The Power of Radius: Exploring the Utility of Maps with Distance Measurement Features
Related Articles: The Power of Radius: Exploring the Utility of Maps with Distance Measurement Features
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Power of Radius: Exploring the Utility of Maps with Distance Measurement Features. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Radius: Exploring the Utility of Maps with Distance Measurement Features

In the realm of spatial analysis and data visualization, maps have long been invaluable tools for understanding and interpreting the world around us. However, the ability to measure distances on a map, specifically by drawing radii, elevates these representations to a new level of functionality and insight. This capability transforms maps from static visual aids into interactive platforms for analyzing spatial relationships, uncovering patterns, and making informed decisions.
Delving into the Essence of Radius Drawing on Maps
The concept of drawing a radius on a map is deceptively simple. It involves selecting a point of interest as the center and defining a circular area around it based on a specified distance. This seemingly straightforward action unlocks a wealth of possibilities across various fields, allowing users to:
- Define Service Areas: Businesses can visualize their service areas, understand potential customer reach, and optimize delivery routes.
- Analyze Spatial Relationships: Researchers can study the distribution of phenomena, such as disease outbreaks or population density, in relation to specific locations.
- Identify Potential Hazards: Emergency responders can quickly determine the impact zone of natural disasters or accidents, facilitating efficient response and resource allocation.
- Plan Infrastructure Development: Urban planners can assess the impact of new infrastructure projects, such as transportation networks or public facilities, on surrounding areas.
- Conduct Market Research: Businesses can identify potential customer segments and assess the competitive landscape within defined geographic areas.
Exploring the Diverse Applications of Radius Drawing
The ability to draw radii on maps finds applications across a wide range of disciplines, each leveraging the unique insights it provides:
1. Business and Marketing:
- Targeted Advertising: By drawing a radius around a store location, businesses can identify potential customers within a specific distance, allowing for targeted advertising campaigns and promotions.
- Market Analysis: Radius drawing helps businesses analyze the competitive landscape, identifying competitors within a defined area and assessing market saturation.
- Sales Territory Management: Sales teams can use radii to define their territories, ensuring efficient coverage and maximizing sales potential.
2. Healthcare and Public Health:
- Epidemiological Studies: Radius drawing assists in studying disease outbreaks by identifying individuals within a specific distance from a confirmed case, facilitating contact tracing and containment efforts.
- Healthcare Access Analysis: Drawing radii around hospitals and clinics helps assess healthcare accessibility for different populations, identifying areas with limited access and informing resource allocation strategies.
- Emergency Response Planning: Radius drawing enables emergency responders to define the impact zone of a disaster, facilitating efficient response and resource allocation.
3. Urban Planning and Development:
- Infrastructure Planning: Drawing radii around proposed infrastructure projects, such as roads or public facilities, helps assess their impact on surrounding areas, facilitating informed decision-making.
- Land Use Planning: Radius drawing assists in zoning and land use planning by identifying areas suitable for different land uses based on proximity to amenities and infrastructure.
- Urban Regeneration Strategies: Drawing radii around areas targeted for regeneration helps identify key stakeholders, assess potential impacts, and develop targeted strategies.
4. Environmental Science and Conservation:
- Habitat Mapping: Radius drawing helps identify and map sensitive habitats, such as endangered species breeding grounds, facilitating conservation efforts and minimizing human impact.
- Pollution Monitoring: Drawing radii around pollution sources allows researchers to assess the impact of pollutants on surrounding areas and inform mitigation strategies.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Radius drawing helps identify areas vulnerable to climate change impacts, such as sea level rise or extreme weather events, informing adaptation strategies.
5. Education and Research:
- Geographic Data Analysis: Radius drawing facilitates the analysis of spatial data, allowing researchers to study the distribution of phenomena and identify patterns.
- Historical Research: Drawing radii around historical events or locations helps visualize their impact on surrounding areas and understand their influence over time.
- Educational Tools: Radius drawing can be used as an engaging and interactive tool for teaching geography, history, and other subjects with a spatial component.
FAQs: Demystifying Radius Drawing on Maps
Q1: What are the different types of radius drawing tools available?
A1: Various tools are available for drawing radii on maps, each with its own features and capabilities. These include:
- Online Mapping Platforms: Google Maps, Bing Maps, and OpenStreetMap offer built-in radius drawing tools, allowing users to define areas based on distance and visualize them on the map.
- GIS Software: Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software, such as ArcGIS and QGIS, provide advanced features for radius drawing, allowing users to analyze spatial relationships, create buffer zones, and perform complex spatial analyses.
- Specialized Apps: Mobile apps dedicated to distance measurement, such as MapMyRun or Strava, allow users to draw radii around specific locations and track their movement within those areas.
Q2: How accurate are radius drawing tools on maps?
A2: The accuracy of radius drawing tools depends on the underlying map data and the projection used. Online mapping platforms typically rely on global projections, which can introduce distortions at higher latitudes. GIS software, however, allows users to work with specific projections, ensuring greater accuracy for local areas.
Q3: What are the limitations of radius drawing tools?
A3: While radius drawing tools offer valuable insights, they have certain limitations:
- Real-world Obstacles: Radius drawing assumes a flat surface, ignoring real-world obstacles like mountains, rivers, or buildings, which can affect the actual distance.
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of the radius depends on the accuracy of the underlying map data, which can vary depending on the source and the scale of the map.
- Visual Representation: Radius drawing tools typically display a circular area, which may not accurately represent the true shape of the area due to the curvature of the Earth.
Tips for Effective Radius Drawing:
- Choose the Right Tool: Select a radius drawing tool that meets your specific needs and offers the desired features and accuracy.
- Define the Center Point: Accurately identify the center point of your radius, ensuring it represents the desired location.
- Specify the Distance: Choose an appropriate distance for your radius, considering the scale of your analysis and the specific purpose.
- Consider Real-world Obstacles: Be mindful of real-world obstacles that may affect the actual distance covered by the radius.
- Interpret Results Carefully: Recognize the limitations of radius drawing tools and interpret results with caution, considering potential inaccuracies and distortions.
Conclusion: Empowering Spatial Analysis through Radius Drawing
Maps with radius drawing capabilities offer a powerful tool for spatial analysis, enabling users to visualize distances, analyze spatial relationships, and make informed decisions. From businesses defining service areas to researchers studying disease outbreaks, the ability to draw radii unlocks a wealth of possibilities across various fields. By understanding the benefits, limitations, and best practices of radius drawing, users can leverage this powerful tool to extract valuable insights from spatial data and gain a deeper understanding of the world around them.



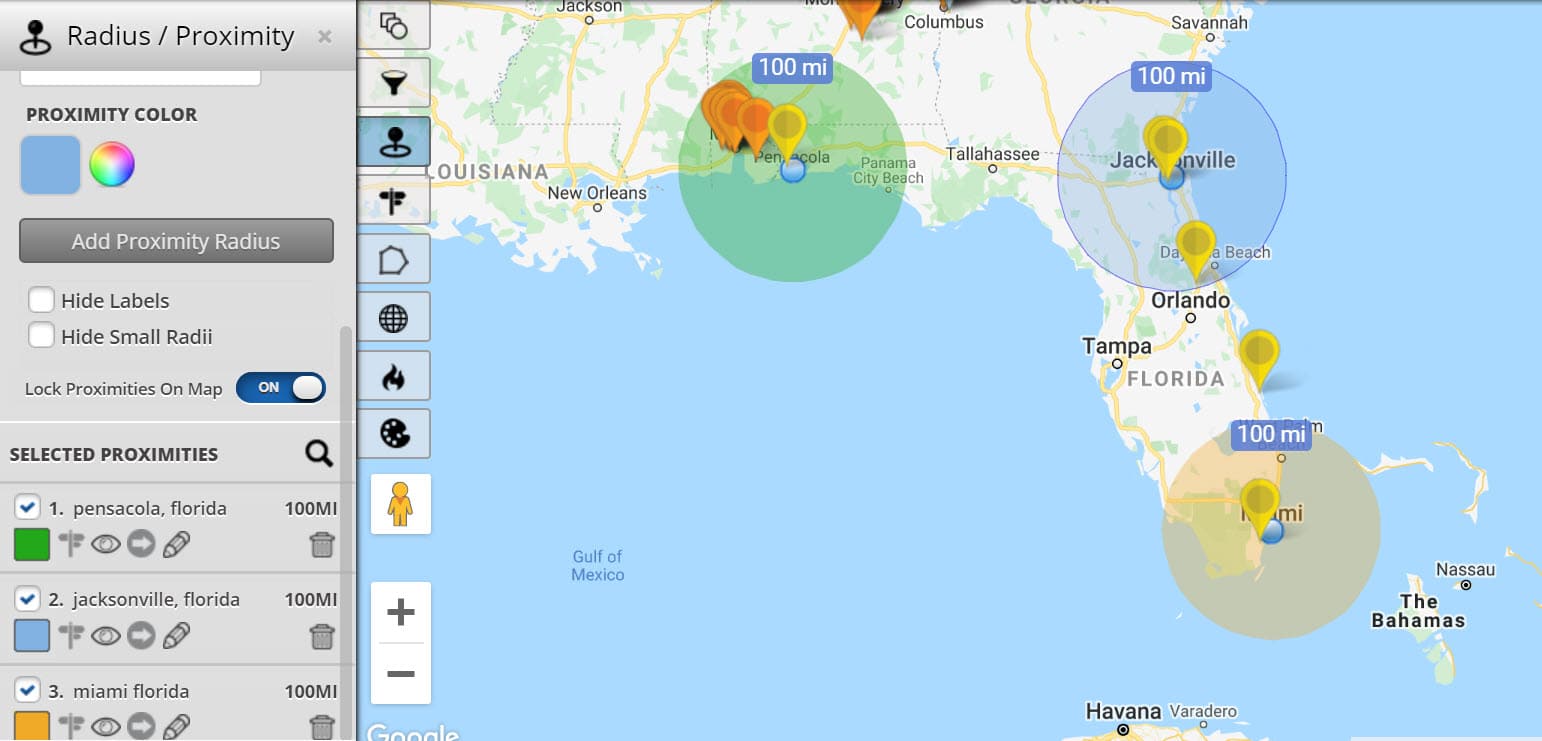
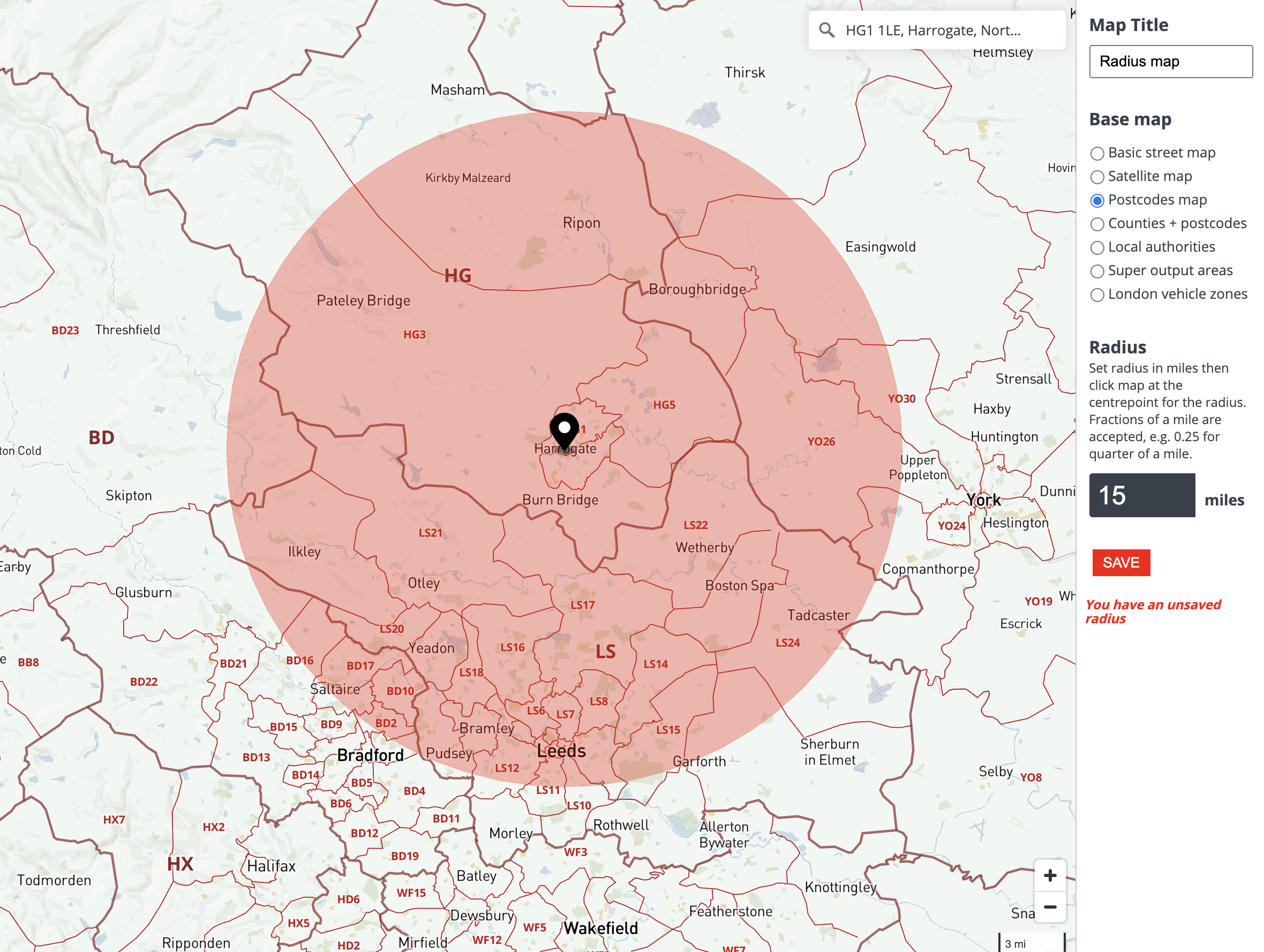
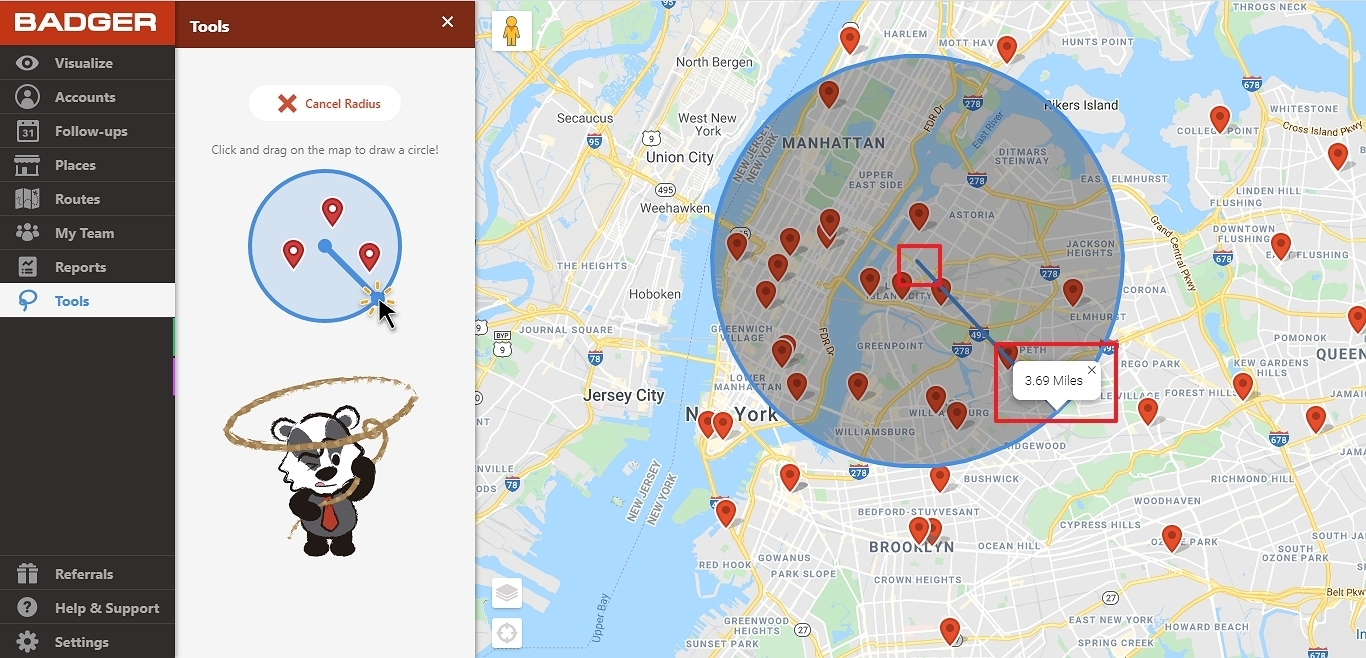
![Radius Map [Tool For Drawing & Creation] Distance & Driving Tim - Smappen](https://www.smappen.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/radius-map-1024x635.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Radius: Exploring the Utility of Maps with Distance Measurement Features. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!