The Political Landscape of Poland: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: The Political Landscape of Poland: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Political Landscape of Poland: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Political Landscape of Poland: A Comprehensive Overview

The political map of Poland, a nation located in Central Europe, reflects a complex and dynamic history, shaped by both internal and external forces. Understanding this map requires delving into the nation’s political structure, its administrative divisions, and the forces that have influenced its evolution.
A Nation Divided: The Administrative Structure
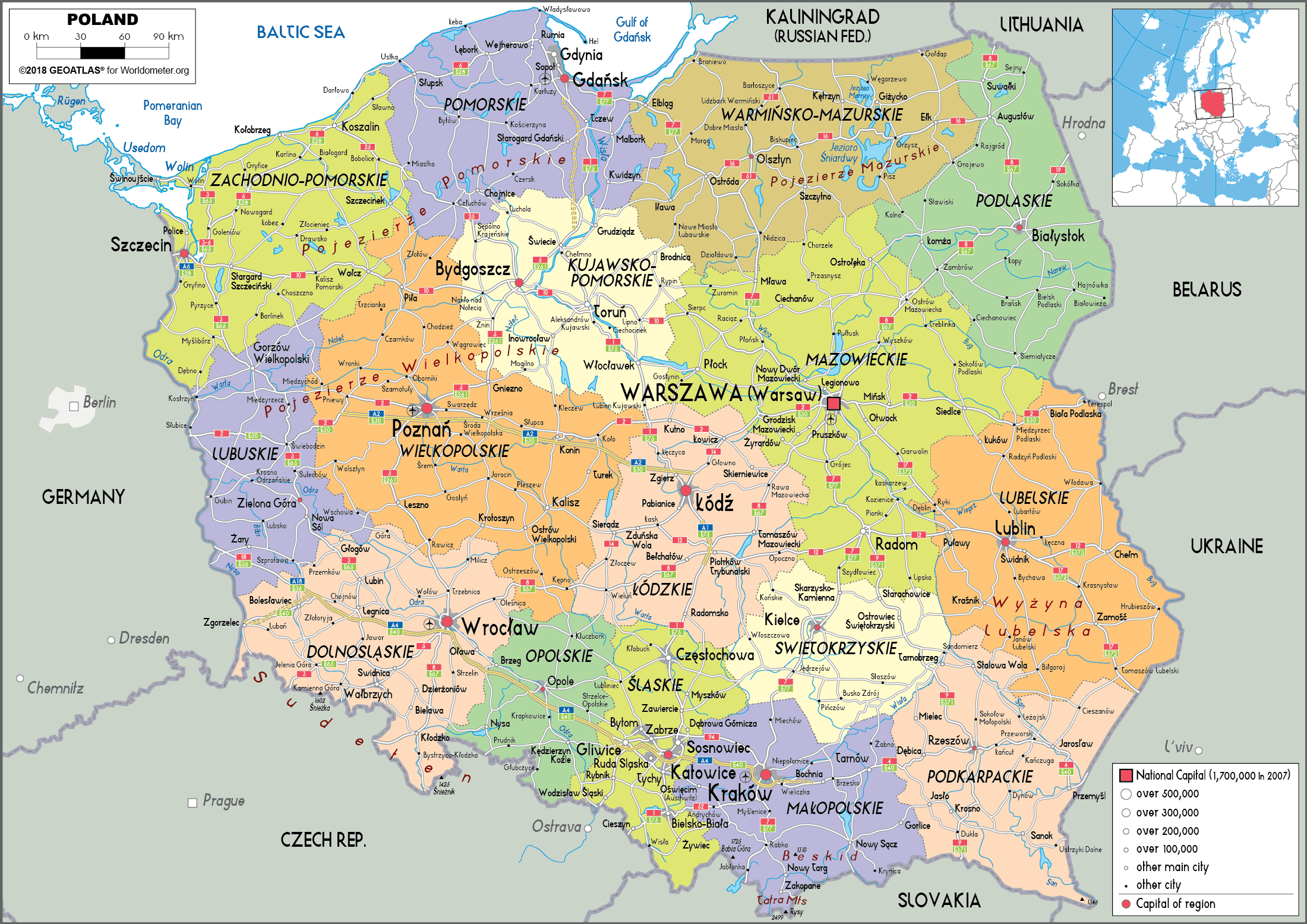
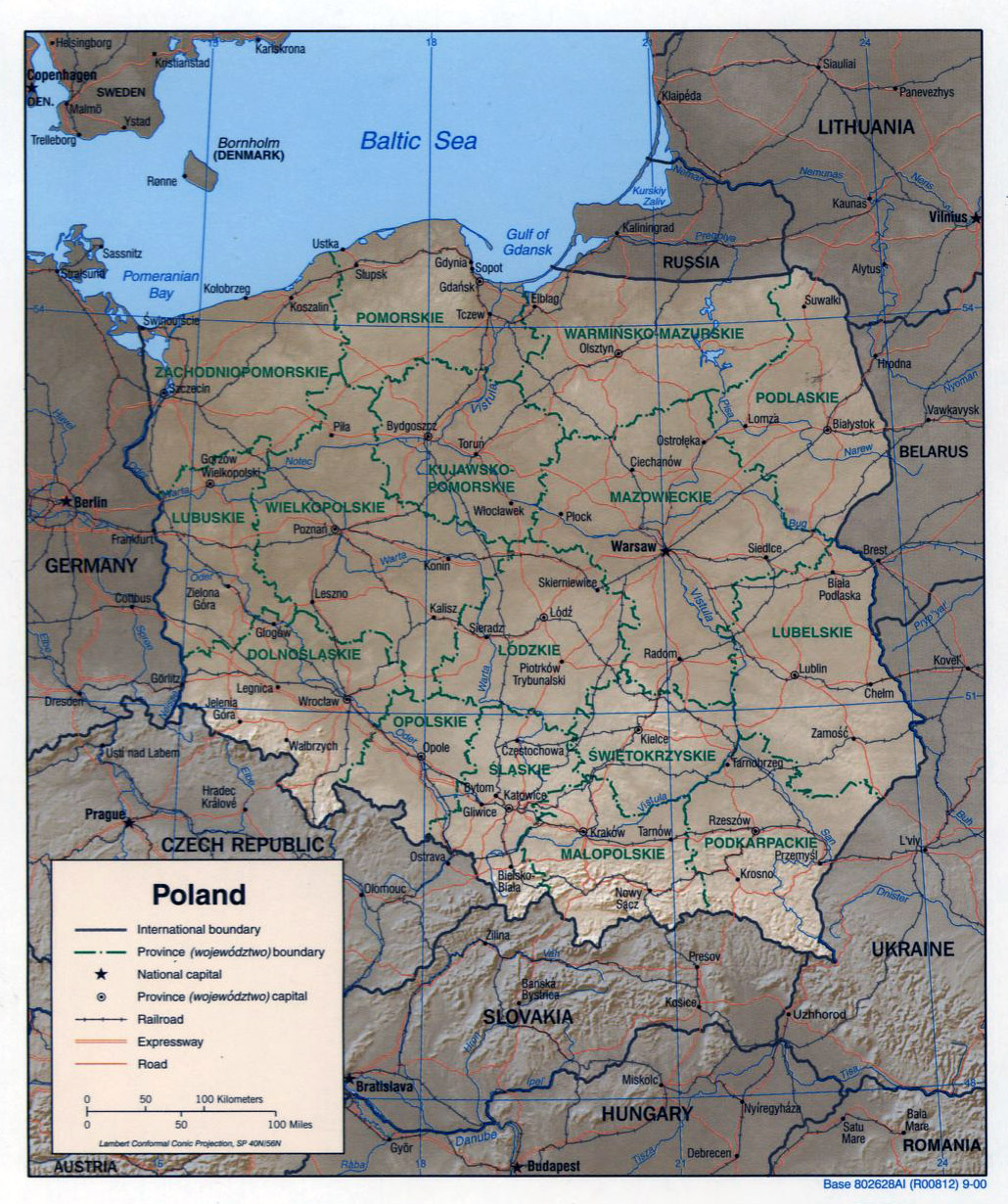
Poland is a unitary state, meaning that power is centralized within the national government. However, the country is divided into 16 administrative regions known as voivodeships. Each voivodeship is further subdivided into smaller administrative units called powiats, which are comparable to counties. These divisions are not merely administrative; they also represent distinct regional identities and economic profiles, contributing to the country’s diverse political landscape.
The Political Spectrum: A Multifaceted Reality
Poland’s political spectrum is characterized by a vibrant and multifaceted landscape. The dominant political force is the Law and Justice (PiS) party, which currently holds a majority in the Sejm (lower house of parliament) and the Senate. Their conservative, nationalist ideology has shaped the political discourse and policies in recent years.
However, the political landscape is not monolithic. Other significant political actors include the Civic Platform (PO), a center-right party with a more liberal approach to social and economic issues. The Polish People’s Party (PSL), a center-left party with a focus on rural communities, also plays a significant role.
Furthermore, a growing number of smaller parties and movements, representing diverse ideological positions, contribute to the dynamic nature of Polish politics. These include the Left, a leftist party advocating for social justice, and the Confederation, a right-wing coalition with a strong nationalist agenda.
Historical Influences: Shaping the Political Map
Poland’s political map is deeply intertwined with its history. The nation’s turbulent past, marked by periods of independence and foreign occupation, has left a lasting impact on its political landscape. The partition of Poland by neighboring empires in the 18th century, followed by a century of struggle for independence, instilled a strong sense of national identity and a desire for autonomy.
The post-World War II period saw Poland fall under the influence of the Soviet Union, with a communist government installed. This era left a legacy of political control and limitations on individual freedoms. However, the fall of communism in 1989 marked a watershed moment, paving the way for a democratic transition and the establishment of a multi-party system.
The Importance of Understanding the Political Map
Understanding the political map of Poland is crucial for comprehending its contemporary challenges and opportunities. The country’s political landscape influences its economic development, its foreign policy, and its social fabric.
For example, the current government’s focus on social welfare programs and infrastructure development has had a significant impact on the Polish economy. Similarly, the nation’s stance on issues like immigration and European integration is directly shaped by the political forces in power.
Navigating the Political Landscape: Key Considerations
When analyzing the political map of Poland, it is essential to consider the following key factors:
- Electoral Systems: Poland employs a mixed electoral system for the Sejm, combining proportional representation with single-member districts. This system can lead to complex coalition-building and shifts in political power.
- Regional Differences: The country’s voivodeships exhibit distinct political identities and voting patterns, highlighting the importance of regional considerations in national elections.
- International Relations: Poland’s strategic location and its membership in the European Union and NATO heavily influence its foreign policy and its role in international affairs.
- Social and Economic Factors: The country’s demographics, economic performance, and social issues all play a role in shaping the political landscape and influencing voter preferences.
FAQs
Q: What are the main political parties in Poland?
A: The dominant political parties in Poland are the Law and Justice (PiS), the Civic Platform (PO), and the Polish People’s Party (PSL).
Q: How does Poland’s political system work?
A: Poland is a parliamentary republic with a semi-presidential system. The President is elected directly by the people, while the Prime Minister is appointed by the President and is accountable to the Sejm (lower house of parliament).
Q: What are the key challenges facing Polish politics today?
A: Some of the key challenges facing Polish politics include:
- Political Polarization: The country has witnessed a growing divide between the ruling party and the opposition, leading to increased political tension.
- Economic Inequality: Despite economic growth, income inequality persists, raising concerns about social justice and the distribution of wealth.
- European Integration: Poland’s relationship with the European Union has become increasingly complex, with concerns about the country’s adherence to EU values and principles.
Tips for Understanding the Political Map
- Follow reputable news sources: Stay informed about current events and political developments by consulting reputable news organizations both in Poland and internationally.
- Engage with academic research: Explore academic journals and research articles to gain a deeper understanding of the country’s political history, institutions, and current trends.
- Participate in discussions: Engage in discussions with experts and individuals with diverse perspectives to broaden your understanding of the complexities of Polish politics.
Conclusion
The political map of Poland is a dynamic and multifaceted landscape, reflecting the country’s rich history, its current challenges, and its aspirations for the future. Understanding this map requires a nuanced approach, taking into account the country’s administrative divisions, its political spectrum, its historical influences, and the key factors shaping its political landscape. By engaging with these complexities, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of Polish politics and its impact on the nation’s development and its role in the international arena.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Political Landscape of Poland: A Comprehensive Overview. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!