The Quest for the Perfect World Map: Exploring the Best Projections for Different Purposes
Related Articles: The Quest for the Perfect World Map: Exploring the Best Projections for Different Purposes
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Quest for the Perfect World Map: Exploring the Best Projections for Different Purposes. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Quest for the Perfect World Map: Exploring the Best Projections for Different Purposes
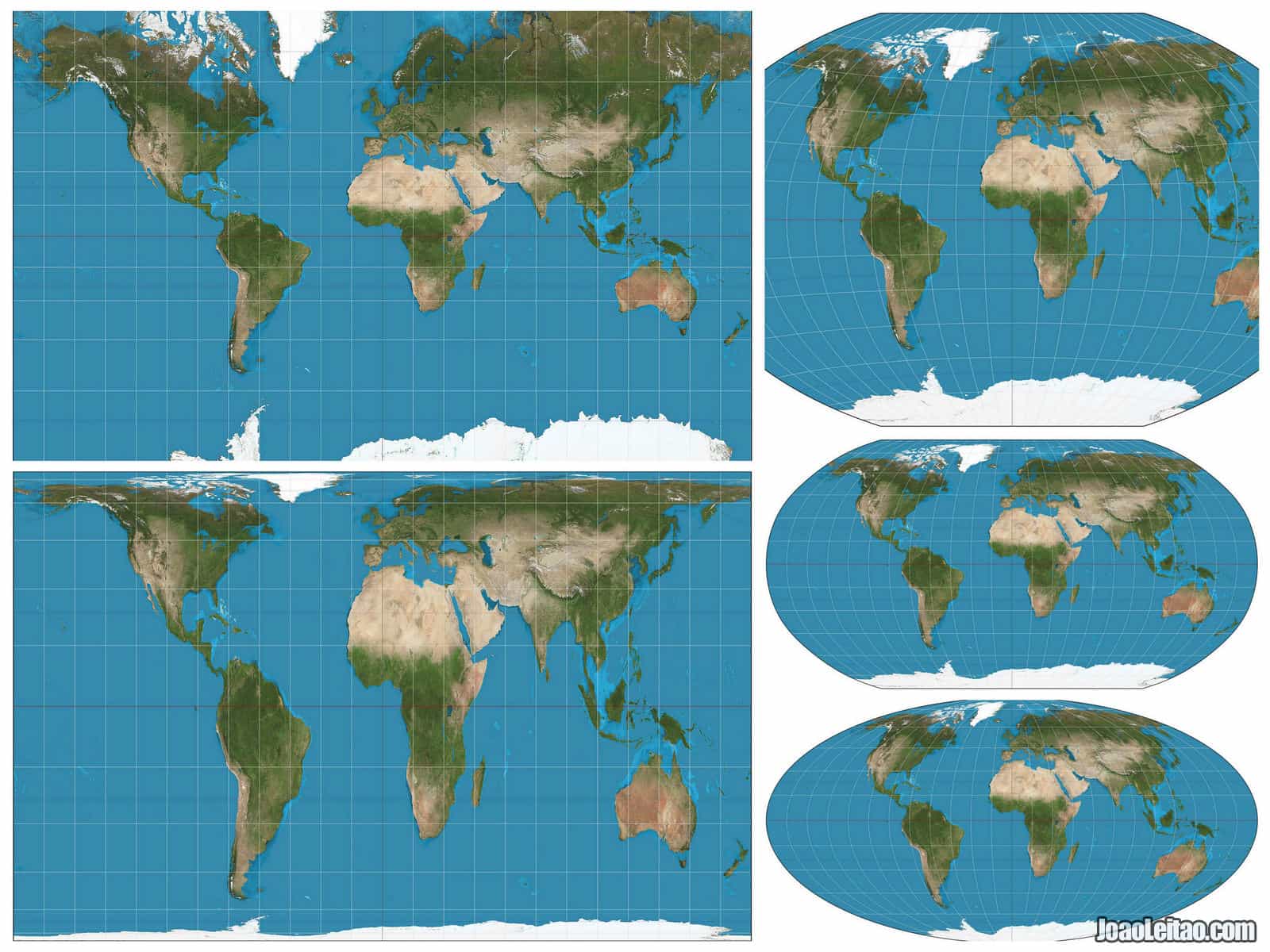
The Earth, a sphere, is inherently difficult to represent accurately on a flat surface. This challenge has led to the development of numerous map projections, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The search for the "best" projection is a complex one, as the ideal choice depends on the specific purpose and desired outcome. There is no single "best" projection that excels in all aspects, but understanding the characteristics of different projections allows for informed selection.
Understanding Map Projections:
Map projections are mathematical transformations that translate the Earth’s spherical surface onto a flat plane. This process inevitably introduces distortions, affecting the accuracy of distances, areas, shapes, and directions. The nature and extent of these distortions vary depending on the projection chosen.
Types of Map Projections:
Projections are broadly categorized based on their properties and the shape of the surface they project onto:
- Conic Projections: These project the Earth onto a cone, with meridians represented as straight lines converging at the apex of the cone. They are particularly useful for representing areas of mid-latitude.
- Cylindrical Projections: These project the Earth onto a cylinder, with meridians and parallels forming a rectangular grid. They are often used for world maps and are generally good for depicting areas near the equator.
- Azimuthal Projections: These project the Earth onto a plane, with meridians and parallels radiating outwards from a central point. They are useful for representing polar regions and are often used in navigation.
Key Considerations for Choosing a Projection:
The selection of the most suitable projection depends on several factors, including:
- Purpose of the Map: Different projections are best suited for specific purposes. For example, a map showing global population distribution may prioritize accurate area representation, while a map used for navigation might focus on preserving angles.
- Area of Focus: The geographical region being depicted influences the choice of projection. Projections that minimize distortions in specific regions are often preferred.
- Desired Properties: The map’s intended use dictates the importance of various properties like area, shape, distance, and direction.
Exploring Popular Projections and Their Strengths:
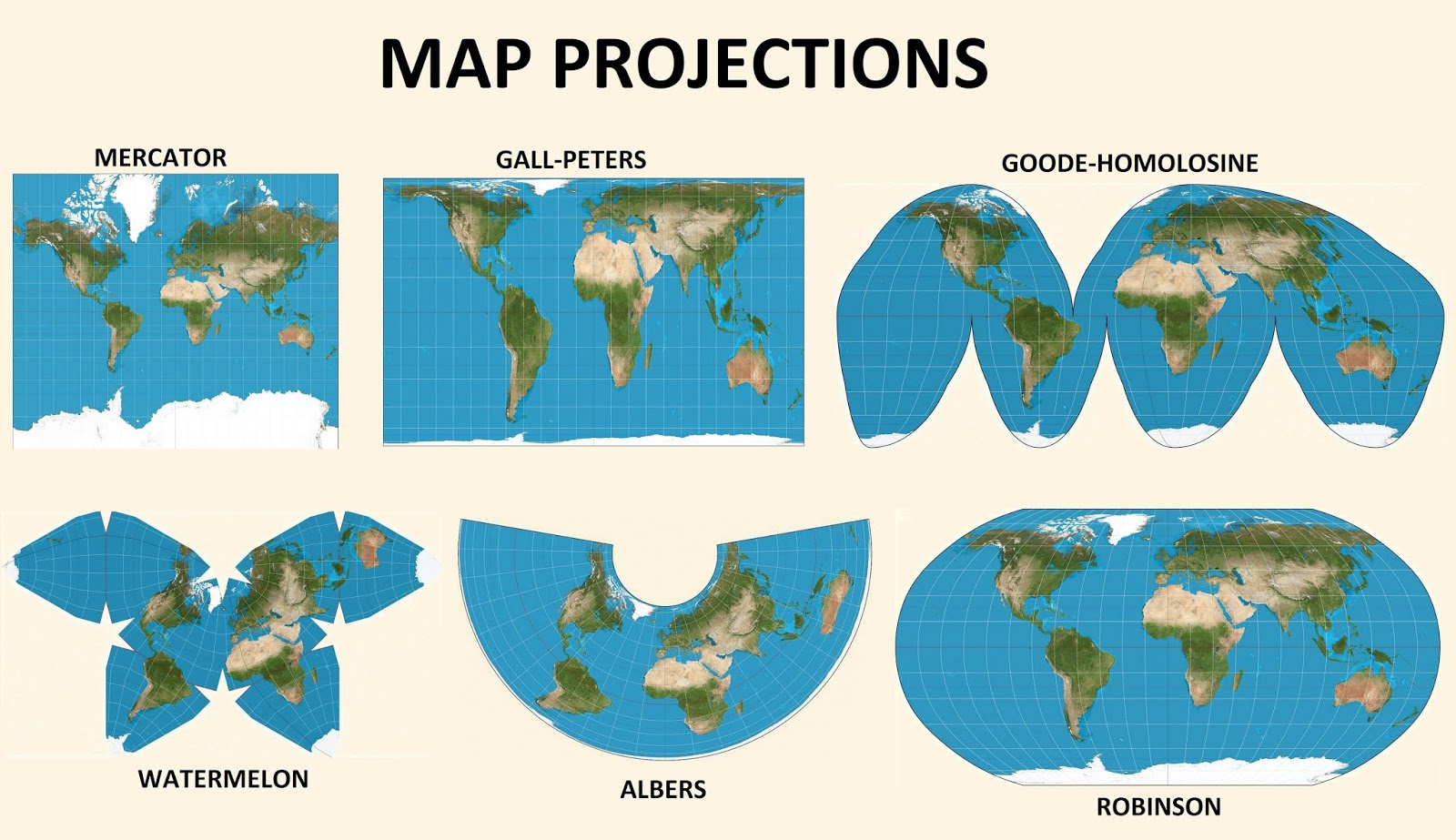
1. Mercator Projection: This cylindrical projection is widely known for its use in navigation. It preserves angles, making it suitable for plotting courses. However, it significantly distorts areas, particularly towards the poles, exaggerating the size of landmasses.
2. Robinson Projection: This compromise projection aims to minimize distortions in both area and shape. It provides a balanced representation of the globe, making it suitable for general-purpose world maps.
3. Winkel Tripel Projection: This projection minimizes area and shape distortions, making it a popular choice for world maps. It also preserves the relative sizes of continents.
4. Gall-Peters Projection: This cylindrical projection is known for its accurate area representation. It distorts shape and angles, but its focus on equal-area representation makes it useful for depicting global population density or resource distribution.
5. Goode Homolosine Projection: This interrupted projection divides the Earth into continents, minimizing distortions within each landmass. It is commonly used for depicting global patterns and trends.
6. Mollweide Projection: This equal-area projection is often used for depicting global patterns and trends. It distorts shapes, especially near the poles, but it preserves the relative sizes of continents.
7. Orthographic Projection: This azimuthal projection shows the Earth as it would appear from space. It is useful for visual representation, but it distorts shapes and areas significantly.
8. Stereographic Projection: This azimuthal projection preserves angles and is commonly used in navigation and cartography. It distorts shapes and areas, particularly near the edges of the map.
Beyond the "Best" Projection:
The concept of a single "best" projection is inherently flawed. Each projection has its own strengths and weaknesses, making the ideal choice dependent on the specific application. For example, a map used for navigation might prioritize angle preservation, while a map showing global population distribution might focus on accurate area representation.
FAQs on Choosing the Right Projection:
- Q: Which projection is best for a world map showing population density?
A: Projections that preserve area, such as the Gall-Peters or Mollweide projections, are suitable for depicting population density accurately.
- Q: Which projection is best for a map used for navigation?
A: The Mercator projection, which preserves angles, is often used for navigation as it allows for accurate plotting of courses.
- Q: Which projection is best for a general-purpose world map?
A: The Robinson projection, Winkel Tripel projection, or Goode Homolosine projection offer a balanced representation of the globe and are suitable for general-purpose world maps.
- Q: How do I choose the best projection for my specific needs?
A: Consider the purpose of the map, the area of focus, and the desired properties (area, shape, distance, direction) when choosing a projection.
Tips for Choosing the Right Projection:
- Understand the strengths and weaknesses of different projections.
- Consider the specific purpose and desired outcome of the map.
- Choose a projection that minimizes distortions in the area of interest.
- Experiment with different projections to find the one that best suits your needs.
- Be mindful of the limitations of all projections and communicate any distortions to your audience.
Conclusion:
The quest for the "best" world map projection is a continuous journey, as no single projection excels in all aspects. Understanding the characteristics of different projections allows for informed selection based on the specific purpose and desired outcome. By considering the factors outlined above, users can choose the most suitable projection for their needs, ensuring accurate and effective representation of our planet on a flat surface.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Quest for the Perfect World Map: Exploring the Best Projections for Different Purposes. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!