Understanding the Power of the map Function in Python
Related Articles: Understanding the Power of the map Function in Python
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Power of the map Function in Python. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Power of the map Function in Python
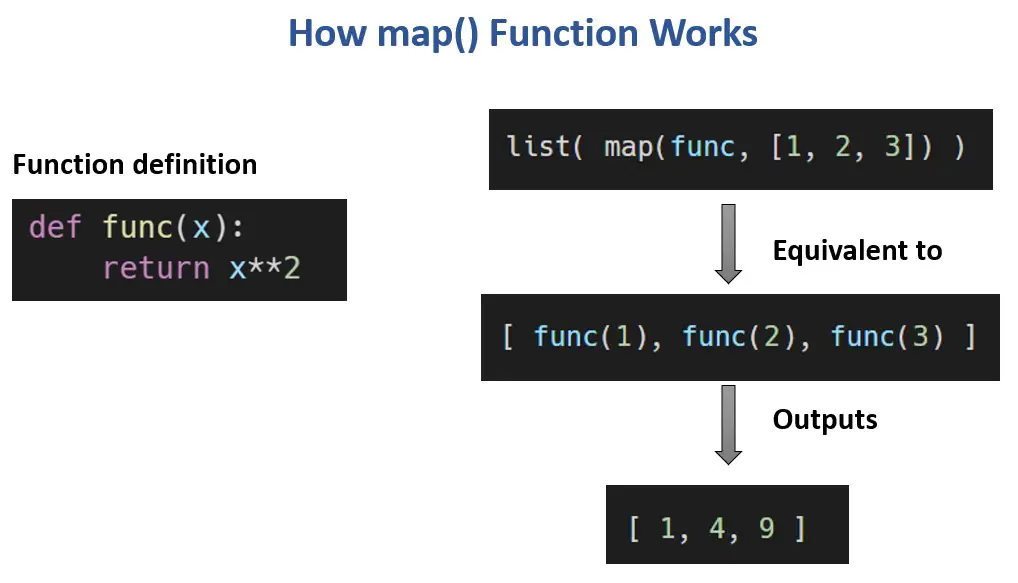
The map function in Python serves as a versatile tool for applying a specific function to every element within an iterable, such as a list, tuple, or string. This function streamlines the process of transforming data, making it a valuable asset for various programming tasks.
How map Works
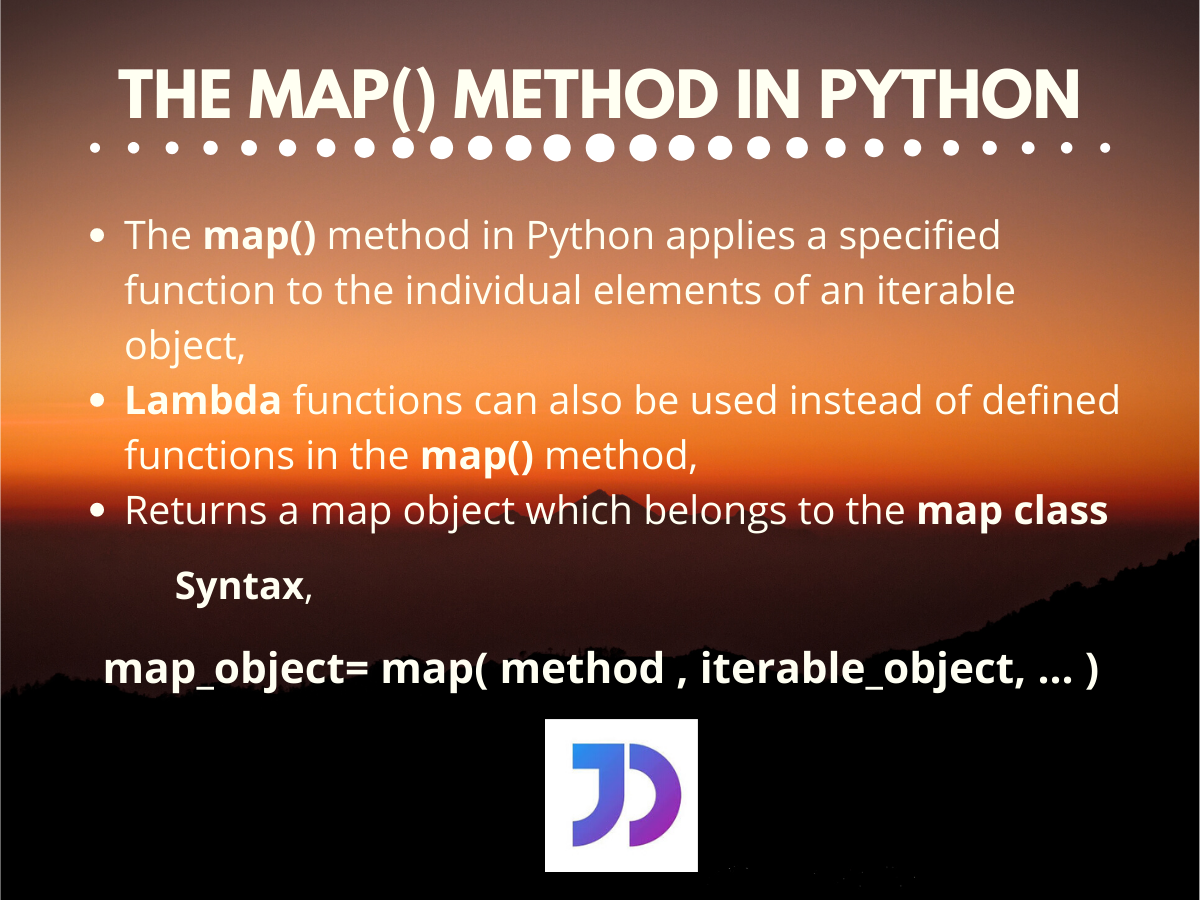
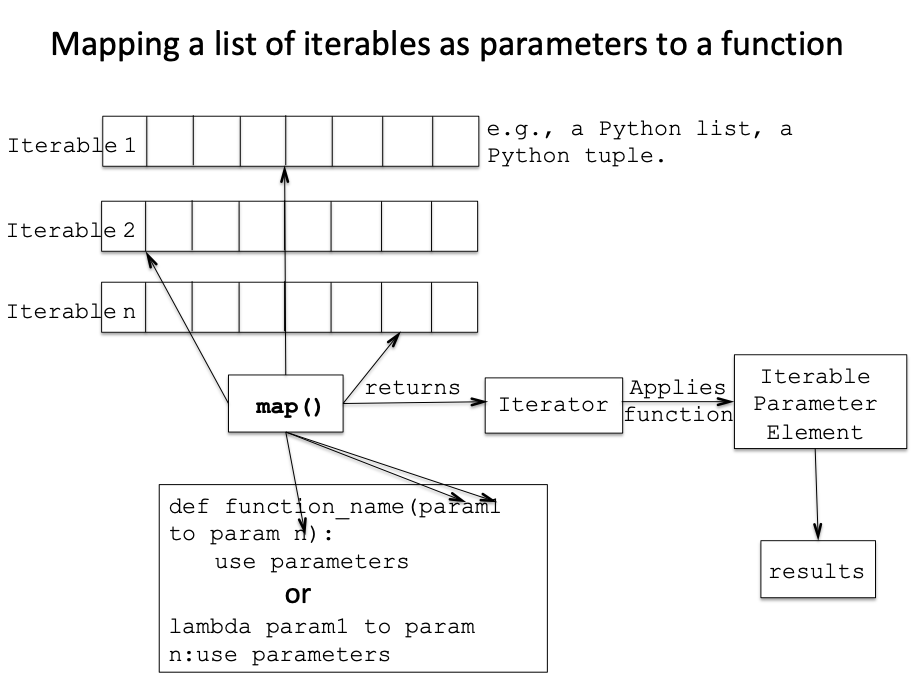
At its core, map takes two arguments:
-
Function: This is the function that will be applied to each element of the iterable. It can be a built-in function like
absorlen, or a custom function defined by the programmer. - Iterable: This is the sequence of elements that the function will operate on.
The map function then iterates through the iterable, applying the specified function to each element and generating a new iterable containing the transformed results. This new iterable can be accessed using various methods like converting it to a list, tuple, or set.
Illustrative Examples
Consider the following examples to visualize the functionality of map:
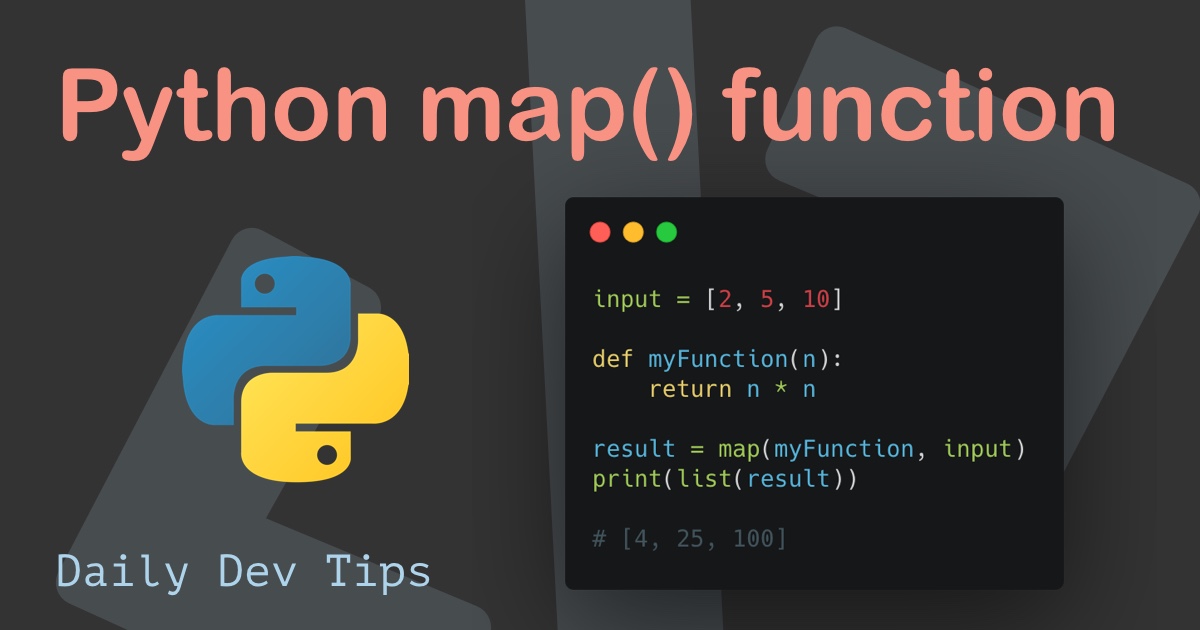
Example 1: Squaring Numbers
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
# Define a function to square a number
def square(x):
return x * x
# Apply the square function to each number in the list
squared_numbers = list(map(square, numbers))
print(squared_numbers) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]In this example, map applies the square function to each element in the numbers list, creating a new list squared_numbers containing the squared values.
Example 2: Converting Strings to Uppercase
names = ["john", "jane", "peter"]
# Apply the built-in upper function to each name
uppercase_names = list(map(str.upper, names))
print(uppercase_names) # Output: ['JOHN', 'JANE', 'PETER']Here, map uses the built-in str.upper function to convert each string in the names list to uppercase, producing a new list uppercase_names.
Benefits of Using map
The map function offers several advantages:
- Conciseness: It provides a compact and elegant way to apply functions to multiple elements, reducing the need for explicit loops.
-
Readability: The syntax of
mapmakes code easier to understand and maintain, as it clearly conveys the intent of applying a function to an iterable. -
Efficiency: While
mapitself doesn’t directly optimize performance, it often leads to more efficient code compared to manual looping, especially when dealing with large datasets. -
Functional Programming:
mapaligns with functional programming principles by emphasizing the transformation of data without modifying the original iterable.
Beyond Basic Usage
The power of map extends beyond simple transformations. It can be combined with other functions and techniques for more complex data manipulation:
-
Lambda Functions:
mapworks seamlessly with anonymous functions defined usinglambda. This allows for concise and flexible transformations without the need for separate function definitions.
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
# Apply a lambda function to square each number
squared_numbers = list(map(lambda x: x * x, numbers))
print(squared_numbers) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]-
Multiple Iterables:
mapcan handle multiple iterables as input, applying the function to corresponding elements from each iterable.
numbers = [1, 2, 3]
letters = ["a", "b", "c"]
# Combine elements from both iterables
combined = list(map(lambda x, y: str(x) + y, numbers, letters))
print(combined) # Output: ['1a', '2b', '3c']Important Considerations
While map offers significant benefits, it’s important to note these points:
-
Laziness: The result of
mapis not evaluated until it’s explicitly converted to a specific data structure (e.g., usinglist,tuple, orset). This can be advantageous for memory efficiency, but it also requires careful consideration when working with large datasets. -
Mutability:
mapitself does not modify the original iterable. It generates a new iterable with the transformed elements. - Alternatives: For specific scenarios, other techniques like list comprehensions or generator expressions might be more suitable or offer better performance.
FAQs about the map Function
Q1: What happens if the function and iterable have different lengths?
A: The map function will continue applying the function to elements of the iterable until the shorter iterable is exhausted. The resulting iterable will be the same length as the shortest input iterable.
Q2: Can I use map with nested iterables?
A: Yes, map can be applied recursively to nested iterables. However, it’s important to understand the nesting structure and the intended transformation for each level.
Q3: Is map suitable for all data transformation tasks?
A: While map is a powerful tool, it may not be the most efficient or appropriate solution for every scenario. Consider using list comprehensions, generator expressions, or other techniques based on the specific requirements of your task.
Tips for Using map Effectively
- Choose the right function: Select a function that accurately reflects the desired transformation.
-
Consider performance: For complex operations or large datasets, analyze the performance impact of using
mapversus alternative methods. - Leverage lambda functions: Use lambda functions for concise and flexible transformations.
-
Handle multiple iterables: Utilize
mapwith multiple iterables for parallel transformations. - Experiment and compare: Explore different techniques and compare their suitability for your specific needs.
Conclusion
The map function in Python provides a powerful and flexible mechanism for applying functions to iterables, enabling concise, readable, and often efficient code for data transformations. Understanding its workings, benefits, and limitations allows programmers to leverage its potential effectively in various programming contexts. By mastering the use of map, developers can enhance their code’s clarity, efficiency, and adherence to functional programming principles.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Power of the map Function in Python. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!