Understanding Map Projectors and Open Blocks: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Map Projectors and Open Blocks: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Map Projectors and Open Blocks: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding Map Projectors and Open Blocks: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding Map Projectors and Open Blocks: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 The Essence of Map Projectors
- 3.2 Delving into Open Blocks: A Key Concept in Map Projection
- 3.3 The Advantages of Open Blocks
- 3.4 The Mechanics of Open Blocks
- 3.5 Applications of Open Blocks in Cartography
- 3.6 FAQs Regarding Open Blocks
- 3.7 Tips for Using Open Blocks Effectively
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding Map Projectors and Open Blocks: A Comprehensive Guide
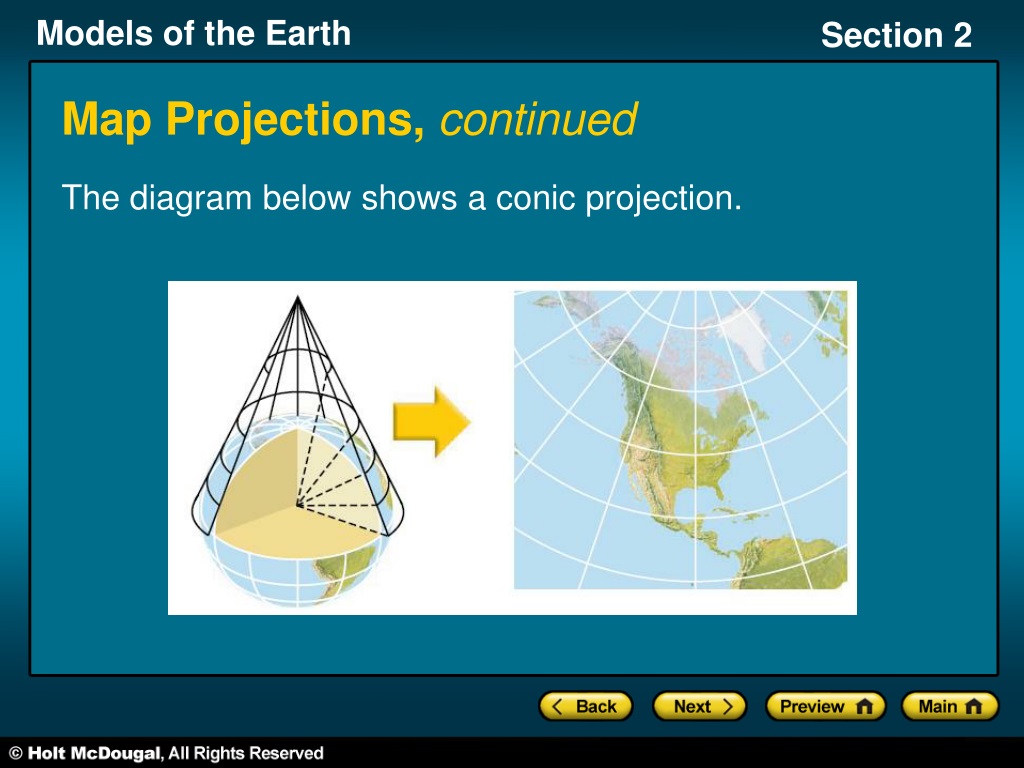
The realm of cartography, the art and science of mapmaking, relies heavily on the ability to project a spherical Earth onto a flat surface. This is where map projectors come into play. They are essential tools for accurately depicting geographical features on maps, enabling us to understand the world around us. This article delves into the intricate world of map projectors, specifically focusing on the concept of "open blocks," shedding light on their significance in the creation of accurate and insightful maps.
The Essence of Map Projectors
Map projectors are mathematical functions that transform the coordinates of points on the Earth’s surface onto a flat plane. They are the backbone of mapmaking, allowing cartographers to create various types of maps for diverse purposes. These projectors employ different techniques to minimize distortion, which is inevitable when projecting a curved surface onto a flat one.
There are numerous map projections, each with its own strengths and weaknesses, depending on the intended use. Some projections are designed to preserve area, others to maintain shape, and some strive to balance both. The choice of projection depends on the specific requirements of the map, such as its purpose, the region being mapped, and the desired level of accuracy.
Delving into Open Blocks: A Key Concept in Map Projection
Within the context of map projections, the term "open blocks" refers to a specific type of projection that is particularly useful for representing large areas. This approach involves dividing the Earth’s surface into sections, or blocks, and then projecting each block individually onto a flat surface. This technique allows for greater accuracy in representing the shapes and sizes of features within each block, reducing the overall distortion inherent in projecting a sphere onto a plane.
The Advantages of Open Blocks
Open blocks offer several advantages over traditional map projections:
- Increased Accuracy: By projecting individual blocks, the distortion associated with single-projection maps is significantly reduced. This results in more accurate representations of geographical features, particularly for large areas.
- Flexibility: The use of open blocks allows for greater flexibility in choosing the projection for each individual block. This means that cartographers can select the most appropriate projection for each specific region, maximizing accuracy based on its unique characteristics.
- Improved Data Integration: Open blocks facilitate the seamless integration of data from various sources, as each block can be projected independently. This is crucial for modern mapmaking, which often relies on integrating data from different sources like satellite imagery, aerial photography, and digital elevation models.
The Mechanics of Open Blocks
The process of creating an open block map involves several steps:
- Dividing the Earth: The first step is to divide the Earth’s surface into blocks, typically along lines of latitude and longitude. The size and shape of the blocks can vary depending on the specific projection and the intended use of the map.
- Projecting Each Block: Each individual block is then projected onto a flat surface using a suitable projection. This projection can be chosen based on the specific characteristics of the block, such as its size, shape, and the features it contains.
- Joining the Blocks: Once all the blocks are projected, they are joined together to create a complete map. This joining process requires careful alignment to ensure that the boundaries between the blocks are seamless and minimize any distortion.
Applications of Open Blocks in Cartography
Open blocks find wide applications in various fields where accurate maps are essential:
- Large-Scale Mapping: Open blocks are particularly valuable for creating maps of large regions, such as continents or entire countries. They allow for greater accuracy in representing the shapes and sizes of features, even across vast distances.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Open blocks are crucial for GIS applications, where data from different sources needs to be integrated seamlessly. They enable the accurate representation of data across large areas, facilitating analysis and decision-making.
- Navigation and Surveying: Open block maps are used in navigation and surveying, where accurate representations of geographical features are essential for safe and efficient operations.
FAQs Regarding Open Blocks
Q: What is the difference between open blocks and traditional map projections?
A: Traditional map projections project the entire Earth onto a flat surface using a single projection. This can result in significant distortion, especially for large areas. Open blocks, on the other hand, divide the Earth into smaller blocks and project each block individually, minimizing distortion.
Q: How do I choose the right projection for each block?
A: The choice of projection for each block depends on several factors, including the size and shape of the block, the features it contains, and the intended use of the map. For example, a projection that preserves area might be suitable for a block containing large geographical features, while a projection that maintains shape might be better for a block with intricate details.
Q: What are the limitations of open blocks?
A: While open blocks offer significant advantages, they also have some limitations. The process of dividing the Earth into blocks and projecting them individually can be complex and time-consuming. Additionally, the boundaries between blocks can sometimes create visual discontinuities, especially when viewing the map at a large scale.
Tips for Using Open Blocks Effectively
- Consider the intended use of the map: Determine the specific requirements of the map, such as the region being mapped, the level of detail required, and the intended audience.
- Choose the appropriate projection for each block: Select a projection that minimizes distortion and maximizes accuracy for the specific features and characteristics of each block.
- Ensure seamless joining of blocks: Carefully align the boundaries between blocks to minimize visual discontinuities and maintain the integrity of the map.
- Use appropriate software tools: Utilize specialized software designed for creating open block maps, as they provide tools for managing and manipulating data across multiple blocks.
Conclusion
Open blocks represent a significant advancement in the field of map projection. By dividing the Earth into smaller sections and projecting each block individually, they minimize distortion and enhance the accuracy of maps, especially for large areas. This technique is crucial for various applications, including large-scale mapping, GIS, navigation, and surveying. As technology continues to evolve, open blocks are likely to play an even more prominent role in the future of mapmaking, enabling us to create increasingly accurate and insightful representations of our world.
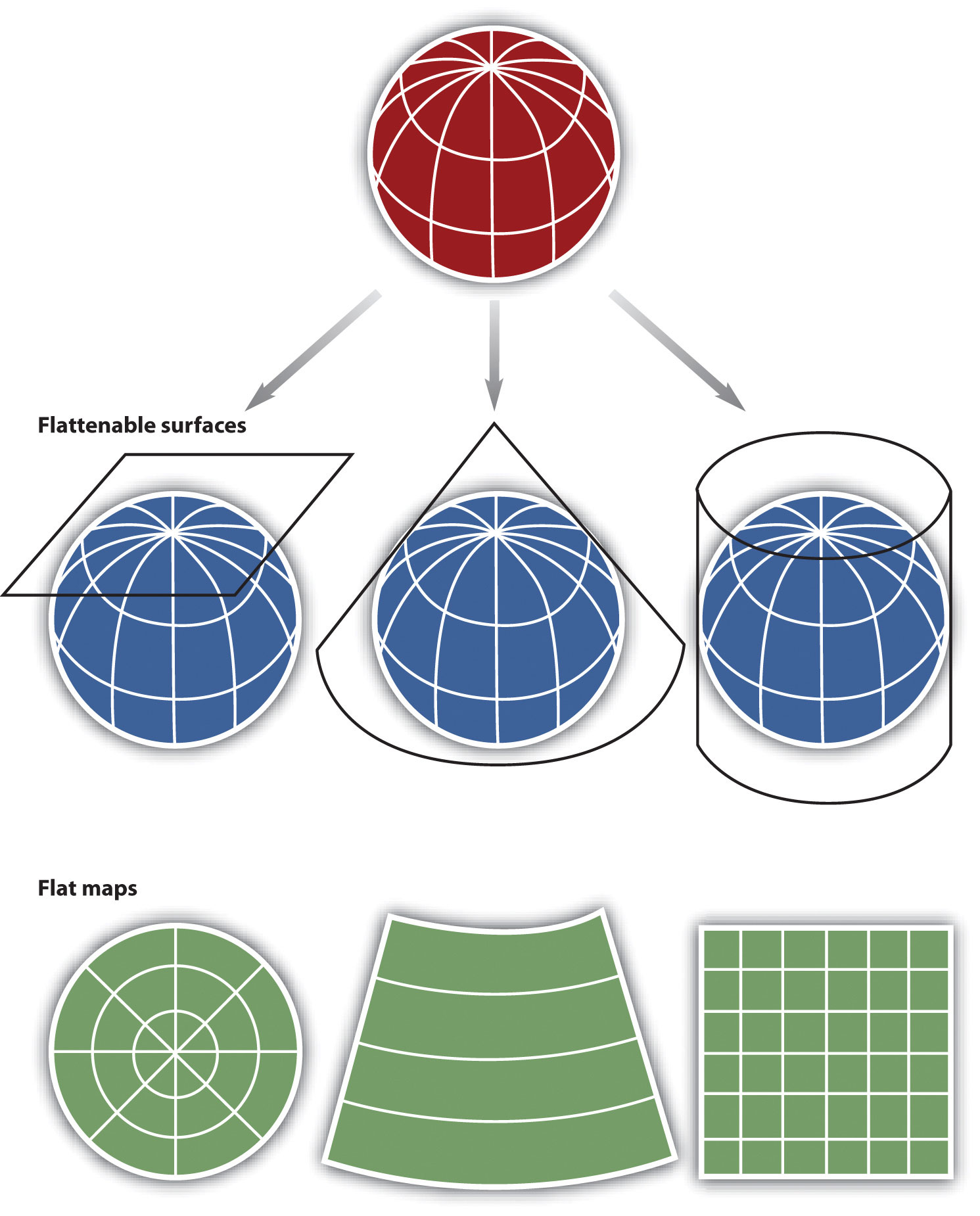

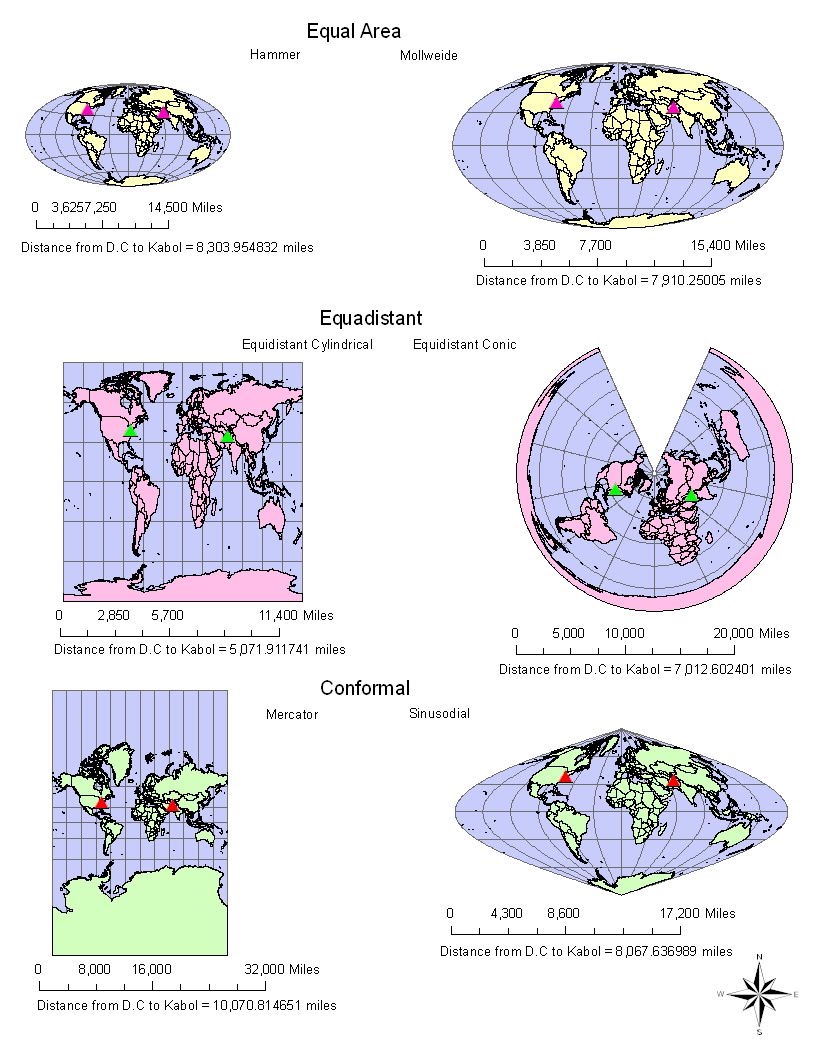




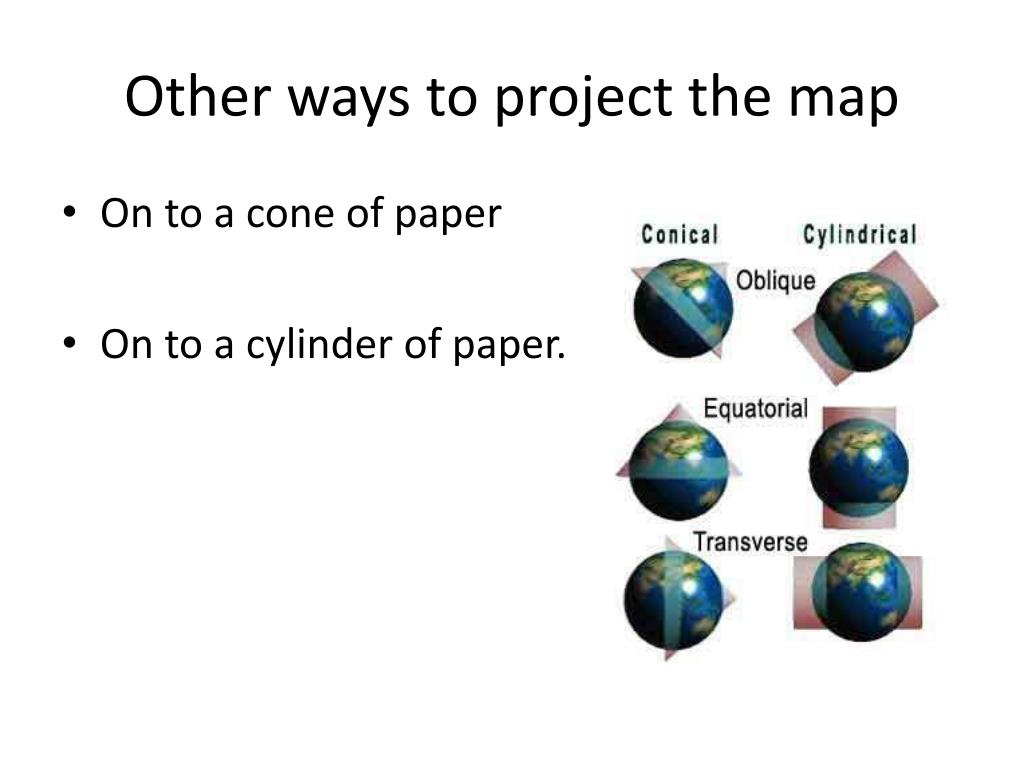
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Map Projectors and Open Blocks: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!