The Power of Circles: Understanding Radius on Maps
Related Articles: The Power of Circles: Understanding Radius on Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Power of Circles: Understanding Radius on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Circles: Understanding Radius on Maps

In the realm of mapping and spatial analysis, the concept of "radius" plays a pivotal role, enabling us to understand and visualize spatial relationships in a clear and concise manner. A radius, essentially a line segment extending from the center of a circle to its edge, becomes a powerful tool for defining areas of influence, proximity, and accessibility. This article delves into the multifaceted applications of radius on maps, exploring its significance in various fields and highlighting its practical benefits.
Defining a Circle of Influence
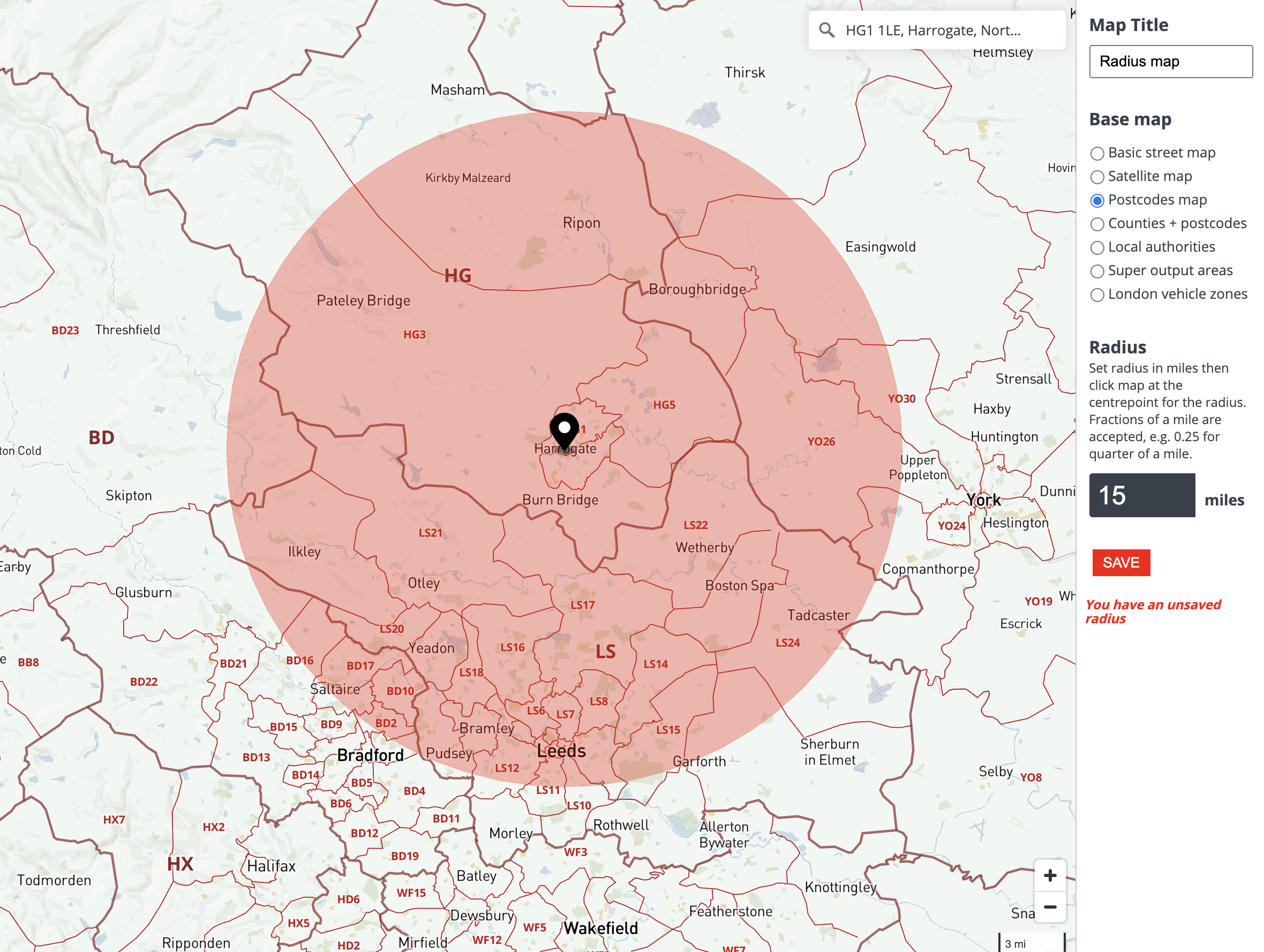
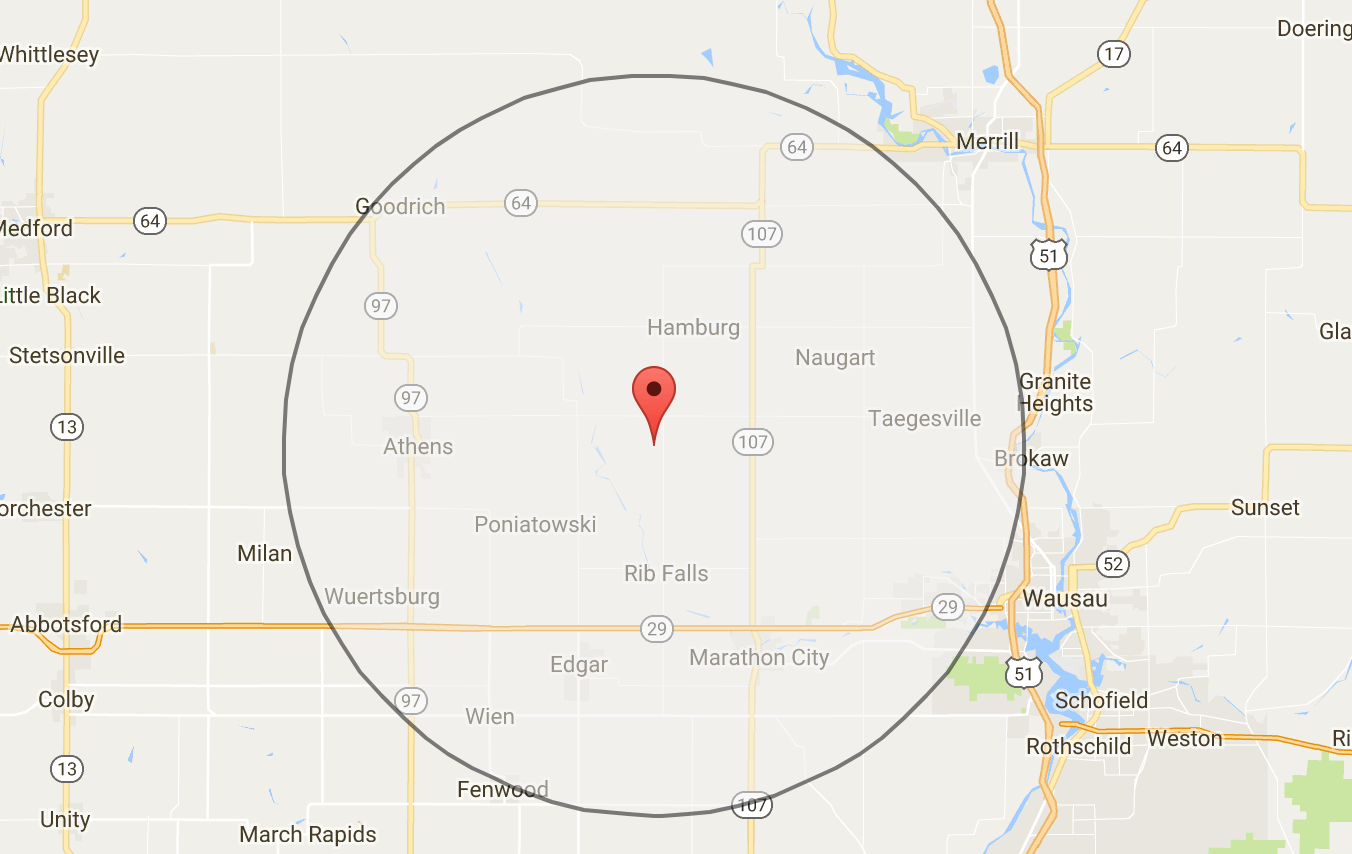
The most intuitive application of radius lies in defining a circular area around a central point. This "circle of influence" can represent a multitude of factors, depending on the context. For instance, in urban planning, a radius around a proposed development can help determine the potential impact on surrounding neighborhoods. In healthcare, a radius around a hospital can highlight the service area it covers. This simple yet effective tool allows for spatial analysis and planning, enabling informed decision-making based on proximity and accessibility.
Navigating with Radius
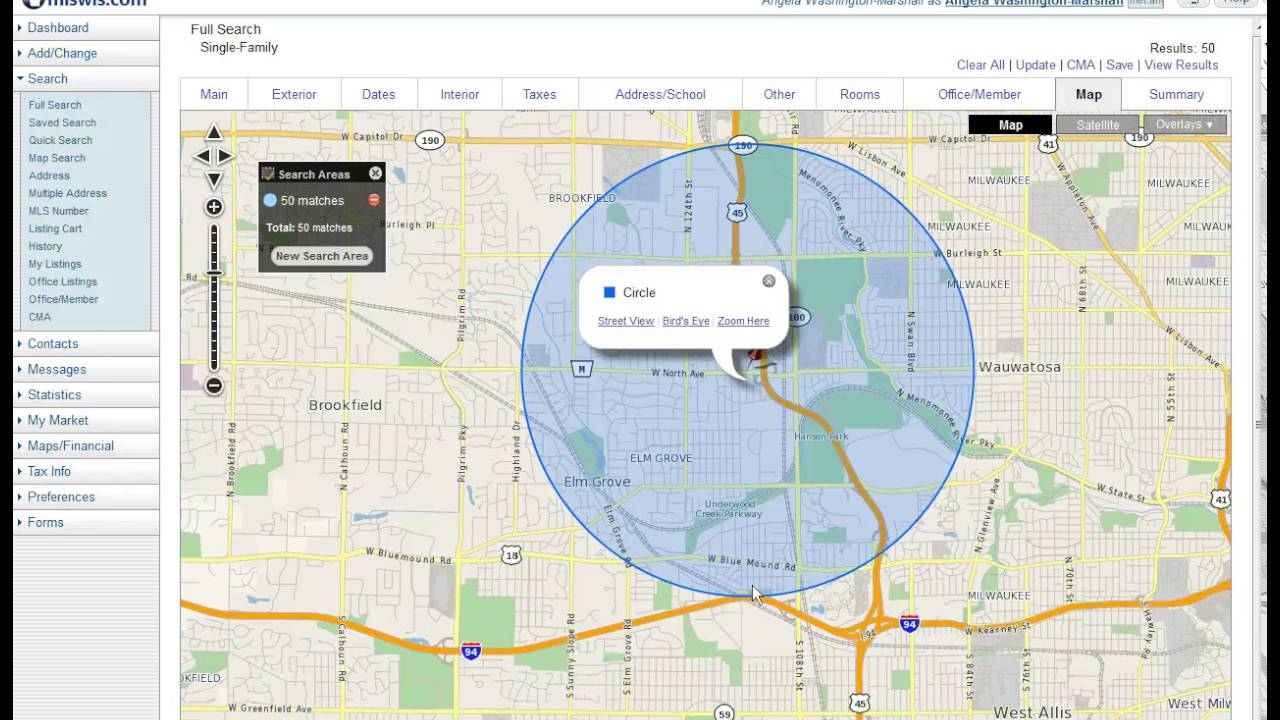
Radius is instrumental in navigation and location-based services. When searching for a restaurant, store, or other point of interest, users often rely on radius-based searches. This functionality allows users to specify a maximum distance from their current location or a designated point, ensuring that results are within a desired range. This feature enhances the user experience by providing relevant and manageable search results, optimizing navigation and saving time.
Analyzing Spatial Patterns
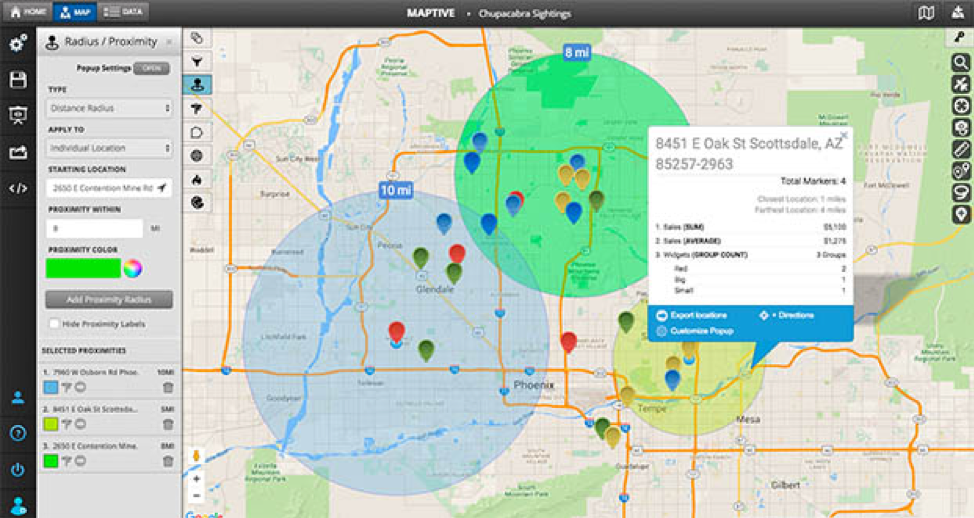
Radius also plays a crucial role in spatial analysis, allowing researchers and analysts to identify and understand patterns within geographic data. By creating buffers around specific locations or features, analysts can analyze the distribution of other data points in relation to the central point. This technique can be used to study various phenomena, such as:
- Proximity analysis: Determining the number of businesses, schools, or other features within a specific distance of a particular location.
- Accessibility analysis: Assessing the accessibility of services, resources, or infrastructure to different populations based on their proximity to specific points.
- Density analysis: Identifying areas of high concentration or clustering of specific data points based on their proximity to a central point.
Applications Across Industries
The versatility of radius extends beyond its use in mapping and spatial analysis. Its application spans various industries, including:
- Retail: Determining the optimal location for new stores based on customer density and proximity to existing competitors.
- Logistics: Optimizing delivery routes by minimizing the distance traveled and ensuring timely delivery within a specified radius.
- Environmental science: Analyzing the impact of pollution sources, identifying areas of contamination, and assessing the effectiveness of mitigation measures.
- Epidemiology: Studying the spread of diseases, identifying areas with high infection rates, and implementing targeted public health interventions.
Benefits of Using Radius
Employing radius in mapping and analysis offers numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced visualization: Radius provides a clear and intuitive way to visualize spatial relationships, making complex data more accessible and understandable.
- Improved decision-making: By understanding proximity and accessibility, radius empowers informed decision-making across various sectors.
- Increased efficiency: Radius-based analysis allows for efficient identification of patterns, trends, and anomalies within spatial data.
- Cost-effectiveness: By optimizing resource allocation and minimizing unnecessary travel, radius can contribute to cost savings and improved efficiency.
FAQs About Radius on Maps
Q: What are the common units used for radius on maps?
A: Radius is typically measured in units of distance, such as kilometers, miles, meters, or feet, depending on the scale of the map and the specific application.
Q: How can I create a radius on a map?
A: Most mapping software and online platforms provide tools for creating radius buffers around specific points. These tools often allow users to specify the radius size and select the appropriate units.
Q: What are some limitations of using radius on maps?
A: While radius is a powerful tool, it does have some limitations. For instance, it assumes a circular shape, which may not accurately represent real-world situations. Additionally, radius analysis can be influenced by the scale of the map and the accuracy of the underlying data.
Tips for Using Radius Effectively
- Choose the appropriate radius size: Consider the scale of the map and the specific application when determining the radius size.
- Use multiple radius sizes: Employing different radius sizes can provide a more comprehensive understanding of spatial relationships.
- Consider real-world limitations: Account for factors such as terrain, obstacles, and travel time when interpreting radius-based analysis.
- Combine radius with other analysis techniques: Integrate radius analysis with other spatial analysis tools, such as proximity analysis, density analysis, and network analysis, to gain a more complete picture of the data.
Conclusion
Radius, a simple yet powerful tool, plays a crucial role in mapping and spatial analysis. Its ability to define areas of influence, facilitate navigation, and analyze spatial patterns makes it an indispensable element in various fields. By understanding the concept of radius and its applications, individuals and organizations can leverage its potential to make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and gain a deeper understanding of the world around them. As technology continues to advance, radius will likely play an even more prominent role in shaping our understanding of spatial relationships and driving innovation across diverse sectors.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Circles: Understanding Radius on Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!