The Polish Voivodeship Map: A Framework for Governance and Development
Related Articles: The Polish Voivodeship Map: A Framework for Governance and Development
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Polish Voivodeship Map: A Framework for Governance and Development. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Polish Voivodeship Map: A Framework for Governance and Development
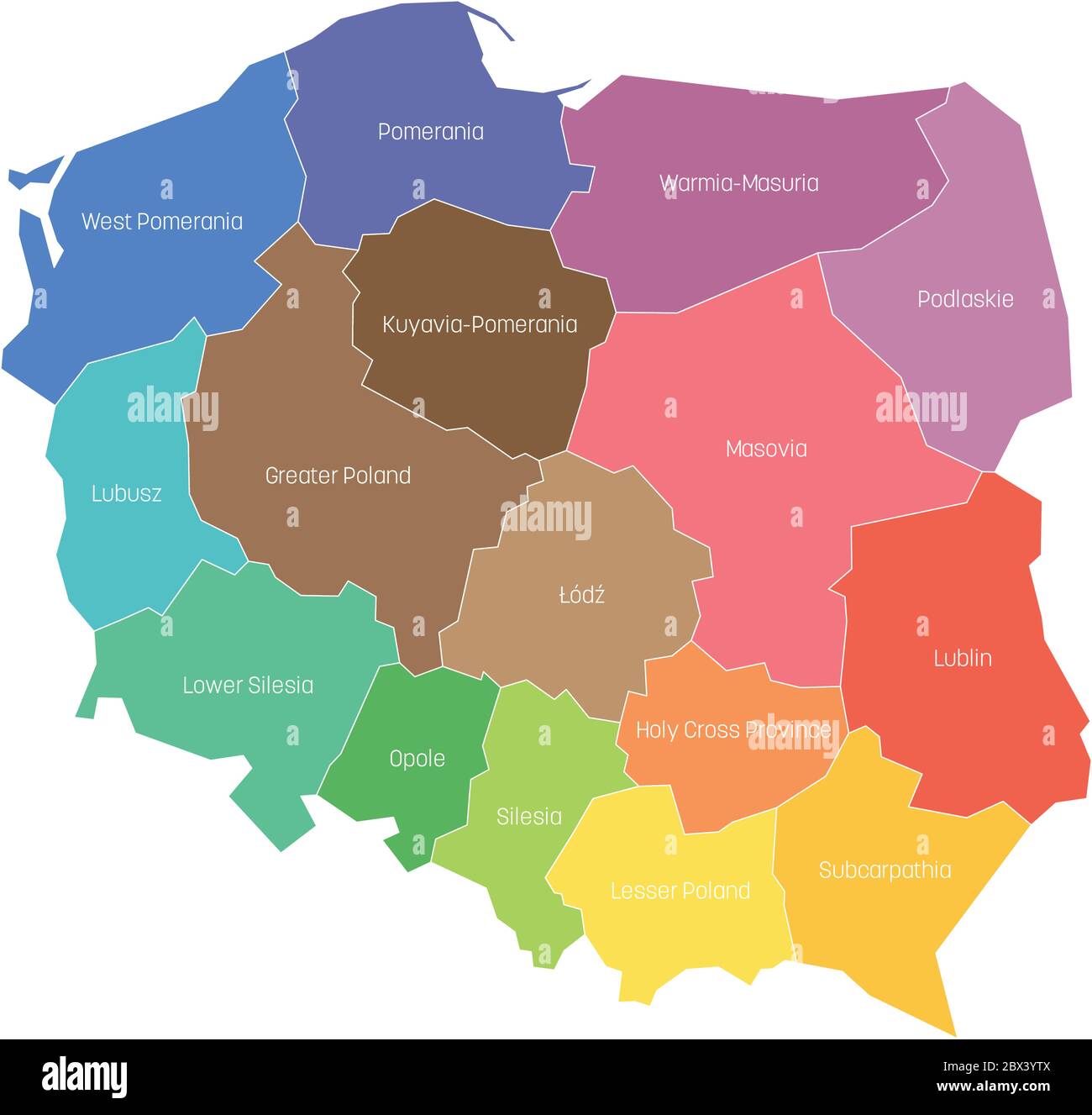
The Polish voivodeship map, a visual representation of Poland’s administrative divisions, is a crucial element in understanding the country’s governance structure and its multifaceted development. This map, with its distinct regions and boundaries, reflects the historical, cultural, and economic nuances of Poland, offering a valuable tool for navigating the country’s diverse landscape.
A Glimpse into History: The Evolution of Voivodeships
The concept of voivodeships, or provinces, in Poland has a rich history, evolving alongside the country’s political and administrative landscape. From the medieval era, when voivodeships were primarily defined by the authority of a voivode (governor), the system underwent numerous transformations.
- 1918-1939: After regaining independence, Poland adopted a system of 16 voivodeships, reflecting the country’s newly established borders.
- 1944-1975: During the communist era, the number of voivodeships was increased to 22, reflecting a desire for greater administrative control.
- 1975-1998: This period saw a significant shift with the introduction of 49 voivodeships, aiming to decentralize power and improve local governance.
- 1999-Present: The current system of 16 voivodeships was implemented in 1999, aiming to balance administrative efficiency with regional identity and development.
Understanding the Structure: The 16 Voivodeships
The current voivodeship map of Poland features 16 distinct regions, each with its own unique characteristics and significance. These regions are:
- Lower Silesian Voivodeship: Located in southwestern Poland, it encompasses the historical region of Silesia, known for its industrial heritage and picturesque landscapes.
- Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship: Situated in central Poland, it combines the historical regions of Kuyavia and Pomerania, featuring a rich agricultural heritage and vibrant cities.
- Lesser Poland Voivodeship: Located in southern Poland, it encompasses the historical region of Lesser Poland, home to Krakow, a major cultural and historical hub.
- Lublin Voivodeship: Situated in eastern Poland, it includes the historical region of Lublin, known for its agricultural production and cultural heritage.
- Lubusz Voivodeship: Located in western Poland, it encompasses the historical region of Lubusz Land, characterized by its fertile plains and historic castles.
- Łódź Voivodeship: Situated in central Poland, it is known as the "City of Textile," with a long industrial history and a vibrant cultural scene.
- Małopolska Voivodeship: Located in southern Poland, it encompasses the historical region of Lesser Poland, known for its stunning mountains and rich cultural heritage.
- Masovian Voivodeship: Situated in central Poland, it is the largest voivodeship by area and population, encompassing the capital city of Warsaw.
- Opole Voivodeship: Located in southwestern Poland, it encompasses the historical region of Upper Silesia, known for its industrial heritage and vibrant cultural life.
- Podkarpackie Voivodeship: Situated in southeastern Poland, it encompasses the historical region of Subcarpathian Voivodeship, known for its picturesque mountains and rich cultural heritage.
- Podlaskie Voivodeship: Located in northeastern Poland, it encompasses the historical region of Podlasie, known for its unique cultural traditions and natural beauty.
- Pomeranian Voivodeship: Situated in northern Poland, it encompasses the historical region of Pomerania, known for its Baltic Sea coastline and vibrant cities.
- Silesian Voivodeship: Located in southern Poland, it encompasses the historical region of Silesia, known for its industrial heritage and vibrant cultural life.
- Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship: Situated in central Poland, it encompasses the historical region of Świętokrzyskie Mountains, known for its natural beauty and rich cultural heritage.
- Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship: Located in northeastern Poland, it encompasses the historical regions of Warmia and Masuria, known for its picturesque lakes and natural beauty.
- West Pomeranian Voivodeship: Situated in northwestern Poland, it encompasses the historical region of Western Pomerania, known for its Baltic Sea coastline and vibrant cities.
The Importance of Voivodeships: A Framework for Development
The voivodeship map serves as a crucial framework for the development of Poland’s economy, infrastructure, and society. Each voivodeship is responsible for:
- Regional Governance: Each voivodeship is governed by a voivode, appointed by the Polish government, and a regional assembly, elected by the people. This structure ensures local representation and involvement in decision-making processes.
- Economic Development: Voivodeships play a vital role in promoting economic growth within their respective regions. This includes attracting investment, supporting local businesses, and developing infrastructure.
- Social Welfare: Voivodeships are responsible for providing essential social services to their residents, including healthcare, education, and social assistance.
- Cultural Preservation: Voivodeships play a significant role in preserving and promoting the cultural heritage of their regions. This includes supporting local museums, theaters, and cultural events.
The Benefits of the Voivodeship System
The current voivodeship system offers several benefits:
- Decentralization of Power: The system empowers regional authorities to address local needs and priorities, fostering greater autonomy and responsiveness.
- Efficient Governance: By dividing the country into distinct regions, the system streamlines administrative processes and promotes efficient resource allocation.
- Regional Development: The system encourages regional development initiatives, fostering economic growth and social progress in diverse areas.
- Preservation of Cultural Identity: Voivodeships act as guardians of their regions’ unique cultural heritage, promoting local traditions and artistic expressions.
FAQs about the Polish Voivodeship Map
Q: How many voivodeships are there in Poland?
A: There are 16 voivodeships in Poland.
Q: What is the largest voivodeship in Poland by area and population?
A: The Masovian Voivodeship is the largest by area and population, encompassing the capital city of Warsaw.
Q: What are the main economic activities in each voivodeship?
A: Economic activities vary across voivodeships, ranging from industrial production in Silesia and Łódź to agriculture in Lublin and Kuyavian-Pomeranian.
Q: How are voivodes elected?
A: Voivodes are appointed by the Polish government, while regional assemblies are elected by the people.
Q: What are the key cultural attractions in each voivodeship?
A: Each voivodeship offers unique cultural attractions, from historic cities like Krakow and Gdańsk to stunning natural landscapes and traditional festivals.
Tips for Navigating the Voivodeship Map
- Use a Digital Map: Interactive online maps provide detailed information about each voivodeship, including its borders, major cities, and points of interest.
- Explore Regional Websites: Each voivodeship has its own official website, offering insights into local government, economic development, and cultural attractions.
- Consult Travel Guides: Travel guides provide comprehensive information about specific voivodeships, highlighting key attractions, accommodation options, and transportation details.
- Engage with Local Residents: Talking to locals can offer valuable insights into the unique characteristics and hidden gems of each voivodeship.
Conclusion: A Framework for Progress and Identity
The Polish voivodeship map, with its intricate network of regions and boundaries, is more than just a geographical representation. It is a testament to Poland’s history, its cultural diversity, and its commitment to decentralized governance. The system fosters regional development, preserves cultural identity, and ensures that the needs and aspirations of each region are reflected in the country’s overall progress. As Poland continues to evolve, the voivodeship map will remain a vital tool for navigating its diverse landscape and fostering a prosperous future for all its citizens.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Polish Voivodeship Map: A Framework for Governance and Development. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!