Understanding Map Projections in ArcGIS: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Map Projections in ArcGIS: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Map Projections in ArcGIS: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Map Projections in ArcGIS: A Comprehensive Guide

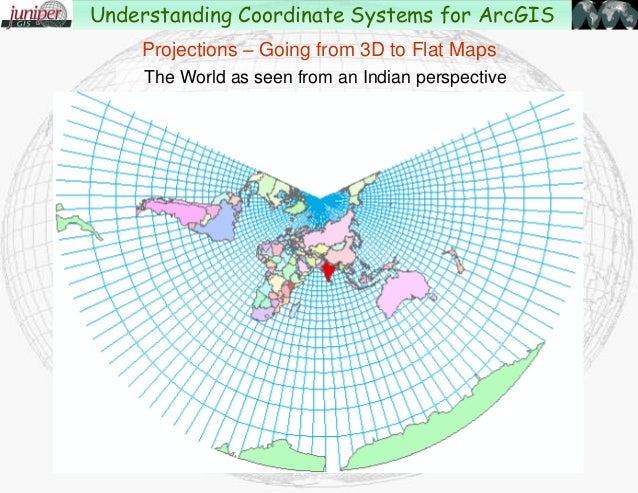
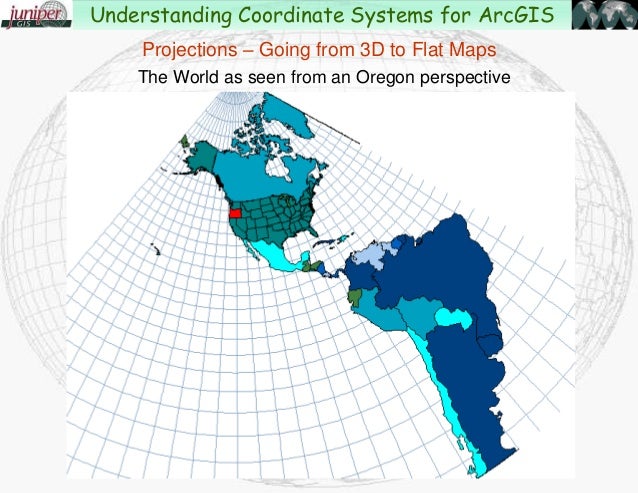
The Earth, a sphere, presents a challenge when attempting to represent it on a flat surface. This is where map projections come into play. Map projections are mathematical formulas that transform the Earth’s three-dimensional surface onto a two-dimensional plane. Understanding map projections is crucial for accurately representing geographical data and ensuring that spatial analysis and visualization are conducted with the appropriate context. This article delves into the intricacies of map projections within ArcGIS, highlighting their significance and providing practical insights.
The Fundamentals of Map Projections
The fundamental principle behind map projections is the conversion of spherical coordinates (latitude and longitude) to planar coordinates (x and y). This transformation inevitably introduces distortions, as it is impossible to perfectly represent a curved surface on a flat one. Different projections emphasize different properties, such as area, shape, distance, or direction, at the expense of others.
Types of Map Projections
Map projections are categorized into various types based on their properties and the way they represent the Earth’s surface. Some common categories include:
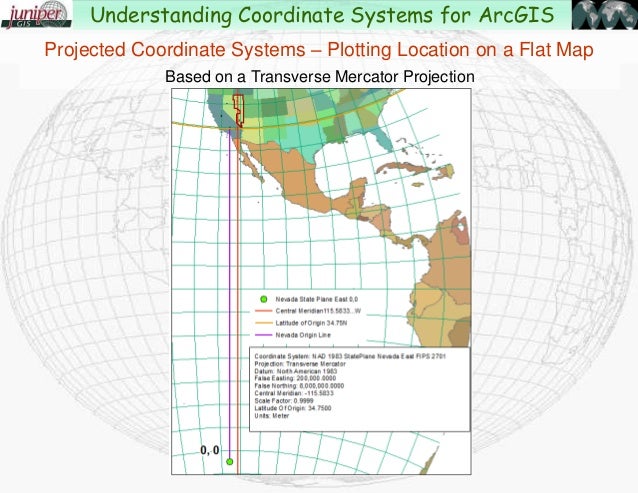
- Cylindrical Projections: These projections wrap a cylinder around the globe, projecting the Earth’s surface onto the cylinder. Examples include the Mercator projection, widely used for navigation, and the Transverse Mercator projection, frequently employed for large-scale mapping.
- Conic Projections: These projections project the Earth’s surface onto a cone. Conic projections are suitable for representing mid-latitude regions with minimal distortion. The Albers Equal Area Conic projection is a popular choice for representing the contiguous United States.
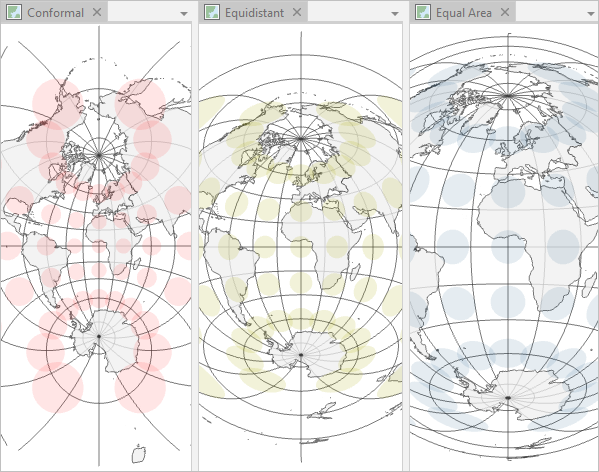
- Planar Projections: Also known as azimuthal projections, these projections project the Earth’s surface onto a flat plane. Planar projections are ideal for representing polar regions and are often used for global maps. The Azimuthal Equidistant projection is an example.
- Other Projections: Beyond these common types, there exist numerous other projections, each designed to minimize distortion for specific geographic areas and purposes.
Choosing the Right Projection in ArcGIS
The choice of map projection in ArcGIS is critical for ensuring accurate spatial analysis and visualization. The ideal projection depends on the specific task at hand, the geographic area of interest, and the desired properties to be preserved.
- Area: If accurate area calculations are paramount, consider projections that preserve area, such as the Albers Equal Area Conic projection.
- Shape: For applications requiring accurate shape representation, projections that preserve shape, such as the Lambert Conformal Conic projection, are suitable.
- Distance: For tasks involving distance measurements, projections that preserve distance, such as the Transverse Mercator projection, are preferred.
- Direction: If accurate direction representation is essential, projections that preserve direction, such as the Mercator projection, should be chosen.
Working with Map Projections in ArcGIS
ArcGIS provides a comprehensive set of tools for managing and utilizing map projections:
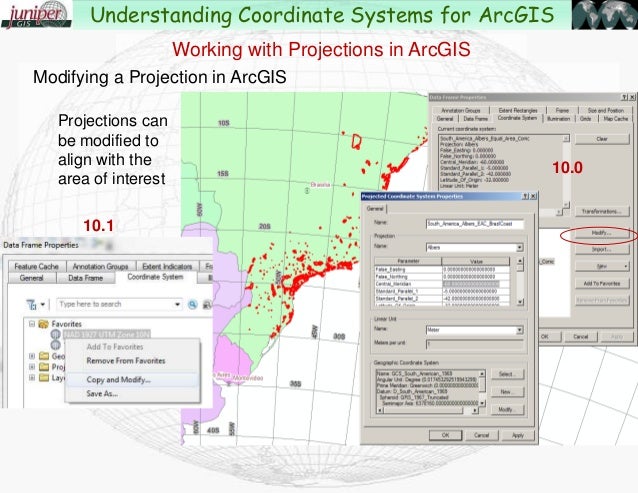
- Defining Projections: ArcGIS allows users to define custom projections by specifying the projection parameters. This enables precise control over the projection used for data analysis and visualization.
- Projecting Data: The "Project" tool in ArcGIS transforms data from one projection to another. This is essential for ensuring that data from different sources are compatible and can be analyzed together.
- Defining Coordinate Systems: ArcGIS utilizes coordinate systems to define the location of points on the Earth’s surface. Coordinate systems can be geographic (latitude and longitude) or projected (x and y coordinates).
- Data Visualization: When visualizing data in ArcGIS, it is crucial to select the appropriate projection to ensure accurate representation and avoid misleading interpretations.
The Importance of Map Projections in ArcGIS
The use of appropriate map projections in ArcGIS is essential for various reasons:
- Accurate Spatial Analysis: Map projections ensure that spatial analysis results are accurate and reliable. Using the wrong projection can lead to errors in distance, area, and shape calculations.
- Consistent Data Integration: Different datasets may use different projections. Projecting data to a common projection ensures consistency and facilitates accurate analysis and visualization.
- Meaningful Visualizations: The choice of projection significantly impacts the visual representation of geographic data. Choosing a projection that minimizes distortion in the desired area enhances the clarity and interpretability of maps.
FAQs on Map Projections in ArcGIS
1. What are the most common projections used in ArcGIS?
Common projections in ArcGIS include the Mercator projection, the Transverse Mercator projection, the Albers Equal Area Conic projection, and the Lambert Conformal Conic projection.
2. How do I know which projection to use for my data?
The choice of projection depends on the specific task, the geographic area, and the desired properties to be preserved. Consider the factors mentioned earlier: area, shape, distance, and direction.
3. Can I change the projection of my data in ArcGIS?
Yes, ArcGIS allows you to project data from one projection to another using the "Project" tool.
4. What is the difference between a geographic coordinate system and a projected coordinate system?
Geographic coordinate systems use latitude and longitude, while projected coordinate systems use planar coordinates (x and y).
5. How can I ensure that my map projections are accurate?
Verify the projection parameters and ensure that the chosen projection aligns with the desired properties. Consult authoritative sources and refer to documentation for specific projections.
Tips for Using Map Projections in ArcGIS
- Understand the properties of different projections.
- Consider the geographic area of interest and the purpose of your analysis.
- Use the "Project" tool to transform data to the desired projection.
- Consult documentation and resources for guidance on specific projections.
- Validate the accuracy of projections through visual inspection and comparison with known data.
Conclusion
Map projections are fundamental to accurately representing and analyzing geographic data in ArcGIS. Understanding the principles of map projections, the different types available, and the tools provided by ArcGIS is crucial for conducting meaningful spatial analysis and creating accurate and informative maps. By carefully selecting and applying appropriate projections, users can ensure the validity and reliability of their spatial data and gain valuable insights from geographic information.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Map Projections in ArcGIS: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!