The Power of Transformation: Understanding the map Function in Python
Related Articles: The Power of Transformation: Understanding the map Function in Python
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Power of Transformation: Understanding the map Function in Python. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Transformation: Understanding the map Function in Python
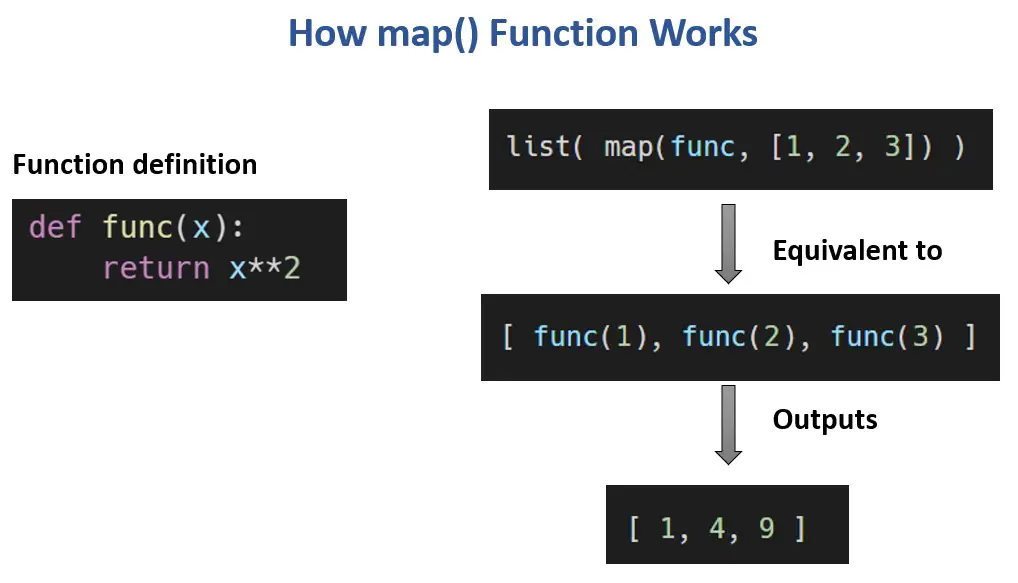
The map function in Python stands as a powerful tool for transforming data, allowing programmers to apply a function to each element of an iterable object. This concise and efficient approach streamlines code, enhances readability, and often significantly improves performance compared to manual iteration. This article delves into the intricacies of the map function, showcasing its diverse applications and highlighting its importance in the Python ecosystem.
Understanding the Essence of Transformation
At its core, the map function facilitates the application of a given function to every item within an iterable. This iterable can be a list, tuple, string, dictionary, or any other data structure that supports iteration. The function, in turn, can be any user-defined function or a built-in Python function.
The Mechanics of map
The map function takes two arguments:
- Function: This is the function that will be applied to each element of the iterable.
- Iterable: This is the data structure containing the elements to be transformed.
The map function returns an iterator, which is a special type of object that generates the transformed elements one at a time. To access the transformed elements, one can either iterate through the iterator or convert it into a list using the list() function.
Illustrative Examples
Let’s explore some practical examples to solidify our understanding:
Example 1: Squaring Numbers
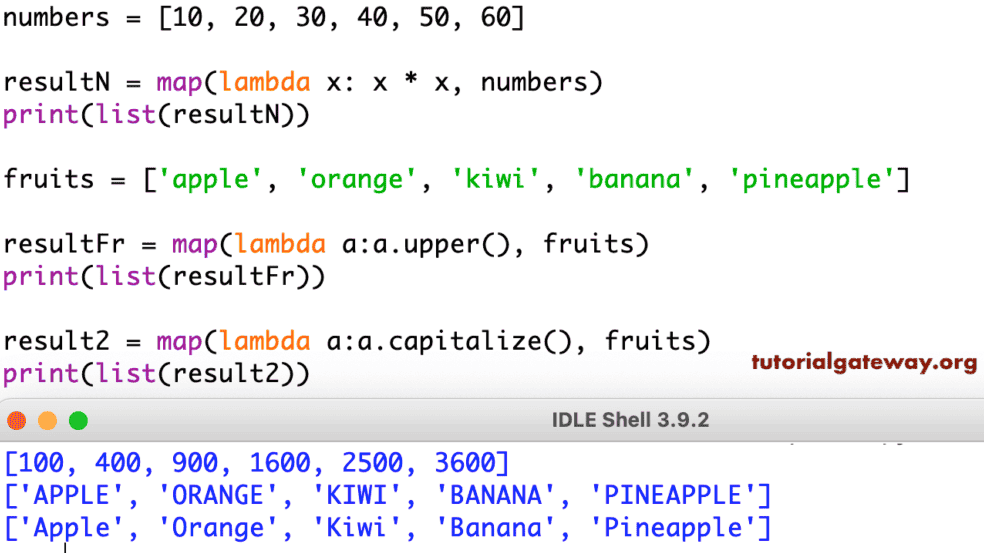
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
def square(x):
return x * x
squared_numbers = list(map(square, numbers))
print(squared_numbers) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]In this example, the square function squares each element of the numbers list, and the map function applies this transformation to every element. The resulting iterator is converted into a list using list(), yielding the squared numbers.
Example 2: Converting Strings to Uppercase
names = ["john", "jane", "peter"]
def uppercase(name):
return name.upper()
uppercase_names = list(map(uppercase, names))
print(uppercase_names) # Output: ['JOHN', 'JANE', 'PETER']This example demonstrates the application of the uppercase function to each name in the names list, transforming them into uppercase strings.
Example 3: Filtering Even Numbers
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
def is_even(x):
return x % 2 == 0
even_numbers = list(map(is_even, numbers))
print(even_numbers) # Output: [False, True, False, True, False, True, False, True, False, True]Here, the is_even function checks if each number in the numbers list is even. The map function applies this check to each element, resulting in a list of boolean values indicating whether each number is even or not.
Beyond Basic Transformation: Leveraging lambda Functions
The map function shines when combined with anonymous functions, known as lambda functions. These concise, single-line functions offer a streamlined approach to defining simple functions within the context of the map function.
Example 4: Doubling Numbers with lambda
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
doubled_numbers = list(map(lambda x: x * 2, numbers))
print(doubled_numbers) # Output: [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]In this example, the lambda function lambda x: x * 2 doubles each number in the numbers list, demonstrating the elegance and efficiency of using lambda functions with map.
The Benefits of map
The map function offers several advantages:
-
Conciseness and Readability: The
mapfunction provides a concise and expressive way to perform transformations on iterables, making code more readable and understandable. -
Efficiency: The
mapfunction often outperforms manual iteration, especially when dealing with large datasets, due to its optimized implementation. -
Flexibility: The
mapfunction can be used with a wide variety of functions, including user-defined functions, built-in functions, and lambda functions, making it a versatile tool for data manipulation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can map be used with multiple iterables?
A: Yes, map can accept multiple iterables. In such cases, the function will be applied to corresponding elements from each iterable. For example:
numbers1 = [1, 2, 3]
numbers2 = [4, 5, 6]
def add(x, y):
return x + y
summed_numbers = list(map(add, numbers1, numbers2))
print(summed_numbers) # Output: [5, 7, 9]Q2: What happens if the iterables are of different lengths?
A: The map function will stop processing elements once the shortest iterable is exhausted.
Q3: Can map be used with nested iterables?
A: While map itself doesn’t directly handle nested iterables, you can combine it with other techniques like nested list comprehensions or recursive functions to achieve this.
Tips for Effective Use
- Choose the Right Function: Select a function that aligns with the desired transformation.
-
Consider
lambdaFunctions: For simple transformations,lambdafunctions can enhance code brevity and readability. -
Use
list()to Access Elements: Convert the iterator returned bymapinto a list if you need to access the transformed elements directly. -
Optimize for Performance: For large datasets,
mapcan significantly improve performance compared to manual iteration.
Conclusion
The map function stands as a testament to Python’s emphasis on elegant and efficient code. By providing a streamlined approach to transforming data, map empowers developers to write concise, readable, and often performant code. Its versatility and ease of use make it an indispensable tool for data manipulation, enhancing the efficiency and expressiveness of Python programs. Understanding and effectively utilizing the map function is a valuable skill for any Python programmer seeking to write clean and powerful code.


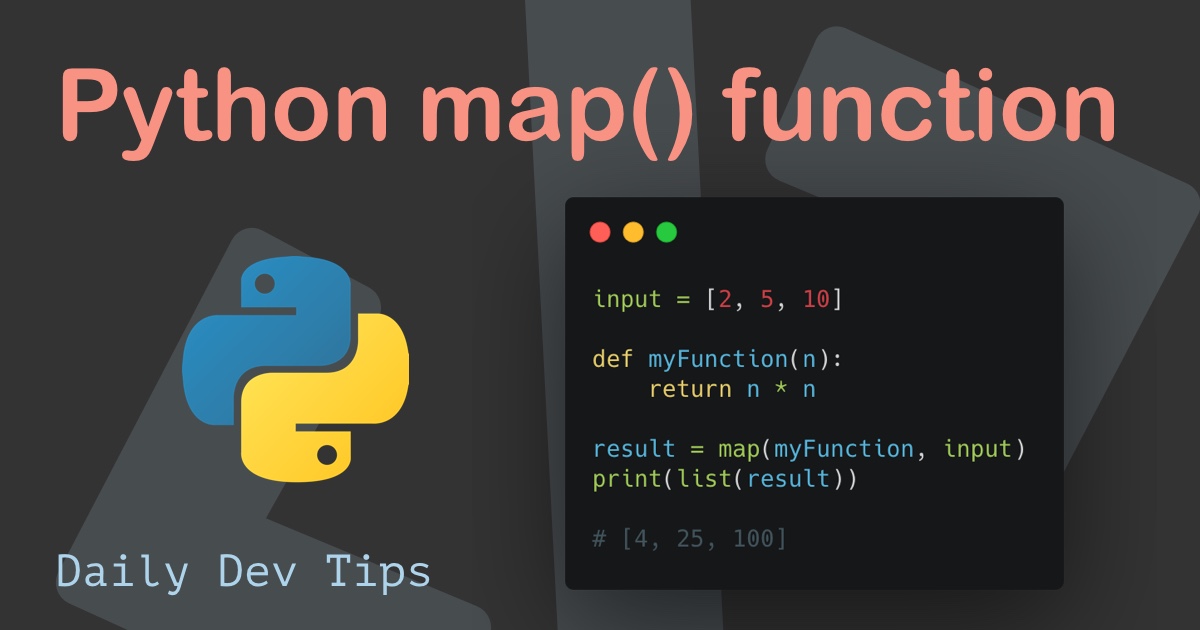
![Python map() — Finally Mastering the Python Map Function [+Video] – Be on the Right Side of Change](https://blog.finxter.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/Map-Python-Kopie.png)
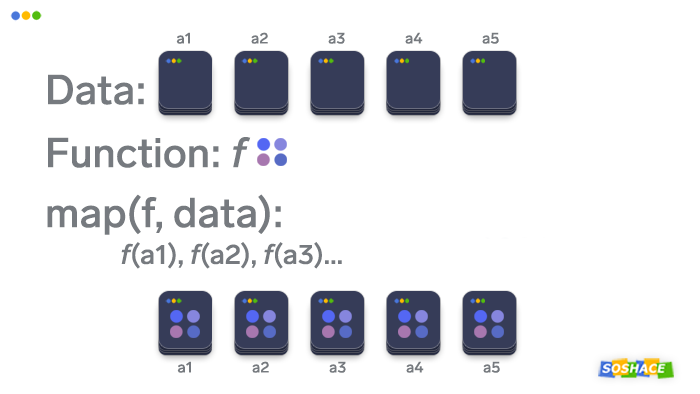
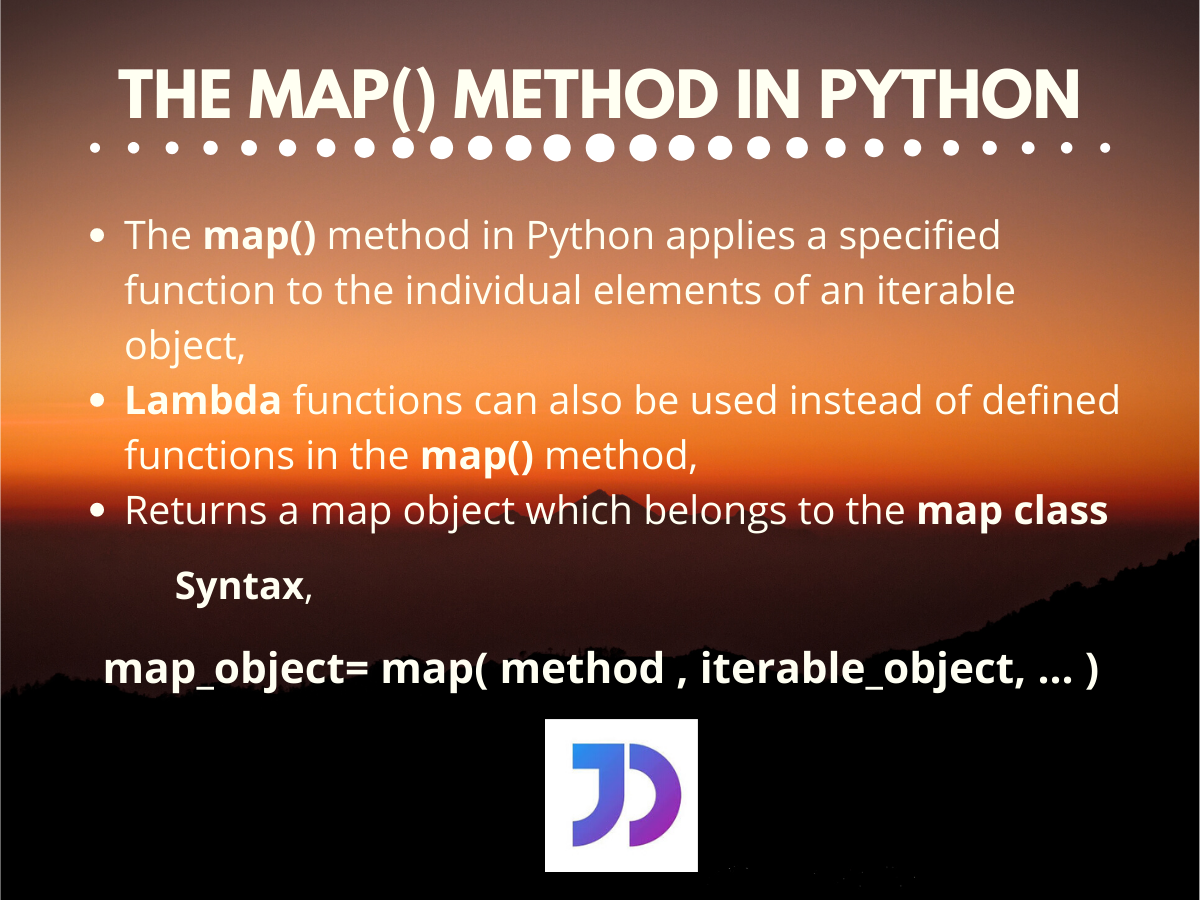

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Transformation: Understanding the map Function in Python. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!