The Power of Proximity: Understanding and Utilizing Radius Maps
Related Articles: The Power of Proximity: Understanding and Utilizing Radius Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Power of Proximity: Understanding and Utilizing Radius Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Proximity: Understanding and Utilizing Radius Maps
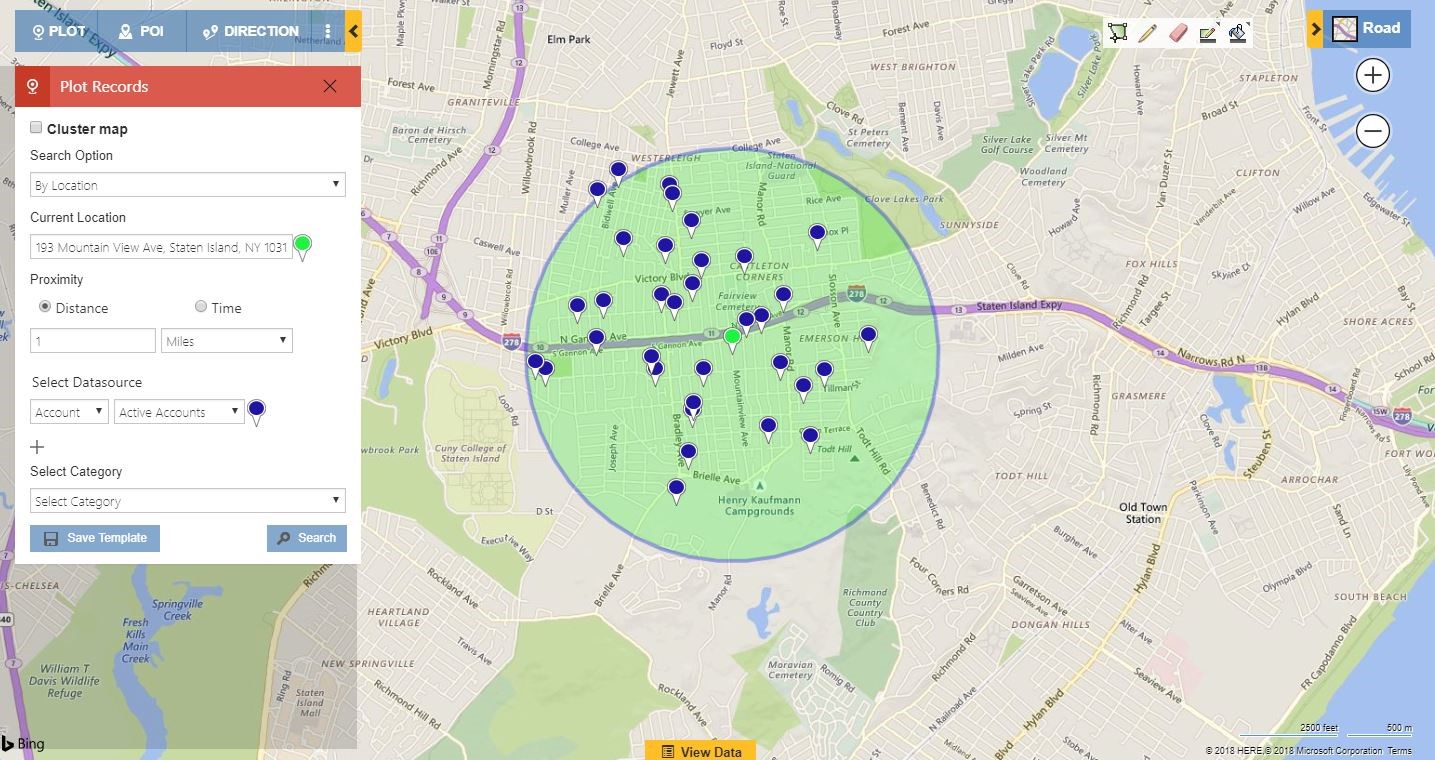
In the modern age of data-driven decision-making, the ability to visualize and analyze spatial relationships is paramount. A powerful tool in this realm is the radius map, a visual representation that highlights a defined area surrounding a specific point of interest. This seemingly simple concept holds immense potential across various fields, from business strategy to urban planning and even personal exploration.
Defining the Radius Map:
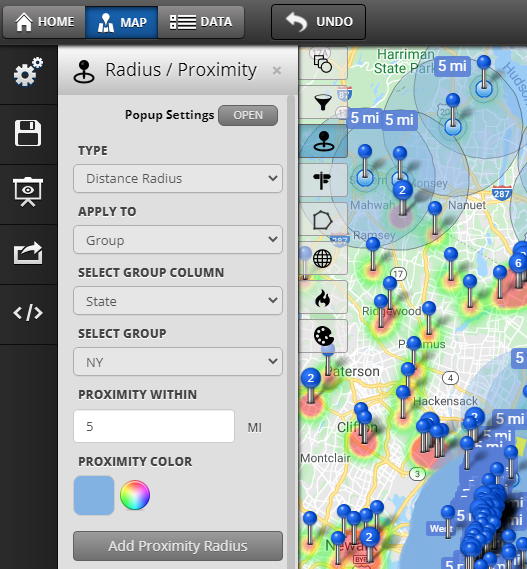
At its core, a radius map depicts a circular area with a specified radius emanating from a central point. This point can be a physical location, such as a store, a landmark, or a geographical feature, or it can represent a more abstract concept, like a customer’s address or a data point on a map. The radius, measured in units like miles, kilometers, or even minutes of travel time, determines the extent of the area encompassed by the map.
The Significance of Radius Maps:
The significance of radius maps lies in their ability to provide clear and concise visual information about spatial relationships. They offer a tangible representation of proximity, enabling users to:
- Identify potential customers or clients: Businesses can use radius maps to target individuals or businesses within a specific distance from their location, optimizing marketing campaigns and sales outreach.
- Analyze service area coverage: Companies offering services like delivery, repairs, or emergency response can utilize radius maps to assess the reach of their operations and identify potential gaps in coverage.
- Understand population density and distribution: Urban planners can leverage radius maps to analyze the spatial distribution of population groups, aiding in the development of infrastructure and services.
- Explore potential locations for new ventures: Businesses can use radius maps to identify promising locations for new stores, offices, or facilities based on factors like proximity to customers, competitors, and resources.
- Assess the impact of events and infrastructure projects: Radius maps can be employed to understand the potential impact of events like festivals or construction projects on surrounding areas, facilitating effective planning and mitigation strategies.
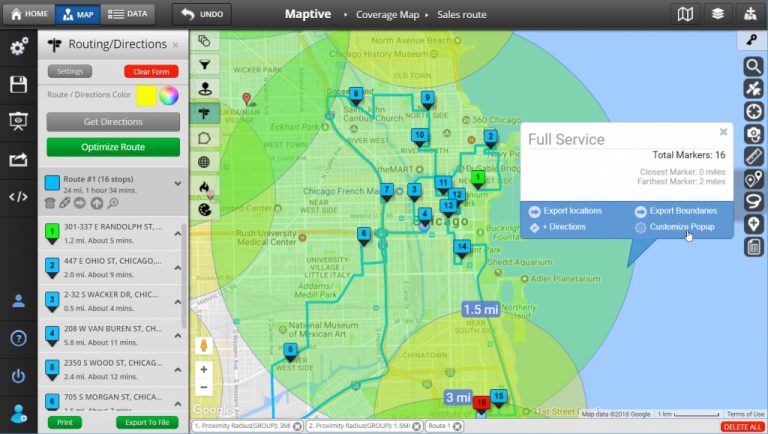
- Visualize travel time and distance: Radius maps are valuable for understanding travel time and distance between points, aiding in route planning, transportation logistics, and even personal travel decisions.
Beyond the Basic Radius:
While the core concept of a radius map is simple, its applications extend beyond a basic circle. Advanced features can enhance its utility, including:
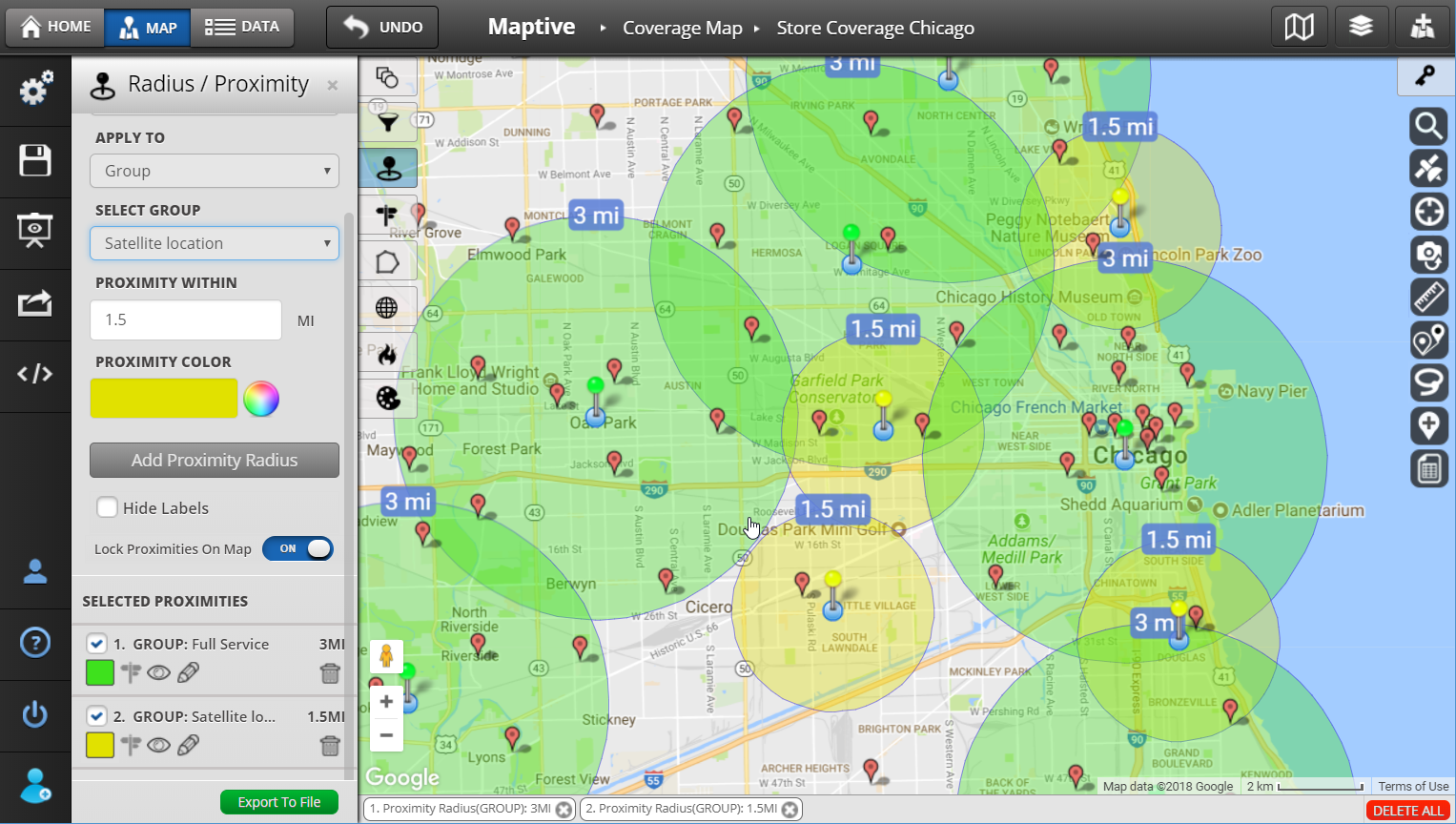
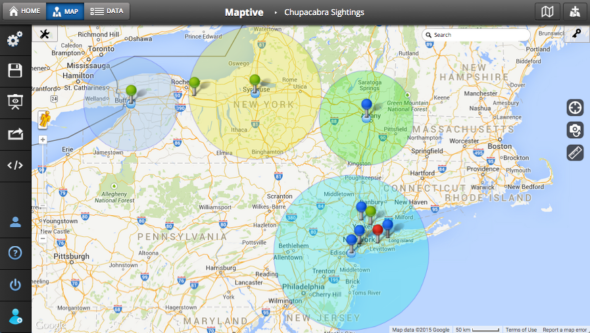
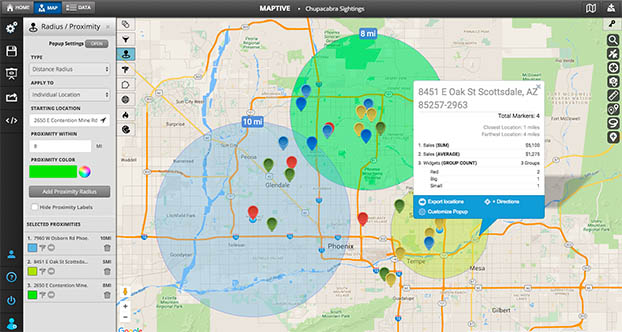
- Multiple radii: Displaying multiple concentric circles with different radii allows for visual comparison of different areas of influence or coverage.
- Custom shapes: Instead of a perfect circle, radius maps can be customized to encompass irregular shapes, such as polygons representing specific neighborhoods or regions.
- Data overlay: Superimposing data points like customer locations, demographics, or business density onto the radius map provides valuable insights into the characteristics of the target area.
- Dynamic radius adjustment: Interactive radius maps allow users to adjust the radius in real-time, enabling dynamic exploration of different geographic areas and their associated data.
Tools and Technologies for Creating Radius Maps:
Numerous tools and technologies are available for creating and utilizing radius maps:
- Mapping software: Popular mapping platforms like Google Maps, Bing Maps, and Mapbox offer built-in tools for creating radius maps with customizable features.
- GIS software: Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software like ArcGIS and QGIS provide advanced capabilities for creating and analyzing radius maps with complex data overlays.
- Data visualization libraries: Programming libraries like Leaflet and D3.js enable developers to create interactive and dynamic radius maps within web applications.
- Online mapping services: Several online services offer dedicated tools for creating radius maps, often with specific features tailored to business needs, like territory mapping and customer analysis.
FAQs About Radius Maps:
1. How do I choose the right radius for my map?
The optimal radius depends on the specific application and the desired level of granularity. Consider factors like the size of the area you are interested in, the intended use of the map, and the available data.
2. Can radius maps be used for different types of data?
Yes, radius maps can be used to visualize a wide range of data, including:
- Location data: Customer addresses, store locations, event venues
- Demographic data: Population density, income levels, age groups
- Business data: Competitor locations, customer spending patterns, service area coverage
- Environmental data: Air quality, pollution levels, natural hazards
3. Are there any limitations to radius maps?
While radius maps are powerful tools, they do have limitations:
- Simplification of reality: Radius maps provide a simplified view of reality, often neglecting complex geographic factors like terrain and barriers.
- Data availability: The accuracy of radius maps depends on the quality and availability of underlying data.
- Bias in data: The data used to create radius maps may be biased, leading to skewed results.
Tips for Using Radius Maps Effectively:
- Clearly define the purpose of the map: Before creating a radius map, determine the specific objective and target audience.
- Choose the appropriate radius and units: Select a radius that accurately reflects the scope of your analysis and use appropriate units for the target audience.
- Utilize data overlays effectively: Choose data overlays that provide relevant insights and avoid overwhelming the map with too much information.
- Ensure map clarity and readability: Use clear colors, fonts, and legends to ensure the map is easily understood.
- Test and refine the map: Iteratively test and refine the map based on feedback and analysis to optimize its usefulness.
Conclusion:
Radius maps offer a powerful and versatile tool for visualizing and analyzing spatial relationships. By understanding their core principles and utilizing available tools and technologies, individuals and organizations can harness the power of proximity to make informed decisions, optimize operations, and gain valuable insights into the world around them. As data continues to grow and the need for spatial analysis intensifies, radius maps will undoubtedly play an increasingly vital role in shaping our understanding of the world and guiding our actions.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Proximity: Understanding and Utilizing Radius Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!