Understanding Map Radius Areas: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Map Radius Areas: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Map Radius Areas: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Map Radius Areas: A Comprehensive Guide

In the realm of geography, mapping, and spatial analysis, the concept of a radius area plays a crucial role in defining and visualizing spatial relationships. It is a fundamental tool used in various applications, from urban planning and resource management to market research and disaster response. This article delves into the intricacies of radius areas, exploring their definition, calculation, significance, and applications.
Defining the Radius Area
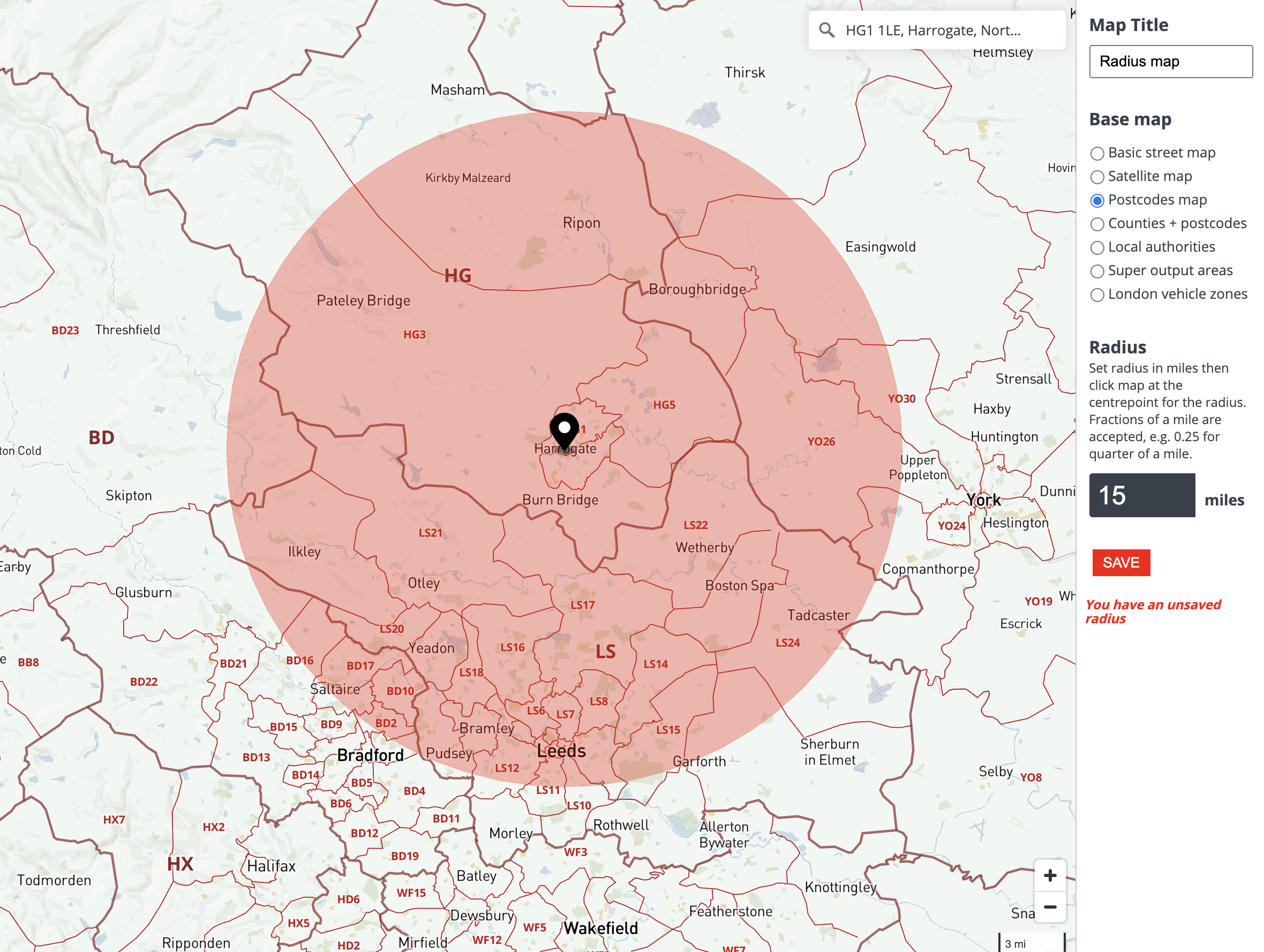
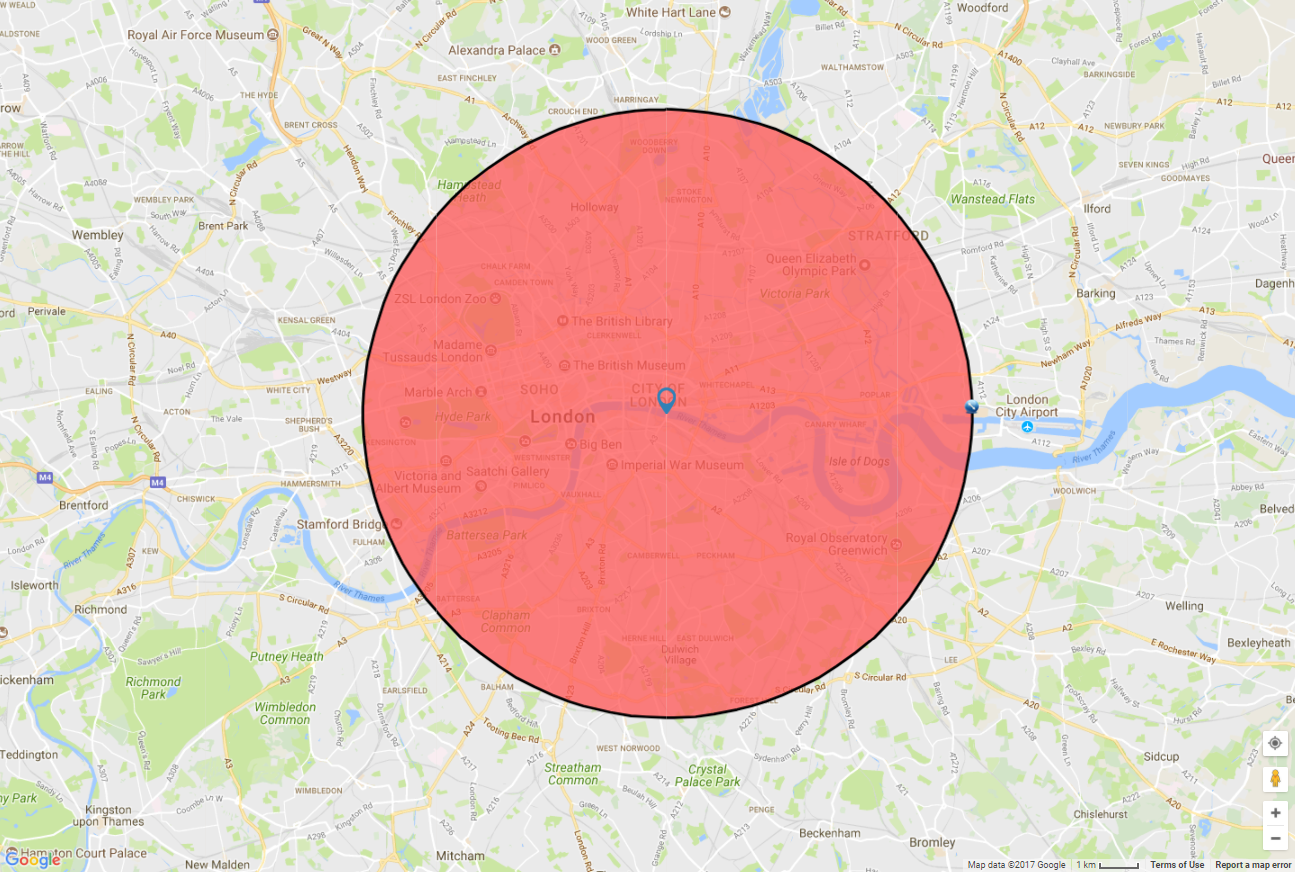
A radius area, often referred to as a circular buffer or geospatial buffer, is a circular region defined by a central point and a specific distance extending outward. This distance, known as the radius, determines the size of the area. In essence, a radius area encompasses all points within a given distance from the central point.
Visualizing the Radius Area
Imagine a map with a single point marked as the center. Drawing a circle around this point, with the radius representing the specified distance, creates the radius area. This area can be visualized as a disc or a pie slice, depending on whether the entire circle or a portion of it is being considered.
Calculating the Radius Area
The calculation of a radius area involves determining its surface area. For a complete circular radius area, the formula is:
- *Area = π r²**
Where:
- π (pi) is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159
- r is the radius of the circle
Significance and Applications of Radius Areas
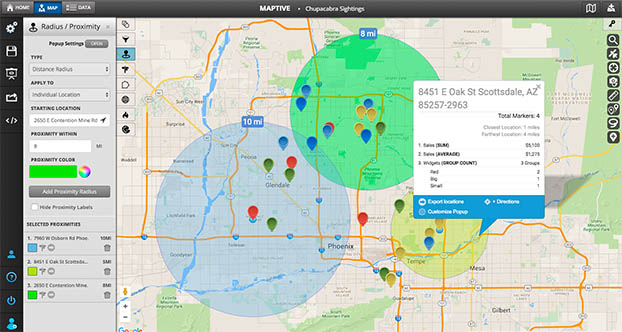
Radius areas hold significant importance across numerous disciplines, enabling efficient spatial analysis and decision-making. Some key applications include:
- Urban Planning: Determining the impact of new infrastructure projects on surrounding areas, assessing the accessibility of public services, and identifying potential development zones.
- Resource Management: Identifying areas within a specific distance from natural resources, such as water sources, forests, or mineral deposits, for resource allocation and conservation efforts.
- Market Research: Defining target markets based on proximity to businesses, identifying potential customer bases, and understanding market reach.
- Disaster Response: Defining evacuation zones based on the distance from the disaster epicenter, identifying areas requiring immediate assistance, and facilitating efficient resource allocation.
- Environmental Studies: Analyzing the impact of pollution sources on surrounding areas, identifying areas vulnerable to climate change, and monitoring ecological changes.
- Transportation Planning: Determining service areas for public transportation, assessing the efficiency of transportation networks, and identifying potential bottlenecks.
Factors Influencing Radius Area Calculations
Several factors can influence the calculation and interpretation of radius areas:
- Projection: The choice of map projection can affect the accuracy of distance calculations, particularly for large areas.
- Earth Curvature: For large radius areas, accounting for the Earth’s curvature is essential to ensure accurate distance calculations.
- Terrain: Uneven terrain can distort distance calculations, requiring adjustments to account for elevation changes.
- Spatial Resolution: The resolution of the map data used can impact the accuracy of radius area calculations, especially for smaller radius areas.
Beyond Simple Circular Areas
While circular radius areas are commonly used, more complex geometries can be incorporated to represent real-world scenarios. For example:
- Sector Radius Areas: These areas are defined by a central point, a radius, and an angle, creating a pie slice-shaped area.
- Polygon Radius Areas: These areas are defined by a central point and a polygon shape, allowing for the creation of irregularly shaped radius areas.
FAQs Regarding Radius Areas
1. What are the units used for radius areas?
Units for radius areas are dependent on the units used for the radius. If the radius is measured in kilometers, the area will be measured in square kilometers. Similarly, if the radius is measured in miles, the area will be measured in square miles.
2. How do I determine the optimal radius for my analysis?
The optimal radius for analysis depends on the specific application and the scale of the study. Consider the distance over which the phenomenon you are studying is likely to have an impact.
3. What are some tools for creating radius areas?
Various software programs and online tools are available for creating radius areas, including:
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): ArcGIS, QGIS, and other GIS software offer advanced tools for creating and analyzing radius areas.
- Online Mapping Platforms: Google Maps, Mapbox, and other online mapping platforms offer tools for creating basic radius areas.
- Programming Languages: Python libraries like Geopandas and R packages like sf provide functionalities for creating and analyzing radius areas.
Tips for Effective Use of Radius Areas
- Clearly Define the Purpose: Before creating a radius area, clearly define the objective of the analysis and the relevant distance for the study.
- Consider Data Resolution: Ensure the map data used has a sufficient resolution for the desired level of detail in the radius area.
- Account for Earth Curvature: For large radius areas, use tools that account for the Earth’s curvature to ensure accurate distance calculations.
- Visualize the Results: Use maps and other visualizations to effectively communicate the results of your radius area analysis.
Conclusion
Radius areas are a fundamental tool in spatial analysis, offering a powerful way to define and visualize spatial relationships. Understanding the concept, calculation, and applications of radius areas enables efficient decision-making in diverse fields, from urban planning and resource management to market research and disaster response. By leveraging the capabilities of radius areas, individuals and organizations can gain valuable insights into spatial patterns, optimize resource allocation, and make informed decisions regarding various spatial phenomena.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Map Radius Areas: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!