The Power of Spatial Analysis: Understanding Map Radius Checkers
Related Articles: The Power of Spatial Analysis: Understanding Map Radius Checkers
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Power of Spatial Analysis: Understanding Map Radius Checkers. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Power of Spatial Analysis: Understanding Map Radius Checkers
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Power of Spatial Analysis: Understanding Map Radius Checkers
- 3.1 Defining the Scope: Understanding Map Radius Checkers
- 3.2 The Mechanics of Spatial Analysis: How Map Radius Checkers Work
- 3.3 Beyond Simple Distance: Exploring Advanced Features
- 3.4 Unlocking the Power: Benefits of Map Radius Checkers
- 3.5 Navigating the Landscape: Choosing the Right Tool
- 3.6 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
- 3.7 Tips for Effective Use: Maximizing the Power of Map Radius Checkers
- 3.8 Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Spatial Analysis
- 4 Closure
The Power of Spatial Analysis: Understanding Map Radius Checkers
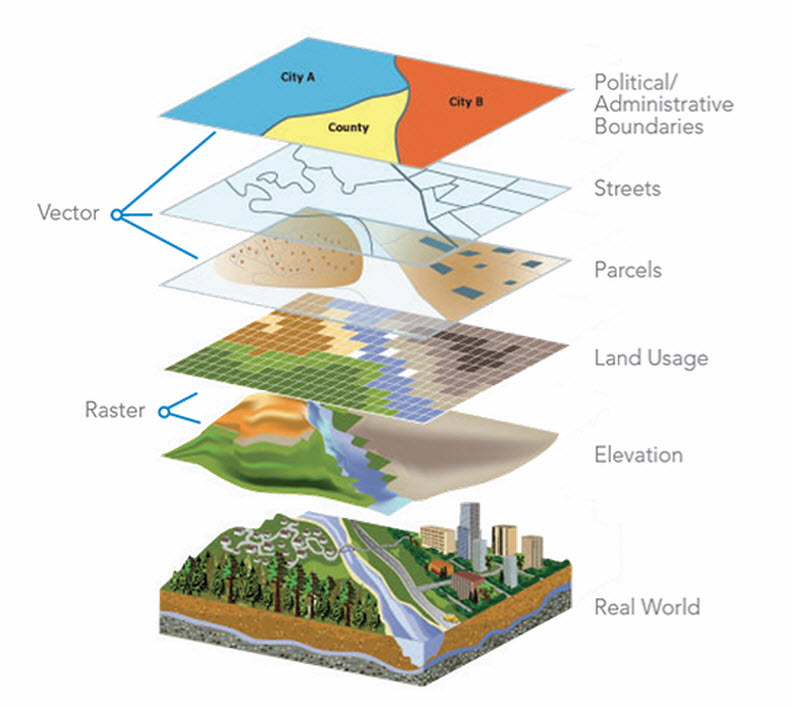
In an increasingly data-driven world, the ability to analyze and visualize spatial information is paramount. Map radius checkers are powerful tools that empower users to understand and leverage the spatial relationships between points of interest and their surrounding areas. This article delves into the mechanics, benefits, and applications of map radius checkers, providing a comprehensive understanding of their significance in various fields.
Defining the Scope: Understanding Map Radius Checkers
At its core, a map radius checker is a digital tool that allows users to define a circular area around a specific location. This "radius" can be adjusted to encompass a desired distance, creating a virtual circle on a map. The tool then identifies all points of interest that fall within this defined area, providing valuable insights into the spatial distribution of data.
This seemingly simple function has profound implications, enabling users to answer crucial questions like:
- "What businesses are within a 5-mile radius of my new store location?" – This helps businesses understand potential customer reach and competitive landscape.
- "Are there any schools within a 1-mile radius of this proposed housing development?" – This aids in assessing the suitability of a location based on proximity to essential amenities.
- "How many hospitals are accessible within a 30-minute drive of this rural community?" – This helps in understanding healthcare access and planning for emergency services.
These examples highlight the versatility of map radius checkers, extending their application across diverse industries and sectors.
The Mechanics of Spatial Analysis: How Map Radius Checkers Work
The functionality of a map radius checker relies on the integration of several key components:
-
Mapping Platform: The tool is typically built on a base map platform, such as Google Maps, OpenStreetMap, or Bing Maps. This provides the visual framework for displaying the defined radius and identifying points of interest.
-
Coordinate System: The map utilizes a specific coordinate system, often latitude and longitude, to accurately locate points on the earth’s surface. This ensures precise measurement and identification of points within the defined radius.
-
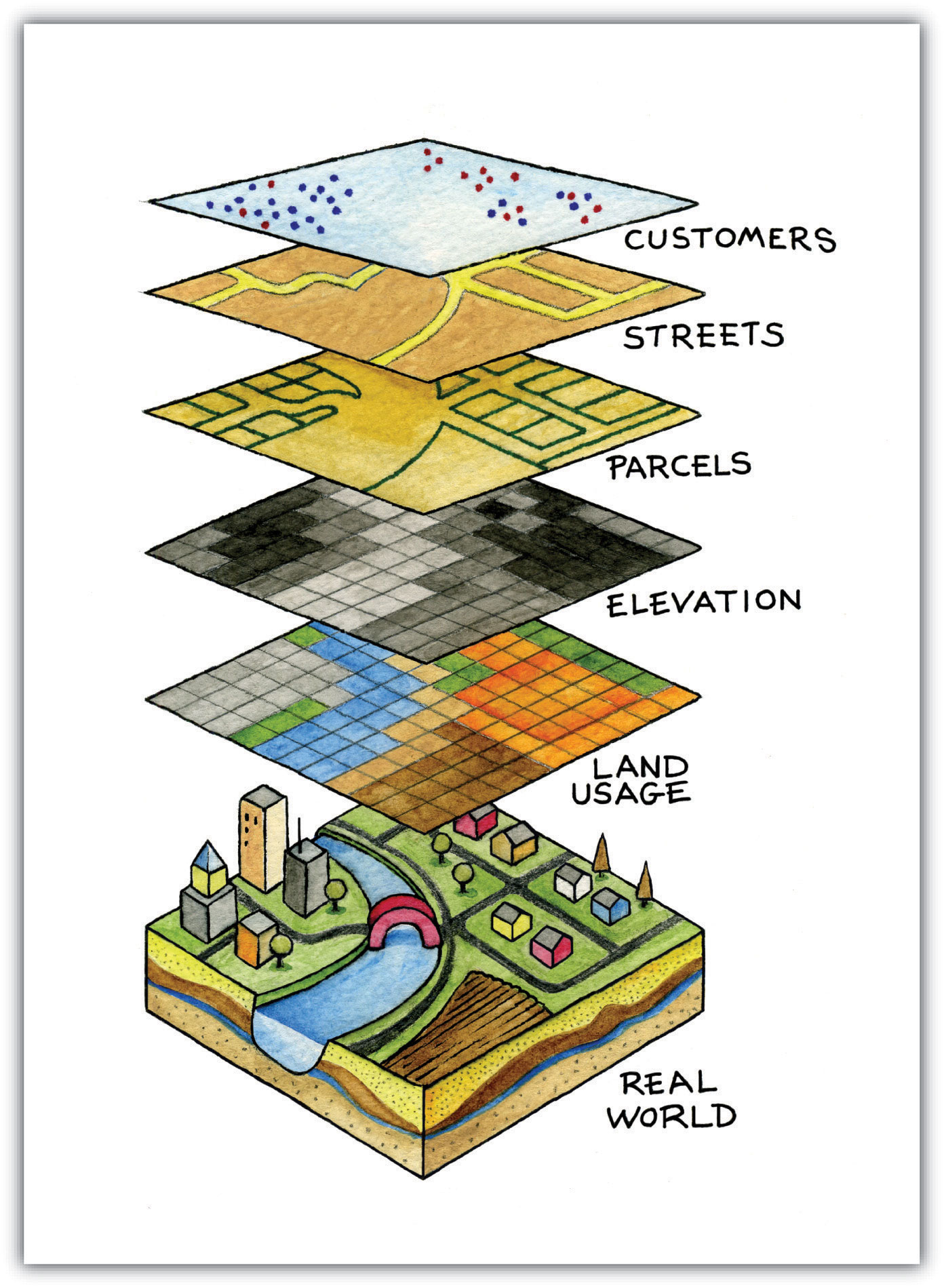
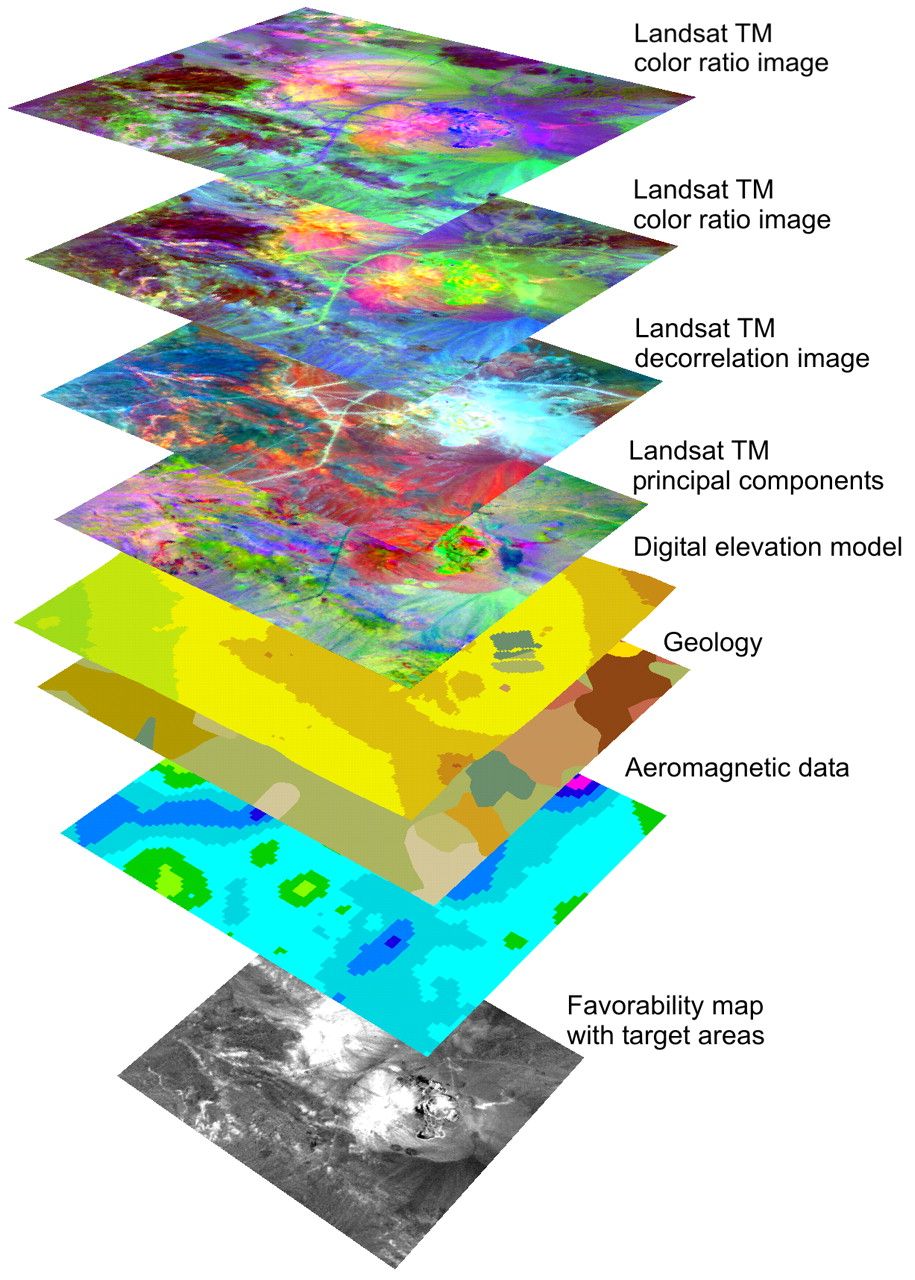
Data Layers: The map incorporates various data layers, each representing a specific type of information. These layers could include businesses, schools, hospitals, or any other relevant data points.
-
Radius Calculation: The user defines the radius, which is typically measured in units like miles, kilometers, or minutes of travel time. The tool calculates the circular area based on the defined radius and the chosen coordinate system.
-
Point Identification: The tool then analyzes the data layers to identify all points of interest that fall within the defined circular area. This identification is achieved by comparing the coordinates of each point with the boundaries of the calculated radius.
-
Visualization: The results are presented visually on the map, highlighting the identified points of interest within the defined radius. This allows users to easily interpret the spatial distribution of data and draw meaningful conclusions.
Beyond Simple Distance: Exploring Advanced Features
While basic radius calculations provide valuable insights, many map radius checkers offer advanced features to enhance spatial analysis capabilities:
-
Polygon Definition: Some tools allow users to define custom shapes, such as polygons or irregular areas, instead of just circles. This enables analysis of complex spatial relationships and provides greater flexibility in defining areas of interest.
-
Data Filtering: Users can filter data layers to focus on specific types of points of interest. This allows for targeted analysis, such as identifying only restaurants within a radius or schools offering specific programs.
-
Distance Calculation: Beyond simple radius calculations, some tools offer advanced distance calculations, considering factors like road networks, travel time, or terrain. This provides more realistic and relevant results, especially for applications involving transportation and logistics.
-
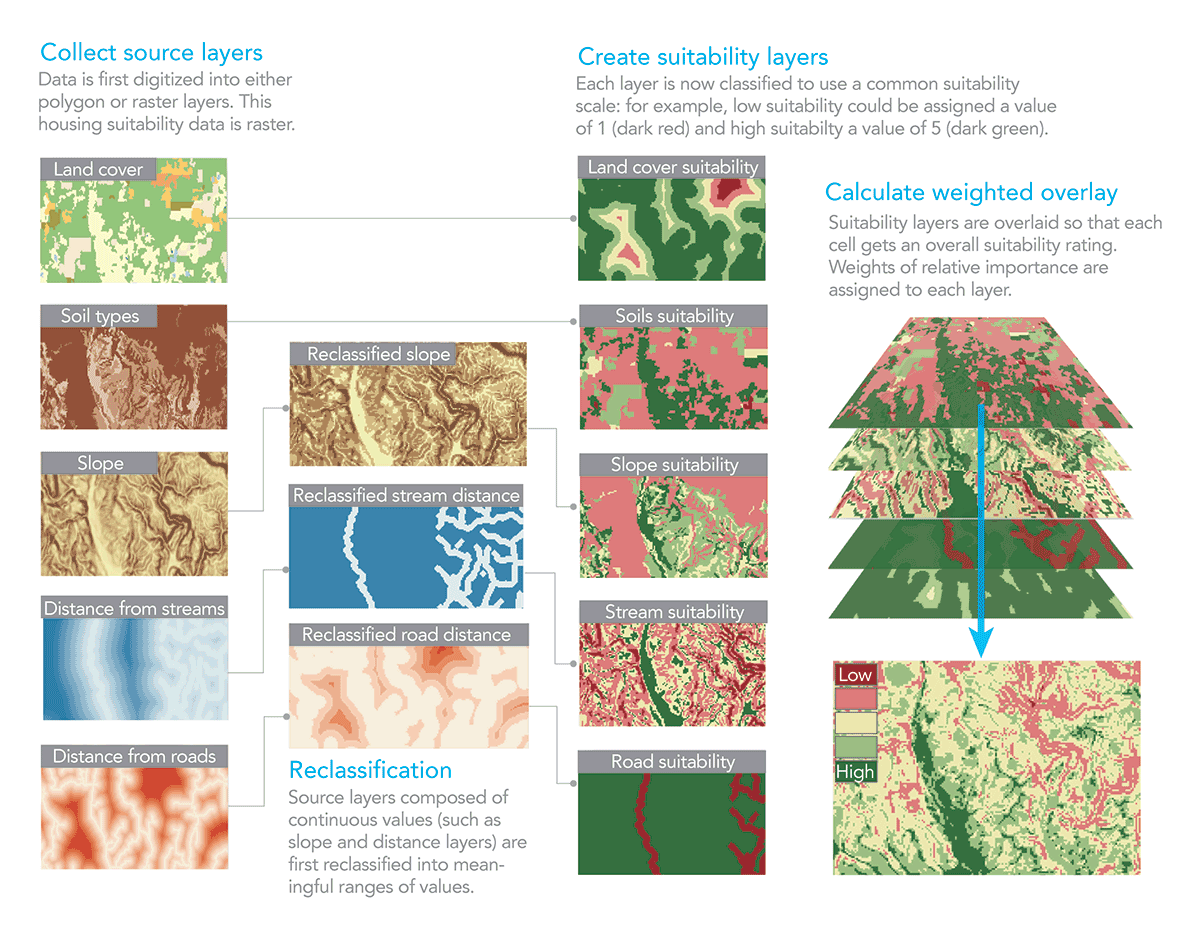
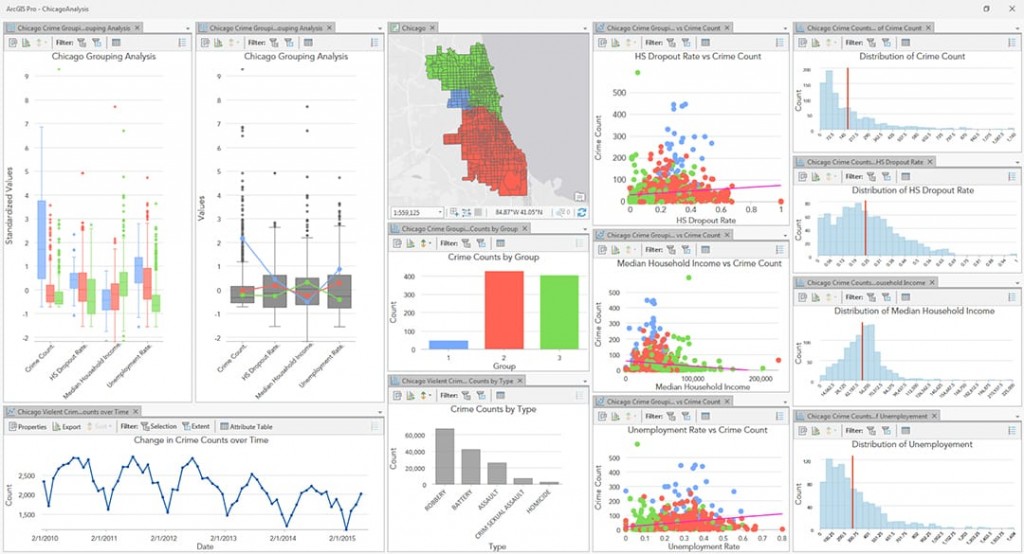
Data Aggregation: Advanced tools can aggregate data points within the defined radius, providing summary statistics like the total number of businesses, average distance to schools, or population density. This allows for comprehensive analysis and informed decision-making.
-
Integration with Other Tools: Some map radius checkers integrate with other data analysis platforms, allowing users to import and analyze data from various sources. This enables more sophisticated spatial analysis and unlocks the potential for cross-platform insights.
Unlocking the Power: Benefits of Map Radius Checkers
The benefits of using map radius checkers extend far beyond basic spatial analysis. These tools offer valuable insights across various fields, empowering users with data-driven decision-making:
-
Business Strategy: Understanding customer reach, identifying competitor locations, and analyzing market potential are crucial for business success. Map radius checkers provide a powerful tool for strategic decision-making, helping businesses optimize location selection, target marketing efforts, and assess competitive landscapes.
-
Real Estate Development: Choosing the right location for a new development requires careful consideration of factors like proximity to amenities, transportation, and community services. Map radius checkers assist in evaluating potential sites, ensuring they meet the needs of residents and investors.
-
Urban Planning: Understanding the distribution of essential services like schools, hospitals, and public transportation is crucial for effective urban planning. Map radius checkers aid in identifying areas with limited access to these services, informing the development of infrastructure and social programs.
-
Emergency Response: During emergencies, rapid and efficient response is crucial. Map radius checkers can be used to identify the locations of hospitals, fire stations, and other emergency services within a specific radius, allowing for swift deployment and optimized resource allocation.
-
Environmental Management: Understanding the spatial distribution of environmental hazards, such as pollution sources or wildlife habitats, is essential for effective environmental management. Map radius checkers help in identifying areas at risk, informing the development of mitigation strategies and conservation efforts.
-
Marketing and Advertising: Targeting potential customers based on their location is a key aspect of effective marketing. Map radius checkers can be used to identify specific geographic areas with high concentrations of target demographics, enabling businesses to tailor their advertising campaigns and maximize reach.
-
Research and Analysis: Across various fields, including social sciences, epidemiology, and economics, understanding the spatial distribution of data is essential for conducting research and drawing meaningful conclusions. Map radius checkers provide a powerful tool for visualizing data, identifying patterns, and uncovering hidden relationships.
Navigating the Landscape: Choosing the Right Tool
With a multitude of map radius checkers available, choosing the right tool for your specific needs is crucial. Consider the following factors:
-
Functionality: Evaluate the tool’s core capabilities, including radius definition, data layers, distance calculation methods, and advanced features like polygon definition and data filtering.
-
Data Sources: Determine the availability and quality of data layers relevant to your specific needs. Some tools offer access to a wider range of data sources, while others may focus on specific industries or regions.
-
Ease of Use: The tool should be intuitive and user-friendly, with clear instructions and a simple interface. Consider the learning curve and the time required to become proficient in using the tool.
-
Integration: Evaluate the tool’s ability to integrate with other software and platforms, allowing for seamless data flow and analysis.
-
Cost: Consider the pricing model, whether it’s a subscription-based service or a one-time purchase. Evaluate the cost in relation to the value offered by the tool and its features.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: What are some popular map radius checker tools available?
A: There are numerous map radius checkers available, both free and paid. Popular options include Google Maps, OpenStreetMap, Bing Maps, and specialized tools like ArcGIS Online, QGIS, and Mapbox. The best choice depends on the specific needs and budget of the user.
Q: How accurate are map radius checkers?
A: The accuracy of map radius checkers depends on several factors, including the quality of the underlying map data, the chosen coordinate system, and the method of distance calculation. In general, tools based on reliable mapping platforms and advanced distance calculation methods offer higher accuracy.
Q: What are the limitations of map radius checkers?
A: While powerful, map radius checkers have limitations. They rely on static data, so real-time changes in factors like traffic conditions or weather patterns are not reflected. Additionally, the accuracy of distance calculations can be affected by terrain, road networks, and other environmental factors.
Q: How can I improve the accuracy of my analysis using map radius checkers?
A: To enhance accuracy, choose tools based on reliable mapping platforms, select appropriate distance calculation methods, and consider factors like terrain and road networks. Additionally, verify data sources and ensure they are up-to-date and relevant to your analysis.
Tips for Effective Use: Maximizing the Power of Map Radius Checkers
-
Define Clear Objectives: Before using a map radius checker, clearly define the purpose of your analysis and the specific questions you aim to answer. This helps in selecting the appropriate data layers, defining the radius, and interpreting the results.
-
Choose Relevant Data: Select data layers that are relevant to your analysis and ensure their accuracy and reliability. Consider the timeliness of the data and the potential for bias or inaccuracies.
-
Experiment with Radius Sizes: Explore different radius sizes to understand the impact on the results. Consider the context of your analysis and the specific questions you are trying to answer.
-
Visualize and Interpret Results: Utilize the tool’s visualization capabilities to gain insights from the data. Look for patterns, trends, and outliers, and draw meaningful conclusions based on the visual representation.
-
Combine with Other Tools: Integrate map radius checkers with other data analysis tools to unlock further insights. This allows for more comprehensive analysis and informed decision-making.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Spatial Analysis
Map radius checkers offer a powerful and versatile tool for analyzing spatial relationships and gaining valuable insights from data. By understanding the mechanics, benefits, and limitations of these tools, users can effectively leverage their capabilities across diverse fields, from business strategy and urban planning to emergency response and environmental management. As the world becomes increasingly data-driven, the ability to analyze and visualize spatial information is essential for informed decision-making and achieving desired outcomes. By embracing the power of map radius checkers, users can unlock the potential of spatial analysis and gain a deeper understanding of the world around them.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Spatial Analysis: Understanding Map Radius Checkers. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!