The Power of Transformation: Understanding When to Utilize Python’s map Function
Related Articles: The Power of Transformation: Understanding When to Utilize Python’s map Function
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Power of Transformation: Understanding When to Utilize Python’s map Function. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Power of Transformation: Understanding When to Utilize Python’s map Function
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Power of Transformation: Understanding When to Utilize Python’s map Function
- 3.1 Unveiling the Essence of map
- 3.2 When to Embrace the Power of map
- 3.3 Illustrative Examples
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions
- 3.5 Tips for Effective map Usage
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Power of Transformation: Understanding When to Utilize Python’s map Function
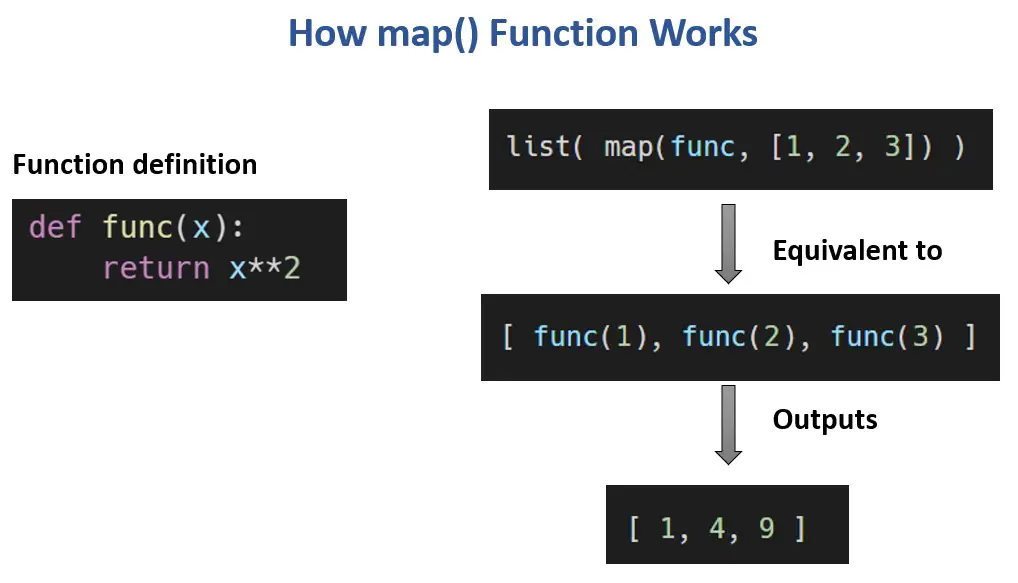
In the world of Python programming, the map function stands as a powerful tool for streamlining code and enhancing efficiency. Its primary purpose is to apply a given function to each element of an iterable, resulting in a new iterable containing the transformed values. While seemingly straightforward, the map function offers a wealth of benefits, particularly when dealing with repetitive operations on sequences of data.
Unveiling the Essence of map
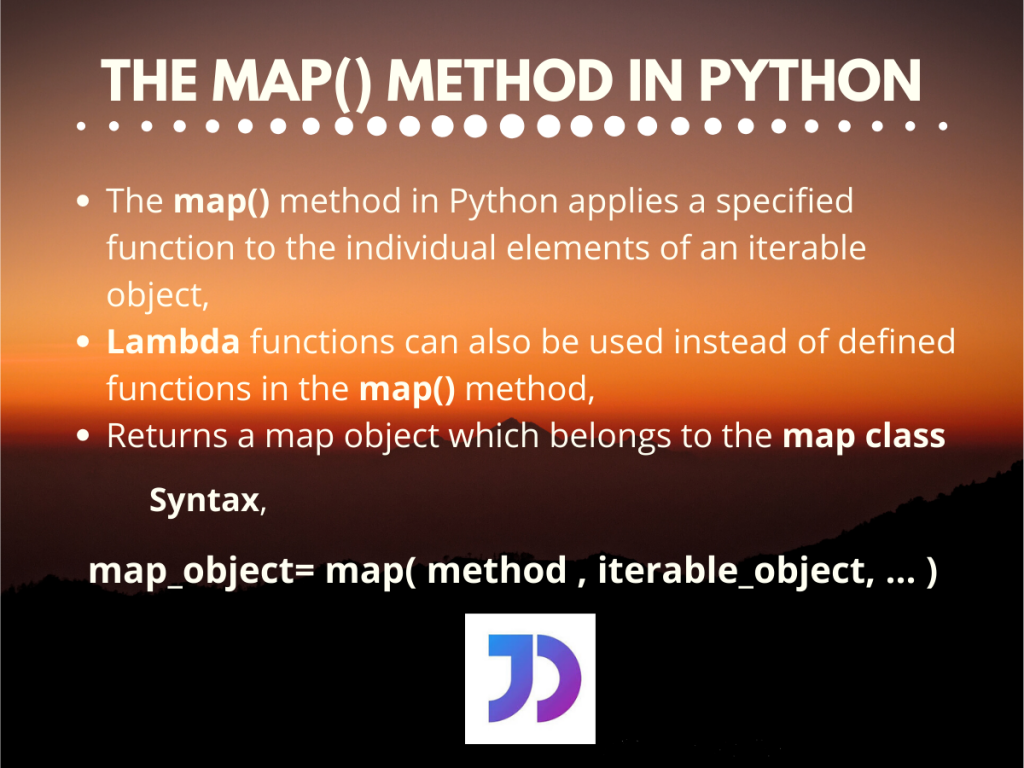
At its core, the map function operates on two fundamental components:
-
A Function: This function defines the transformation to be applied to each element of the iterable. It can be a built-in function, a user-defined function, or even a lambda expression, providing flexibility in defining the desired transformation.
-
An Iterable: This could be a list, tuple, set, dictionary, or any other object that can be iterated over, allowing the
mapfunction to process each element in turn.
The map function then iterates through the iterable, applying the provided function to each element and generating a new iterable containing the transformed results. This process eliminates the need for explicit loops, making code more concise and readable.
When to Embrace the Power of map
The map function shines in situations where you need to apply the same operation to multiple elements within an iterable. Here are some scenarios where map proves particularly beneficial:
1. Transforming Data: When you need to modify data within a list, tuple, or other iterable, map provides a clean and efficient way to apply the transformation across all elements. For instance, converting a list of strings to integers, applying a mathematical function to a series of numbers, or standardizing text formats can be achieved effortlessly using map.
2. Simplifying Complex Operations: When dealing with intricate calculations or manipulations, map can help break down the complexity by applying the operation individually to each element. This not only enhances readability but also reduces the potential for errors in manual iteration.
3. Enhancing Code Readability: The conciseness of map contributes to cleaner and more understandable code. By encapsulating the transformation logic within a function and applying it using map, the code becomes more focused and easier to follow.
4. Achieving Functional Programming Style: map aligns with the principles of functional programming, where functions are treated as first-class citizens and side effects are minimized. By applying functions to iterables, map encourages a more declarative style of programming, making code more robust and maintainable.
Illustrative Examples
To solidify the understanding of map‘s utility, let’s examine some practical examples:
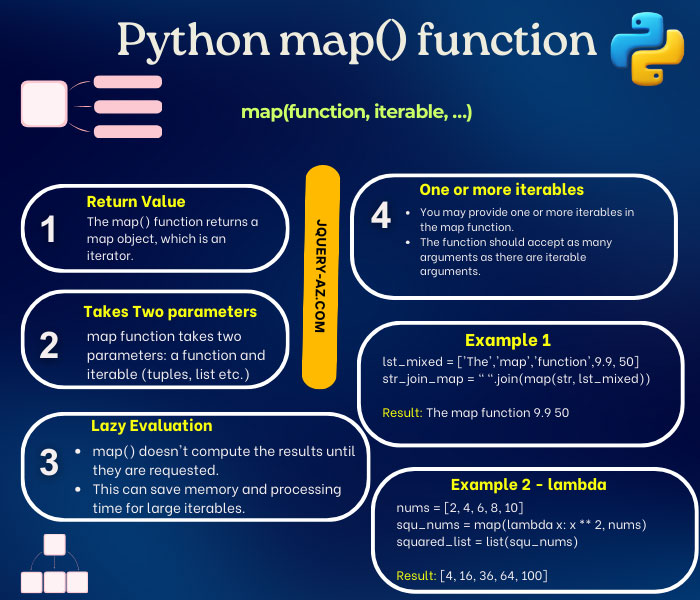
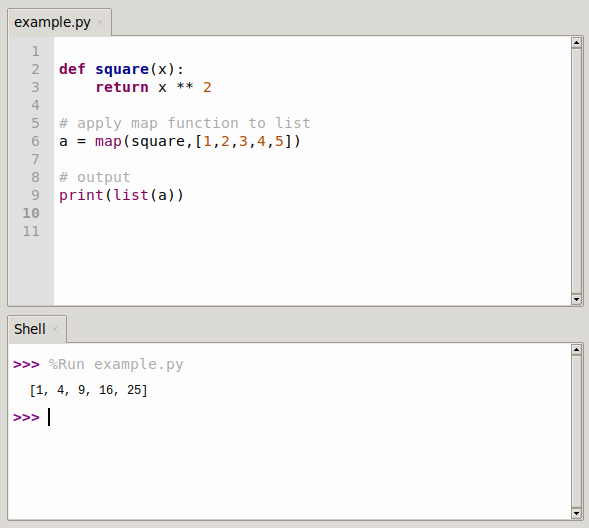
Example 1: Squaring Numbers
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
squared_numbers = list(map(lambda x: x**2, numbers))
print(squared_numbers) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]In this example, a lambda function is used to square each element in the numbers list. The map function applies this lambda function to each element, resulting in a new list containing the squared values.
Example 2: Converting Strings to Integers
strings = ["1", "2", "3", "4", "5"]
integers = list(map(int, strings))
print(integers) # Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]Here, the built-in int function is used to convert each string in the strings list to an integer. map efficiently applies this conversion to every element, producing a list of integers.
Example 3: Formatting Text
names = ["john", "jane", "david"]
formatted_names = list(map(lambda name: name.capitalize(), names))
print(formatted_names) # Output: ["John", "Jane", "David"]This example demonstrates using map to apply a custom formatting function (in this case, capitalizing the first letter) to each element in the names list.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can map handle multiple iterables?
Yes, map can handle multiple iterables, provided that the function it applies takes multiple arguments. The map function will then iterate through each iterable simultaneously, applying the function to corresponding elements from each iterable.
2. What if the function has side effects?
Using map with functions that have side effects might not be the most appropriate approach. The primary focus of map is transformation, and side effects can introduce unintended consequences and make code harder to reason about.
3. Can I use map with nested iterables?
While map itself doesn’t directly handle nested iterables, you can combine it with other techniques like list comprehensions or nested map calls to achieve the desired transformation.
4. How does map compare to list comprehensions?
Both map and list comprehensions offer similar functionality. However, list comprehensions are often considered more readable and concise, especially for simple transformations. map might be preferred when dealing with more complex functions or when working with multiple iterables.
5. Is map always the best choice?
The suitability of map depends on the specific task. For simple transformations, list comprehensions may be more appropriate. However, when working with complex functions or multiple iterables, map provides a more elegant and efficient solution.
Tips for Effective map Usage
-
Choose the Right Function: Carefully select the function to be applied, ensuring it aligns with the desired transformation.
-
Understand Side Effects: Be aware of any side effects associated with the function used in
map. If side effects are present, consider alternative approaches. -
Embrace Conciseness: Leverage the conciseness of
mapto streamline code and enhance readability. -
Consider Alternatives: When working with simple transformations, list comprehensions or other techniques might be more suitable.
Conclusion
The map function in Python empowers developers with a powerful tool for transforming data within iterables. Its ability to apply a function to each element efficiently and elegantly makes it an indispensable tool for various programming tasks. By understanding the benefits and limitations of map, developers can harness its potential to write cleaner, more efficient, and more readable code. As with any tool, the effectiveness of map lies in choosing the right scenarios for its application and utilizing it thoughtfully to achieve the desired results.

![]()


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Transformation: Understanding When to Utilize Python’s map Function. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!