Understanding the Power of Circles on Maps: The Significance of Radius in Geographic Representation
Related Articles: Understanding the Power of Circles on Maps: The Significance of Radius in Geographic Representation
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Power of Circles on Maps: The Significance of Radius in Geographic Representation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Power of Circles on Maps: The Significance of Radius in Geographic Representation

Maps, those ubiquitous tools of navigation and spatial understanding, rely on a diverse array of symbols and techniques to convey information. Among these, the concept of radius plays a crucial role in defining areas of interest and facilitating spatial analysis. This article explores the fundamental principles of radius on maps, examining its applications, benefits, and significance in various fields.
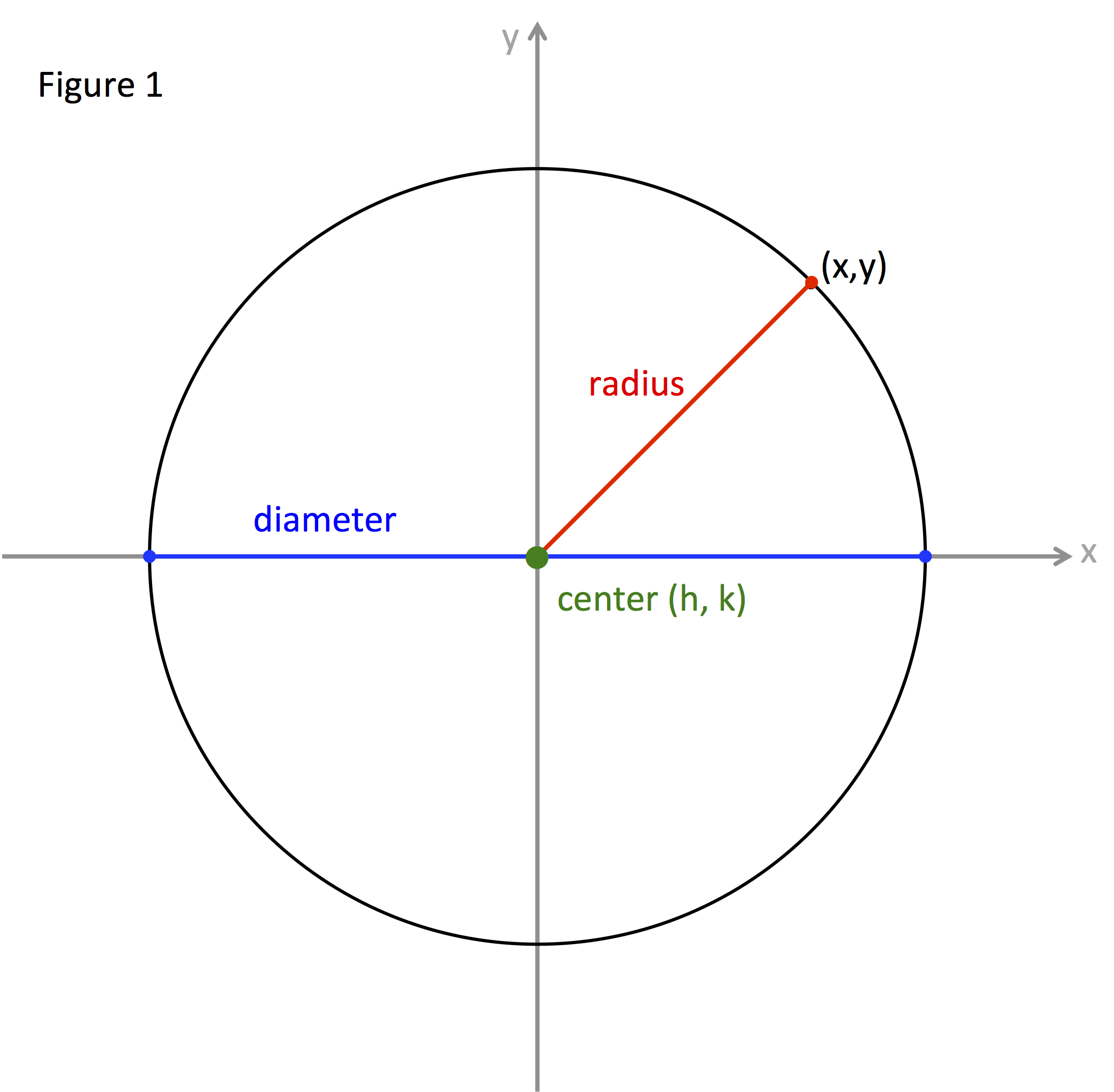
Defining the Radius:
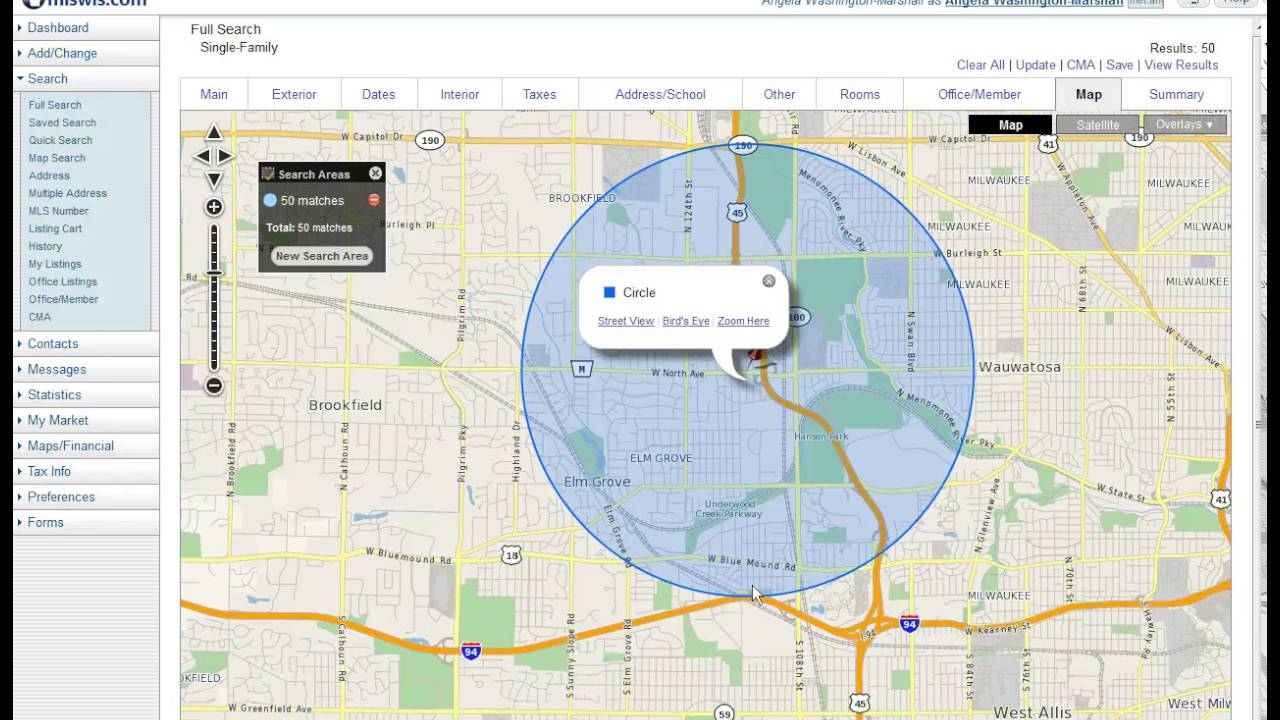
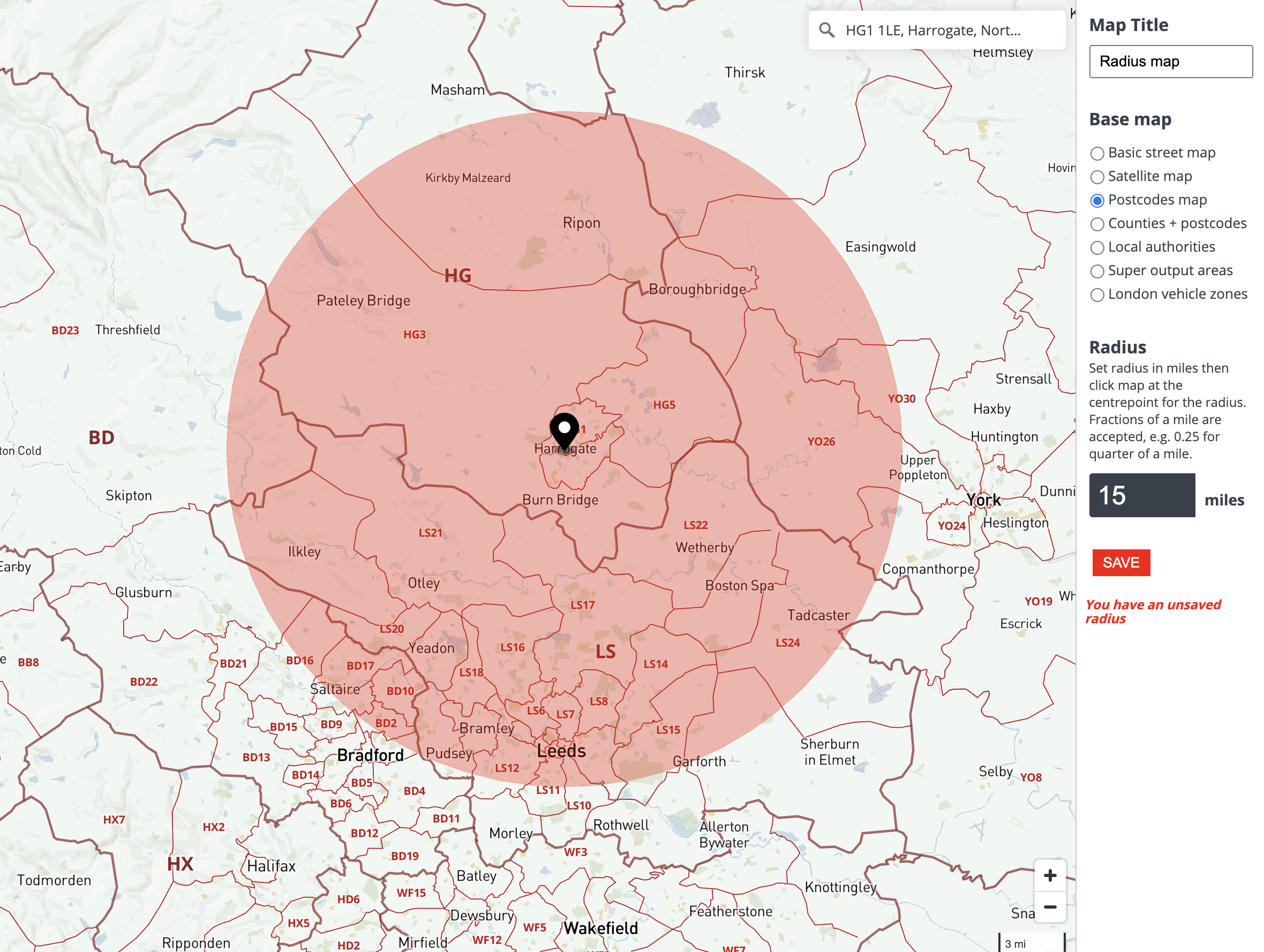
At its core, radius refers to the distance from a central point to the edge of a circle. In the context of maps, this simple concept becomes a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing spatial relationships. By drawing a circle with a specific radius around a point of interest, we can define a region encompassing all locations within that distance. This region, often referred to as a buffer zone or circle of influence, serves as a visual representation of the extent of an area’s impact or accessibility.
Applications of Radius on Maps:
The application of radius on maps extends far beyond simple visual representation. It finds relevance in numerous fields, including:
- Urban Planning: Planners utilize radius to define service areas for hospitals, schools, and other essential infrastructure. By drawing circles around these facilities, they can assess accessibility and identify potential gaps in service coverage.
- Environmental Studies: Radius plays a critical role in environmental impact assessments. By defining buffer zones around sensitive ecosystems or pollution sources, researchers can analyze the potential effects of human activities on the surrounding environment.
- Disaster Management: In emergency situations, radius helps define evacuation zones and the reach of rescue efforts. By drawing circles around disaster epicenters, authorities can effectively coordinate response strategies and prioritize resource allocation.
- Marketing and Business: Radius is a valuable tool for businesses seeking to target customers within specific geographic areas. By drawing circles around store locations or advertising campaigns, companies can optimize their marketing efforts and reach their desired audience.
- Transportation and Logistics: Radius facilitates route planning and optimization by defining service areas for delivery networks, public transportation systems, and emergency response vehicles. This allows for efficient resource allocation and minimizes travel time.
Benefits of Using Radius on Maps:
The use of radius on maps offers numerous benefits, making it an indispensable tool for various applications:
- Clarity and Visualization: Radius provides a clear and intuitive way to visualize spatial relationships, enabling users to easily grasp the extent of an area’s influence or accessibility.
- Data Analysis and Interpretation: By defining buffer zones and analyzing data within those areas, users can gain valuable insights into spatial patterns and trends.
- Decision-Making and Planning: Radius empowers informed decision-making by providing a framework for assessing spatial constraints, optimizing resource allocation, and evaluating potential impacts.
- Communication and Collaboration: Using radius on maps facilitates communication and collaboration among stakeholders, enabling them to share spatial information and coordinate efforts effectively.
- Accessibility and User-Friendliness: The simplicity and intuitive nature of radius makes it easily accessible and user-friendly, even for those without specialized spatial analysis skills.
FAQs about Radius on Maps:
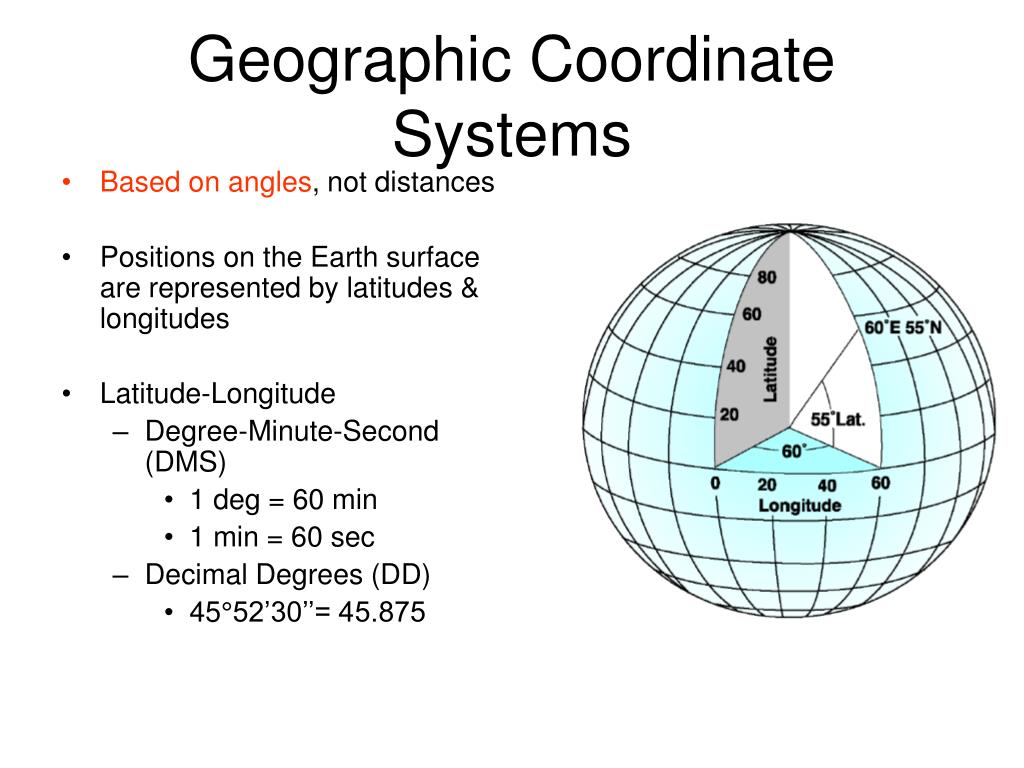
1. How is radius measured on maps?
Radius is typically measured in units of distance, such as kilometers, miles, or meters. The specific unit used depends on the scale of the map and the purpose of the analysis.
2. What factors influence the choice of radius?
The choice of radius depends on several factors, including the scale of the map, the nature of the analysis, and the specific application. For instance, in urban planning, the radius used to define a school’s service area might be different from the radius used to assess the impact of a highway on air quality.
3. How can I create radius circles on maps?
There are various tools and software available for creating radius circles on maps. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software, such as ArcGIS or QGIS, offers advanced capabilities for defining and analyzing buffer zones. Online mapping platforms like Google Maps also provide basic tools for drawing circles around points of interest.
4. What are some limitations of using radius on maps?
While radius is a powerful tool, it has certain limitations. It assumes a uniform spatial distribution of data and may not accurately represent complex or irregular spatial relationships. Additionally, the choice of radius can influence the results of analysis, so it’s crucial to select an appropriate value based on the specific context.
Tips for Using Radius on Maps Effectively:
- Define the purpose of the analysis: Clearly define the objective of using radius on the map to ensure the selection of appropriate values and interpretation of results.
- Consider the scale of the map: The radius used should be proportional to the scale of the map to avoid distortion or misleading results.
- Experiment with different radii: Explore different radius values to identify the most meaningful and relevant insights for the specific analysis.
- Combine radius with other spatial analysis tools: Utilize radius in conjunction with other techniques, such as proximity analysis or spatial interpolation, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of spatial relationships.
- Communicate results clearly: Use clear and concise language to communicate the findings of radius-based analysis, ensuring that stakeholders understand the implications of the results.
Conclusion:
Radius, a seemingly simple concept, plays a vital role in enhancing our understanding of spatial relationships and facilitating informed decision-making. By defining areas of interest, visualizing spatial patterns, and enabling data analysis, radius empowers professionals across diverse fields to tackle complex spatial challenges. From urban planning to environmental management and disaster response, the power of circles on maps continues to shape our world, underscoring the enduring importance of radius in geographic representation.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Power of Circles on Maps: The Significance of Radius in Geographic Representation. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!