Understanding the Power of Geographic Distance: A Comprehensive Guide to Radius Maps
Related Articles: Understanding the Power of Geographic Distance: A Comprehensive Guide to Radius Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Power of Geographic Distance: A Comprehensive Guide to Radius Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Power of Geographic Distance: A Comprehensive Guide to Radius Maps
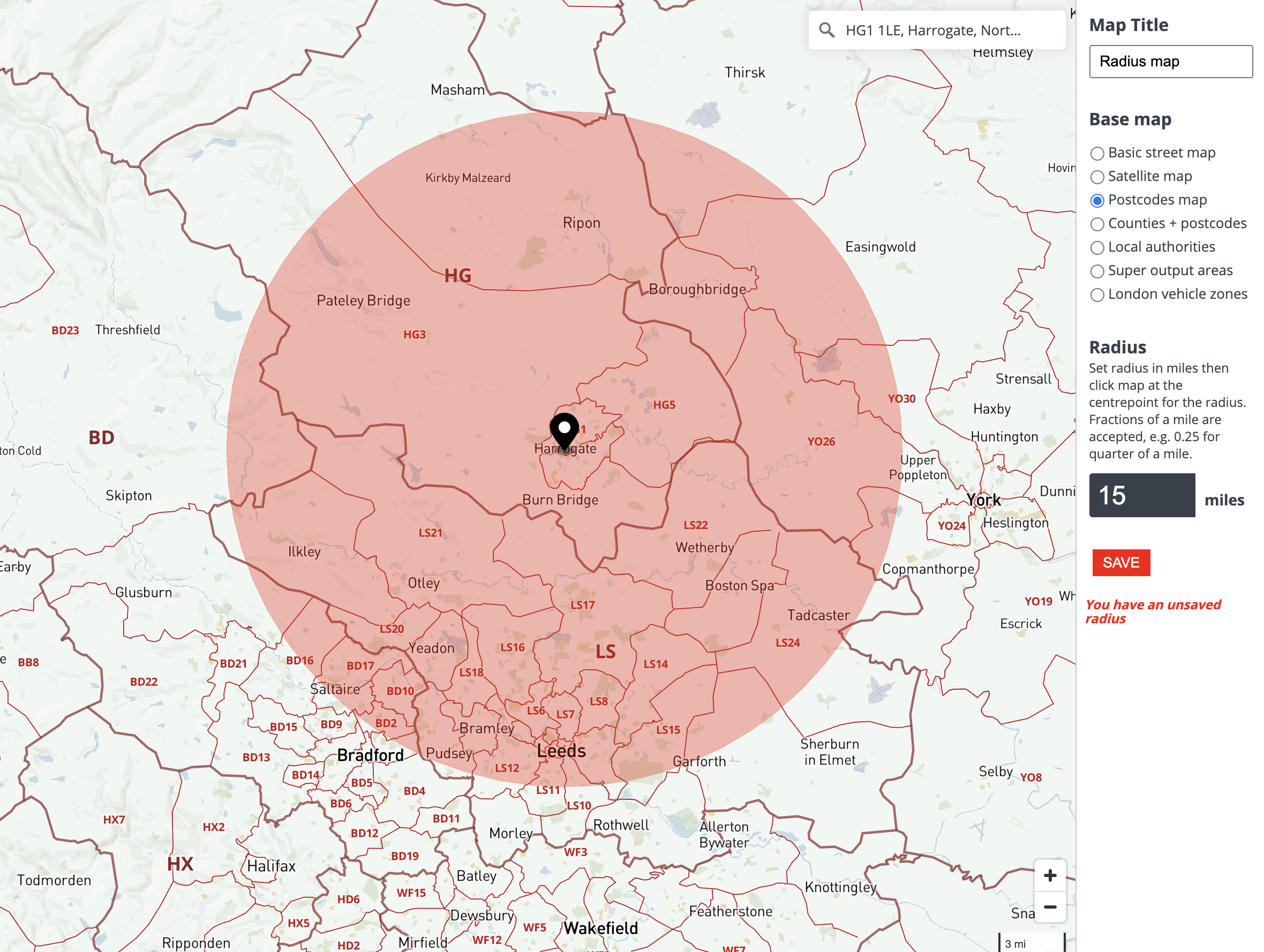
In the realm of spatial analysis and data visualization, the ability to represent and analyze data within a defined geographic area is crucial. This is where the concept of a radius map comes into play. A radius map, often referred to as a circle map, is a powerful tool that allows users to visualize data points within a specific distance from a central location. This visualization technique is widely employed across diverse fields, including:
- Business: Identifying potential customer bases, locating optimal store locations, analyzing market penetration, and understanding service area coverage.
- Urban Planning: Evaluating accessibility to public services, understanding population density, and assessing the impact of infrastructure development.
- Environmental Science: Analyzing the spread of pollution, mapping wildlife populations, and studying the impact of climate change.
- Emergency Response: Determining the reach of emergency services, identifying vulnerable populations, and planning evacuation routes.
- Real Estate: Searching for properties within a specific distance from amenities, schools, and transportation hubs.
Key Concepts and Components of Radius Maps:
A radius map typically consists of the following components:
- Central Point: The starting point from which the radius is measured. This could be a specific location, a point of interest, or a geographic coordinate.
- Radius: The distance from the central point that defines the area of interest. This distance can be measured in various units, such as miles, kilometers, or meters.
- Data Points: The locations of interest that are plotted within the defined radius. These points can represent various entities, such as businesses, schools, hospitals, or points of interest.
- Visualization: The method used to represent the data points within the radius. This can involve using markers, colors, sizes, or other visual cues to highlight specific characteristics or patterns.
Types of Radius Maps:
Radius maps can be categorized based on their purpose and visualization techniques:
- Static Radius Maps: These maps display a fixed radius around a central point, with the area of interest clearly defined. They are typically used for static analysis and visualization.
- Dynamic Radius Maps: These maps allow users to adjust the radius interactively, enabling exploration and analysis of different geographic areas. They are often employed in interactive mapping platforms and web applications.
- Multi-Radius Maps: These maps display multiple radii around different central points, allowing for comparison and analysis of different areas of interest. They are useful for understanding the spatial relationships between multiple locations.
- Heatmaps: These maps use color gradients to represent the density of data points within a defined radius. This provides a visual representation of the concentration of points in different areas.
Creating and Using Radius Maps:
Creating radius maps involves several steps:
- Defining the Central Point: Determine the starting location from which the radius will be measured.
- Setting the Radius: Specify the desired distance from the central point.
- Identifying Data Points: Gather the relevant locations that fall within the defined radius.
- Visualization: Choose a suitable method to represent the data points within the radius, such as markers, colors, or sizes.
- Analysis: Analyze the visualized data to identify patterns, trends, or insights.
Tools for Creating Radius Maps:
Several software tools and platforms are available for creating radius maps:
- Geographic Information System (GIS) Software: ArcGIS, QGIS, and MapInfo are powerful GIS software packages that offer advanced mapping and analysis capabilities, including radius map creation.
- Online Mapping Platforms: Google Maps, Bing Maps, and OpenStreetMap provide interactive mapping tools and APIs that allow users to create radius maps and visualize data.
- Data Visualization Software: Tableau, Power BI, and D3.js are data visualization tools that enable the creation of interactive and dynamic radius maps.
Benefits of Radius Maps:
Radius maps offer numerous benefits for various applications:
- Spatial Understanding: They provide a clear visual representation of data points within a defined geographic area, enhancing spatial awareness.
- Data Exploration: They allow users to explore and analyze data based on geographic proximity, identifying patterns and relationships.
- Decision Making: They support informed decision-making by providing insights into the spatial distribution of data, facilitating strategic planning.
- Problem Solving: They help identify areas of concern or potential issues based on the concentration of data points within a specific radius.
- Communication: They effectively communicate spatial information to diverse audiences, enhancing understanding and engagement.
FAQs about Radius Maps:
1. What is the difference between a radius map and a heatmap?
While both radius maps and heatmaps visualize data within a defined area, they differ in their approach. Radius maps focus on displaying data points within a specific distance from a central point, while heatmaps use color gradients to represent the density of data points across an area.
2. How can I determine the optimal radius for my map?
The optimal radius depends on the specific application and the scale of the data. Consider the distance relevant to your analysis, the size of the area of interest, and the density of data points.
3. What types of data can be visualized using radius maps?
Radius maps can visualize various data types, including locations of businesses, schools, hospitals, points of interest, population density, crime rates, pollution levels, and more.
4. Can I create a radius map for multiple central points?
Yes, you can create multi-radius maps that display multiple radii around different central points. This allows for comparison and analysis of different areas of interest.
5. Are radius maps suitable for large-scale data analysis?
While radius maps are effective for visualizing data within a specific radius, they may not be ideal for analyzing large-scale datasets with millions of data points. In such cases, other visualization techniques may be more appropriate.
Tips for Creating Effective Radius Maps:
- Choose an appropriate radius: Consider the scale of your data and the relevant distance for your analysis.
- Select a clear central point: Ensure the central point is relevant to your analysis and accurately represents the starting location.
- Use meaningful data points: Select data points that are relevant to your analysis and provide valuable insights.
- Choose an effective visualization method: Select a visualization technique that effectively represents the data and conveys the desired message.
- Use color and size effectively: Utilize color and size variations to highlight specific characteristics or patterns within the radius.
- Provide context and labels: Include labels and legends to clarify the meaning of data points and the radius definition.
- Consider interactivity: Explore interactive mapping platforms that allow users to adjust the radius and explore different areas of interest.
Conclusion:
Radius maps are a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing data within a defined geographic area. By representing data points within a specific distance from a central location, radius maps provide valuable insights into spatial relationships, patterns, and trends. Their applications extend across various fields, supporting informed decision-making, problem-solving, and effective communication of spatial information. As technology advances and data availability grows, radius maps will continue to play a crucial role in understanding and interpreting the spatial dimensions of our world.

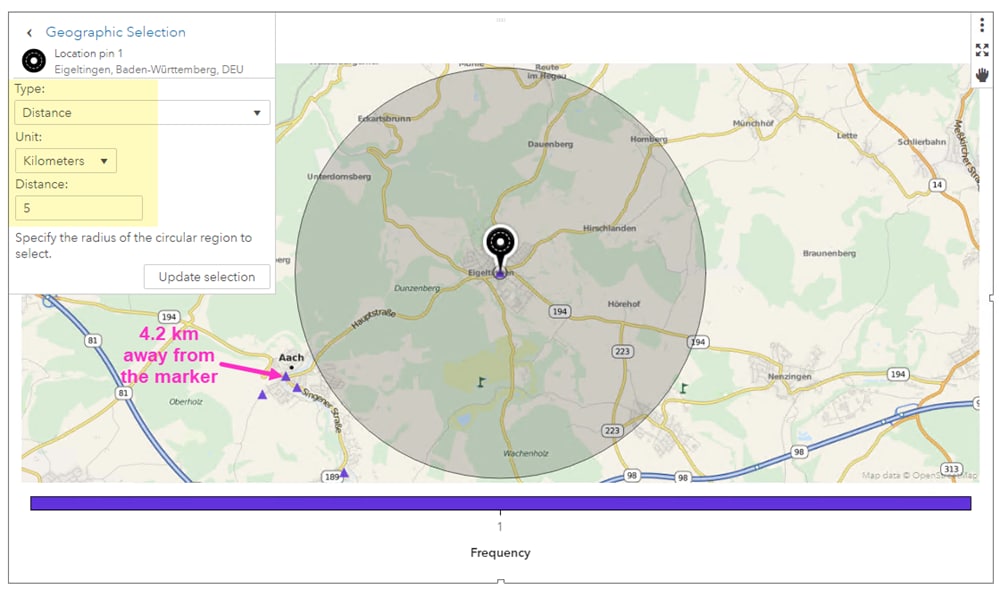



![Radius Map [Tool For Drawing & Creation] Distance & Driving Tim - Smappen](https://www.smappen.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/radiusmap-1024x671.jpg)
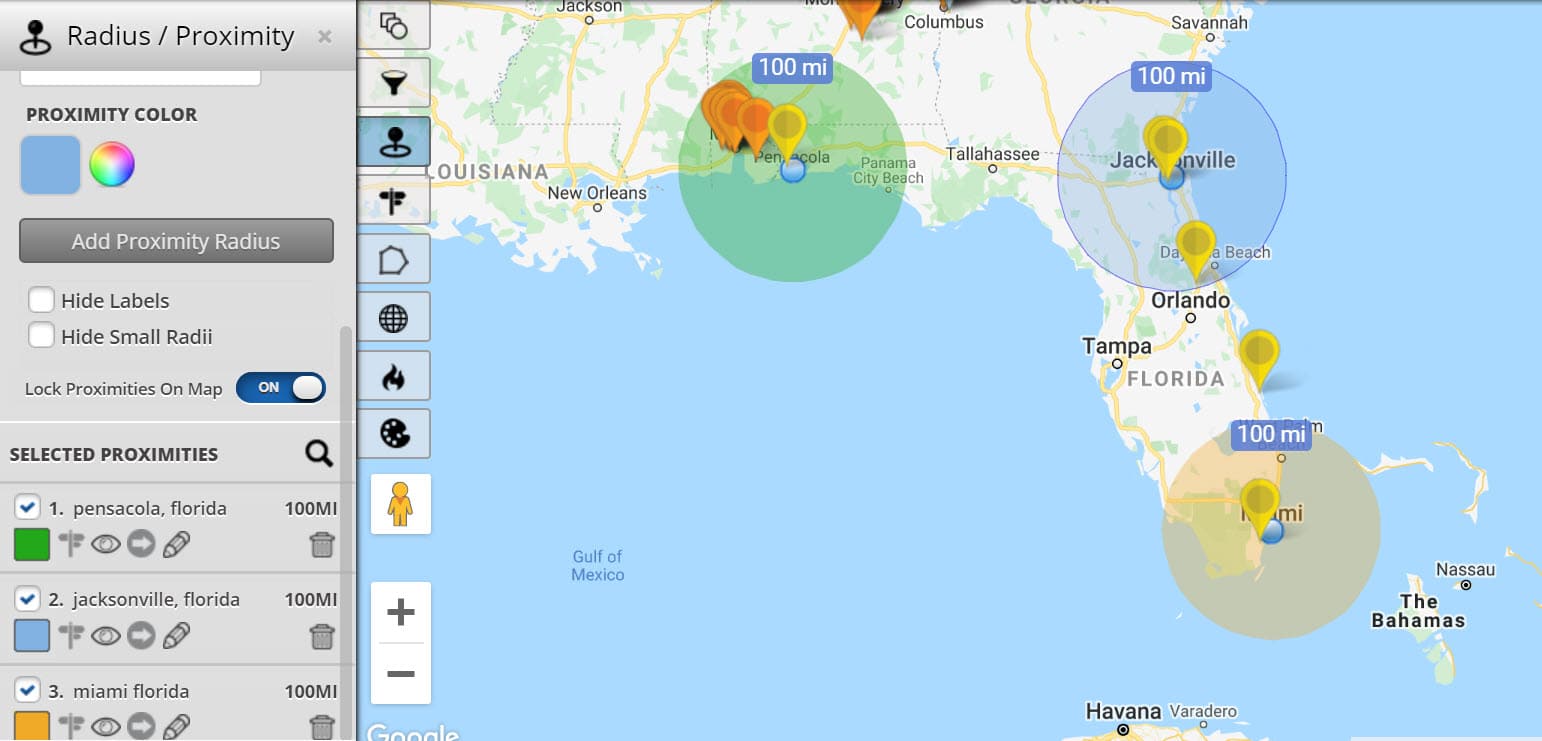
![Radius Map [Tool For Drawing & Creation] Distance & Driving Tim - Smappen](https://www.smappen.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/radius-map-1024x635.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Power of Geographic Distance: A Comprehensive Guide to Radius Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!