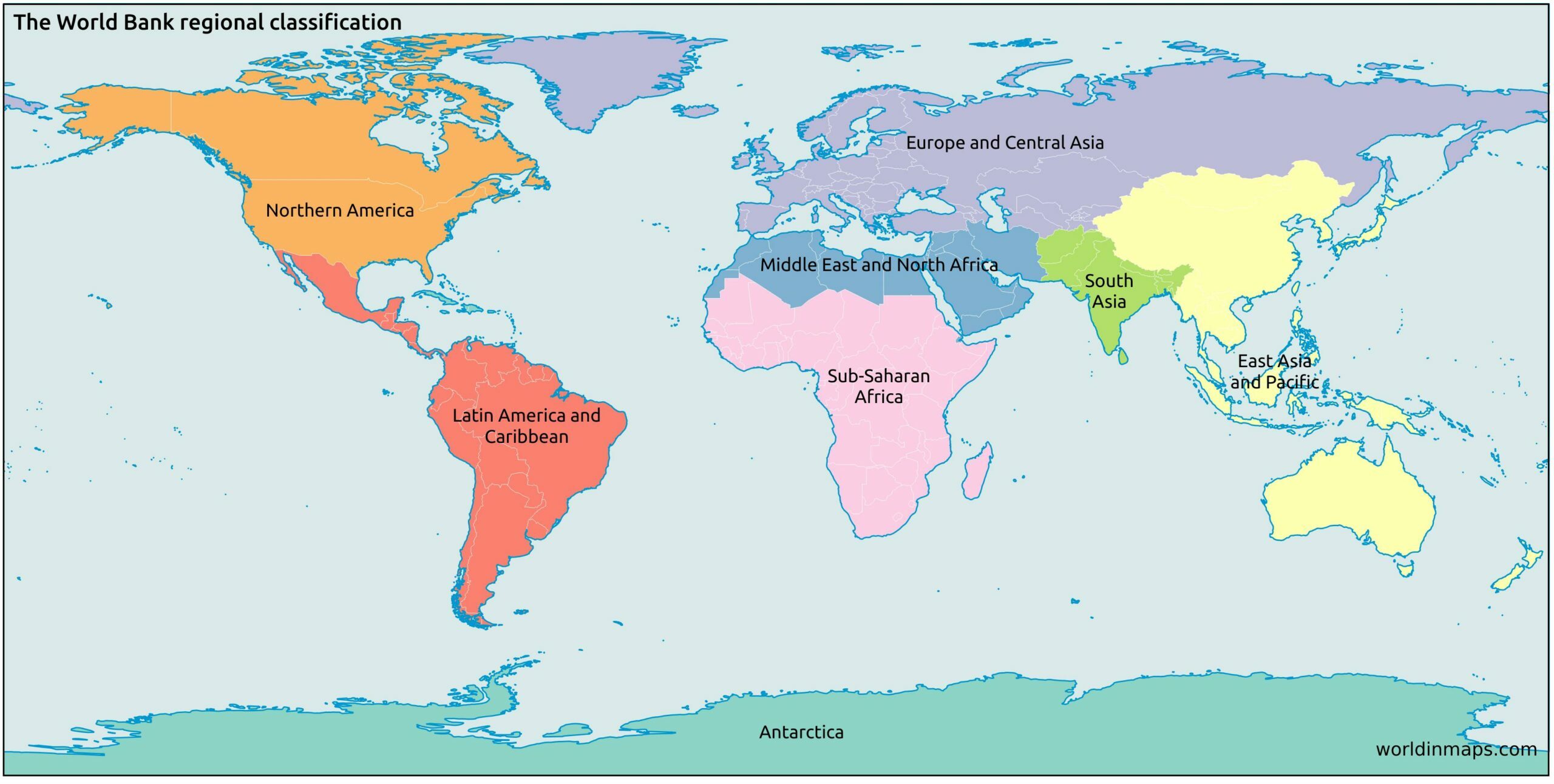
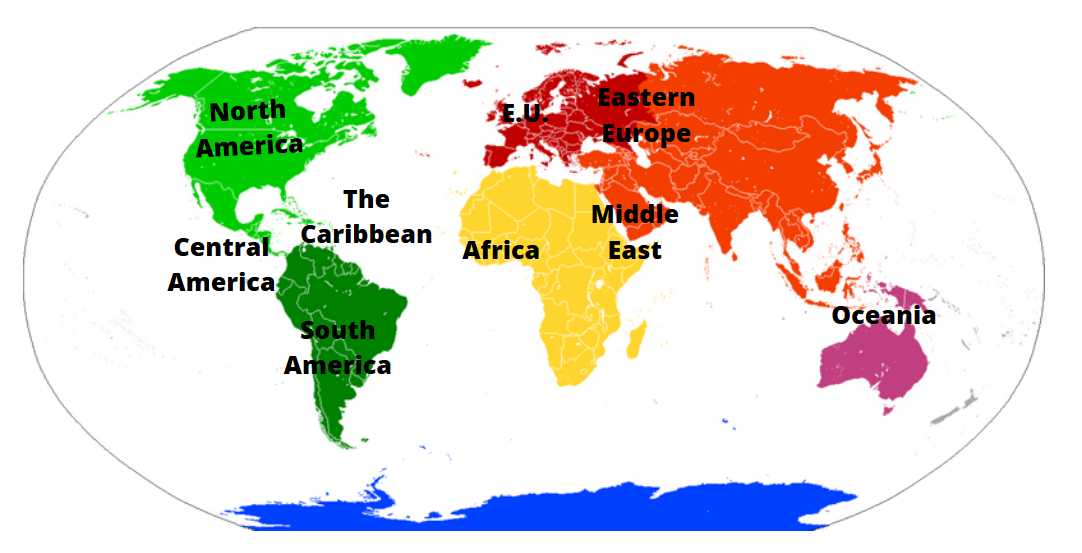
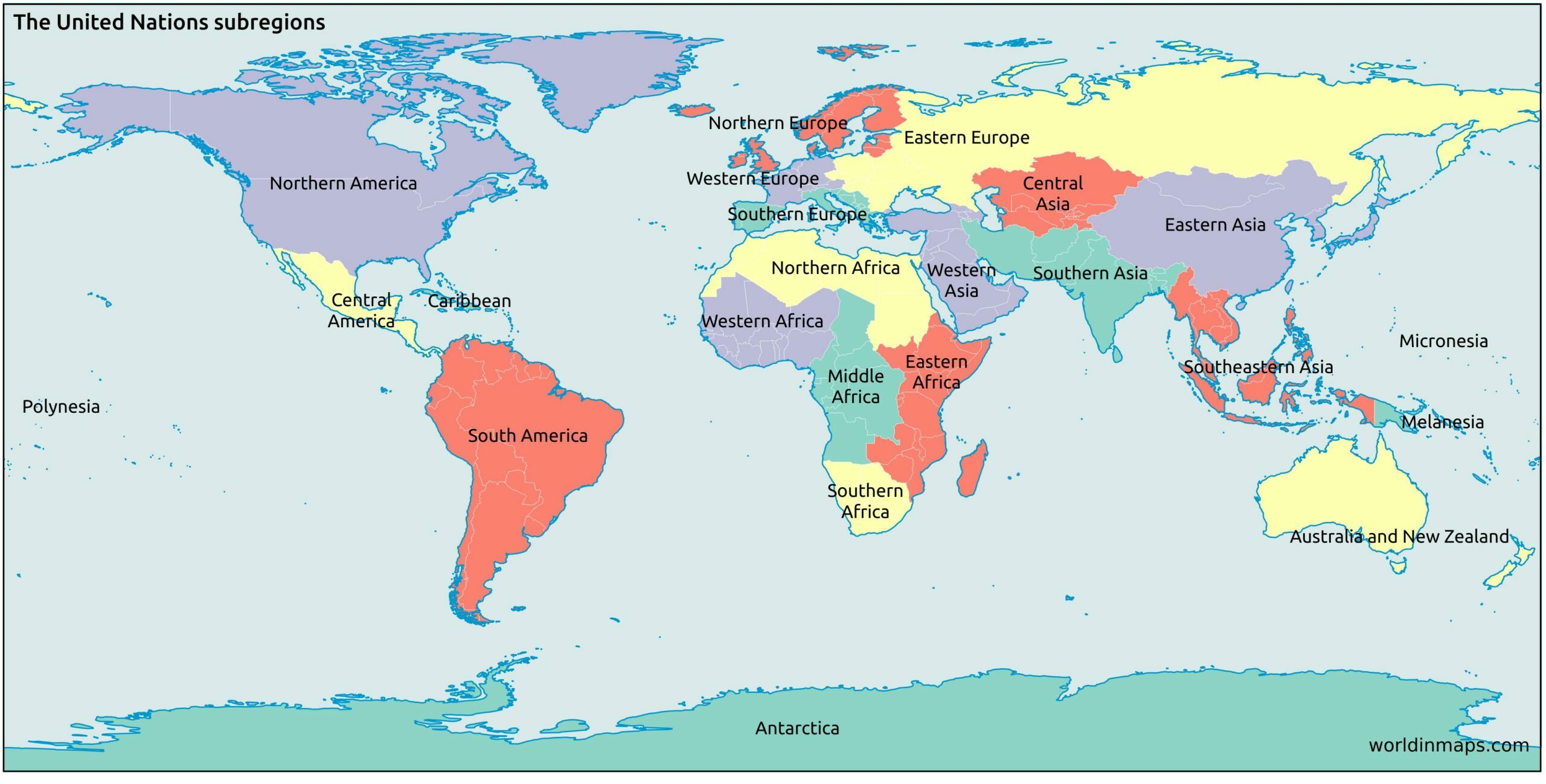
2. Geopolitical Regions: This framework considers political and economic factors, grouping countries based on shared interests, alliances, and historical connections. Examples include the European Union, the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN). These regions highlight the interconnectedness of nations through trade, diplomacy, and shared political goals.
3. Cultural Regions: This classification focuses on shared cultural traits, including language, religion, traditions, and values. Examples include Latin America, the Arab World, and East Asia. Cultural regions offer insight into the diverse expressions of human societies and their shared heritage.
4. Economic Regions: This framework categorizes regions based on economic activity, trade patterns, and levels of development. Examples include the BRICS nations (Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa), the G7 (Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States), and the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Economic regions highlight the global economic landscape and the interconnectedness of economies through trade and investment.
5. Environmental Regions: This classification focuses on shared environmental characteristics, such as climate, vegetation, and topography. Examples include the Amazon rainforest, the Sahara Desert, and the Arctic tundra. Environmental regions highlight the diverse ecosystems of the world and the importance of understanding their interconnectedness.
Benefits of Regional Mapping: A Multifaceted Perspective
Beyond their basic function of organizing the world, regional maps offer several significant benefits:
1. Enhanced Understanding of Global Diversity: By dividing the world into distinct regions, we can better appreciate the vast range of cultures, languages, religions, and landscapes that make up our planet. This understanding fosters a sense of global awareness and respect for diverse perspectives.
2. Facilitating Comparative Analysis: By studying different regions, we can analyze and compare various aspects of human societies, such as economic development, political systems, social structures, and environmental challenges. This comparative approach allows for a deeper understanding of global trends and the factors driving them.
3. Guiding Policy Development: Regional mapping plays a crucial role in informing policy decisions. Understanding the unique characteristics and challenges of different regions helps policymakers tailor strategies to address specific needs and promote sustainable development.
4. Supporting International Cooperation: By highlighting the interconnectedness of different regions, regional maps encourage collaboration and cooperation on shared challenges, such as climate change, poverty, and global health issues.
5. Promoting Regional Integration: Regional maps can facilitate economic integration and trade within specific regions. By identifying shared interests and opportunities, regional organizations can promote economic growth and development within their respective areas.
FAQs on World Map Regions
Q1: Why are there different regional classifications?
A: Different regional classifications reflect various perspectives on the world. Some focus on geographical features, while others emphasize political, economic, cultural, or environmental aspects. The choice of classification depends on the specific purpose of the analysis.
Q2: How do regional maps help us understand global issues?
A: By highlighting the unique characteristics of different regions, regional maps provide context for understanding global issues like climate change, poverty, and conflict. They allow us to see how these issues manifest differently across regions and how they are interconnected.
Q3: Are regional boundaries fixed?
A: Regional boundaries are not always fixed and can evolve over time due to political shifts, economic changes, and cultural transformations. This fluidity reflects the dynamic nature of the global landscape.
Tips for Using Regional Maps Effectively
1. Identify the Purpose: Before using a regional map, determine the specific objective. This will help choose the most appropriate regional classification for the task.
2. Understand the Map’s Focus: Pay attention to the criteria used to define the regions on the map. This will ensure proper interpretation and analysis.
3. Consider Multiple Perspectives: Explore different regional classifications to gain a comprehensive understanding of the world’s complexities.
4. Use Data and Information: Complement regional maps with relevant data and information to deepen analysis and draw meaningful insights.
Conclusion: Navigating the World through Regional Lenses
Regional maps are essential tools for understanding the world’s diversity and interconnectedness. They provide a nuanced perspective on global issues, facilitating comparative analysis, informing policy decisions, and promoting international cooperation. By embracing a regional approach to understanding the world, we can foster greater global awareness, promote sustainable development, and navigate the complexities of the 21st century.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the World Through Regional Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!