The Importance of Preserving Area in Map Projections
Related Articles: The Importance of Preserving Area in Map Projections
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Importance of Preserving Area in Map Projections. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Importance of Preserving Area in Map Projections
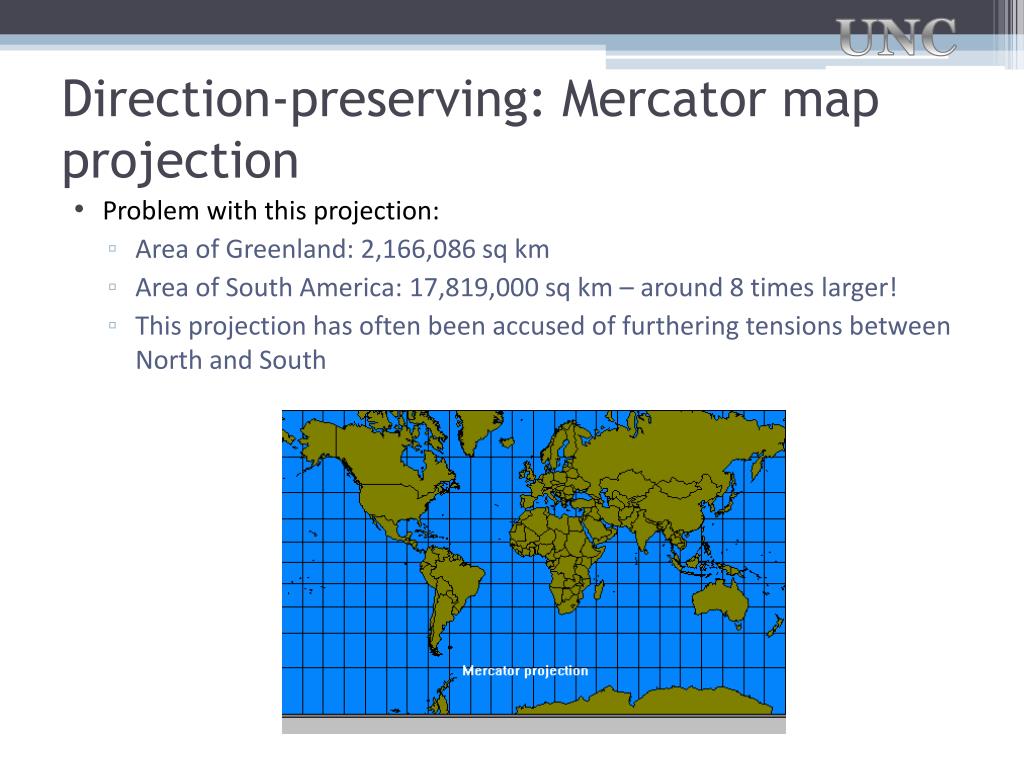
The world is a sphere, yet we represent it on flat maps. This inherent transformation introduces distortions, impacting the accuracy of geographic data. While various map projections exist, a crucial aspect is preserving area, ensuring that the relative sizes of regions on the map accurately reflect their true proportions on the Earth’s surface.
Understanding the Need for Area Preservation
Representing the Earth’s curved surface on a flat map necessitates compromises. Different projections prioritize specific properties, such as shape, distance, or direction, while others aim to minimize distortion in general. However, preserving area is essential for various applications, including:
- Population Density Analysis: Accurately representing the size of countries or regions allows for meaningful comparisons of population density, informing policy decisions on resource allocation and infrastructure development.
- Resource Management: When studying natural resources like forests, mineral deposits, or water resources, maintaining accurate area representation enables effective resource management and planning.
- Environmental Studies: Analyzing environmental data, such as deforestation rates or pollution levels, requires precise area calculations to ensure accurate conclusions and informed environmental policy.
- Cartographic Design: Maps designed for specific purposes, such as thematic maps illustrating population distribution or economic activity, benefit from area preservation to convey accurate information.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS applications heavily rely on accurate area calculations for spatial analysis, data visualization, and decision-making processes.
Common Projections for Preserving Area
Several map projections prioritize area preservation, each with its own strengths and limitations:
-
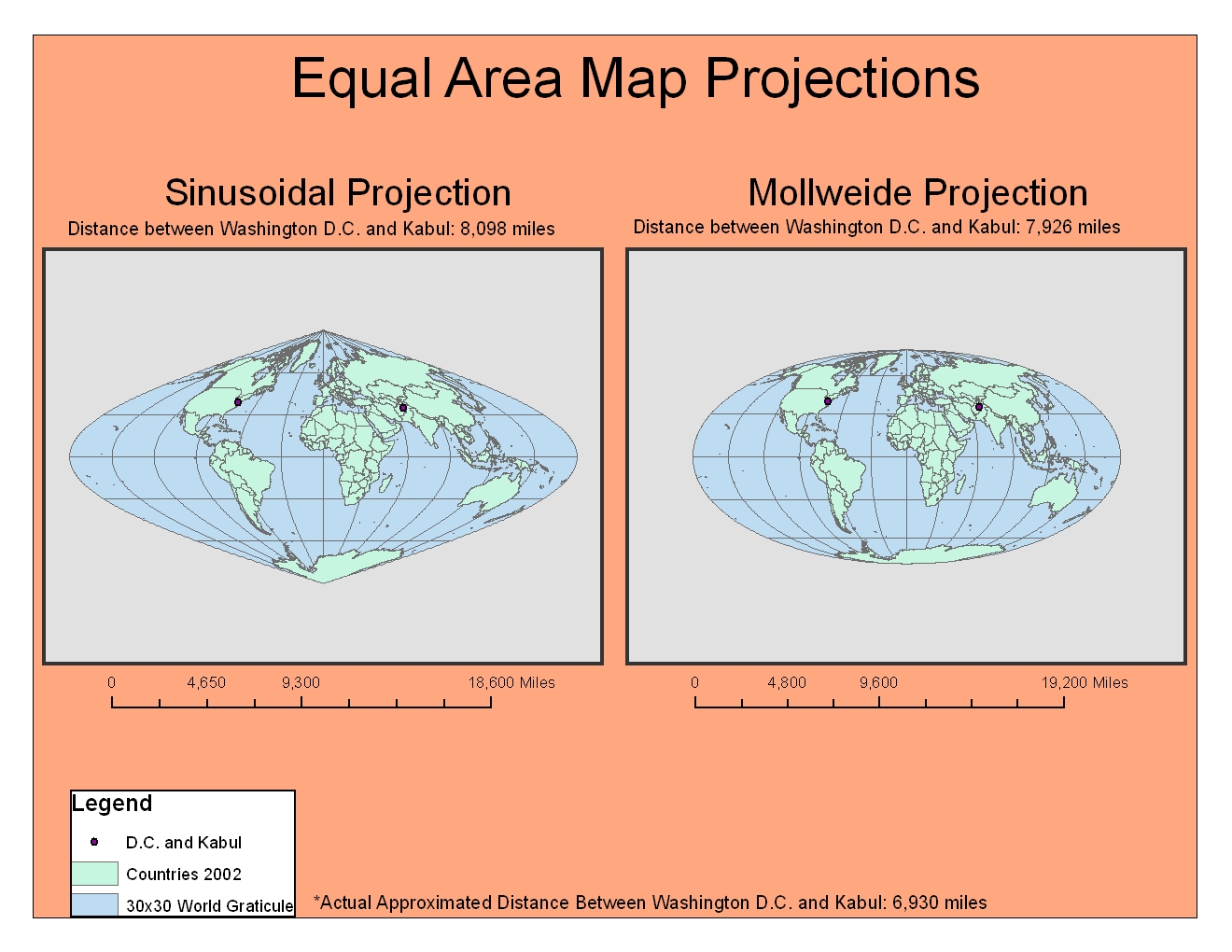
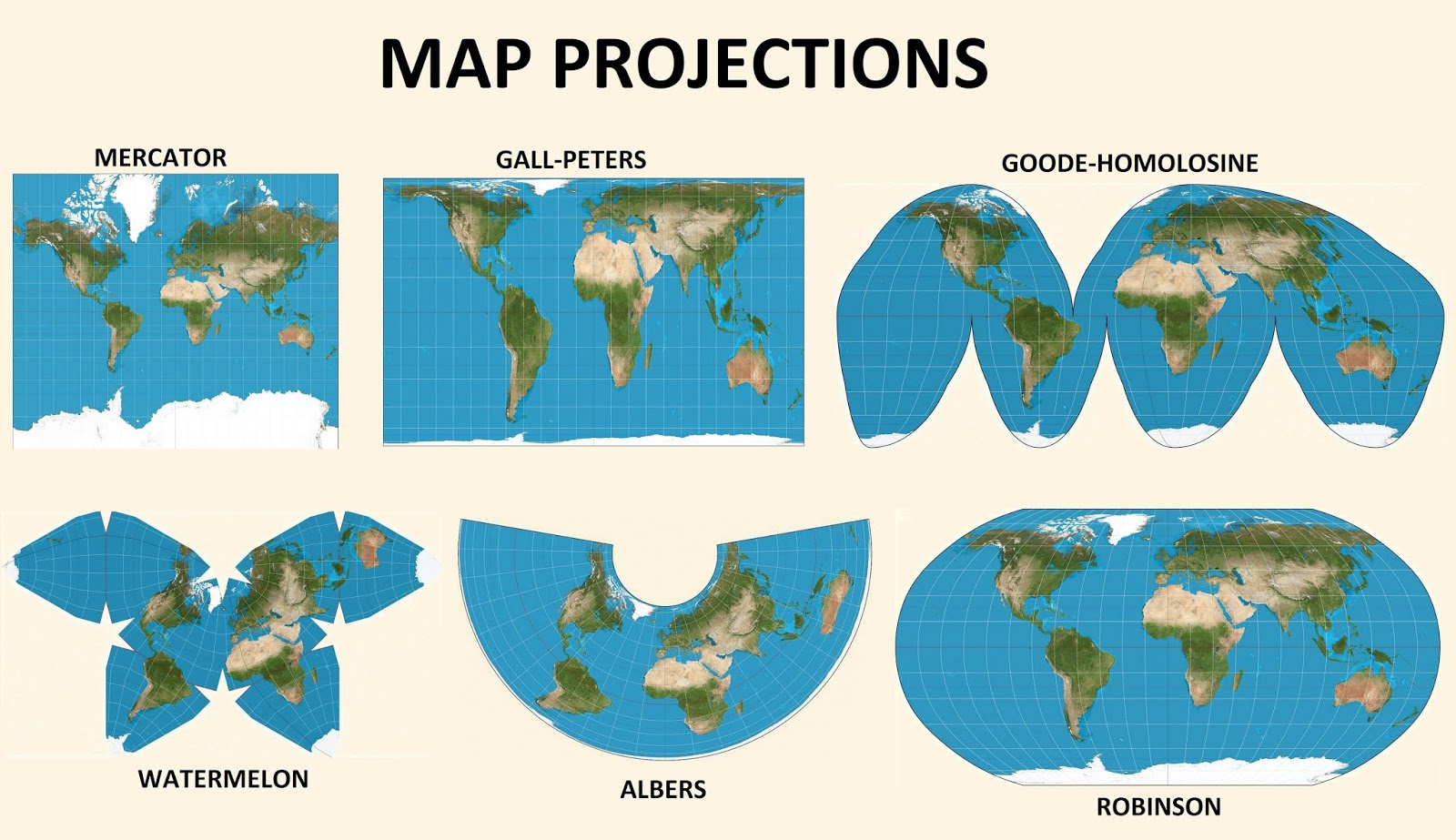
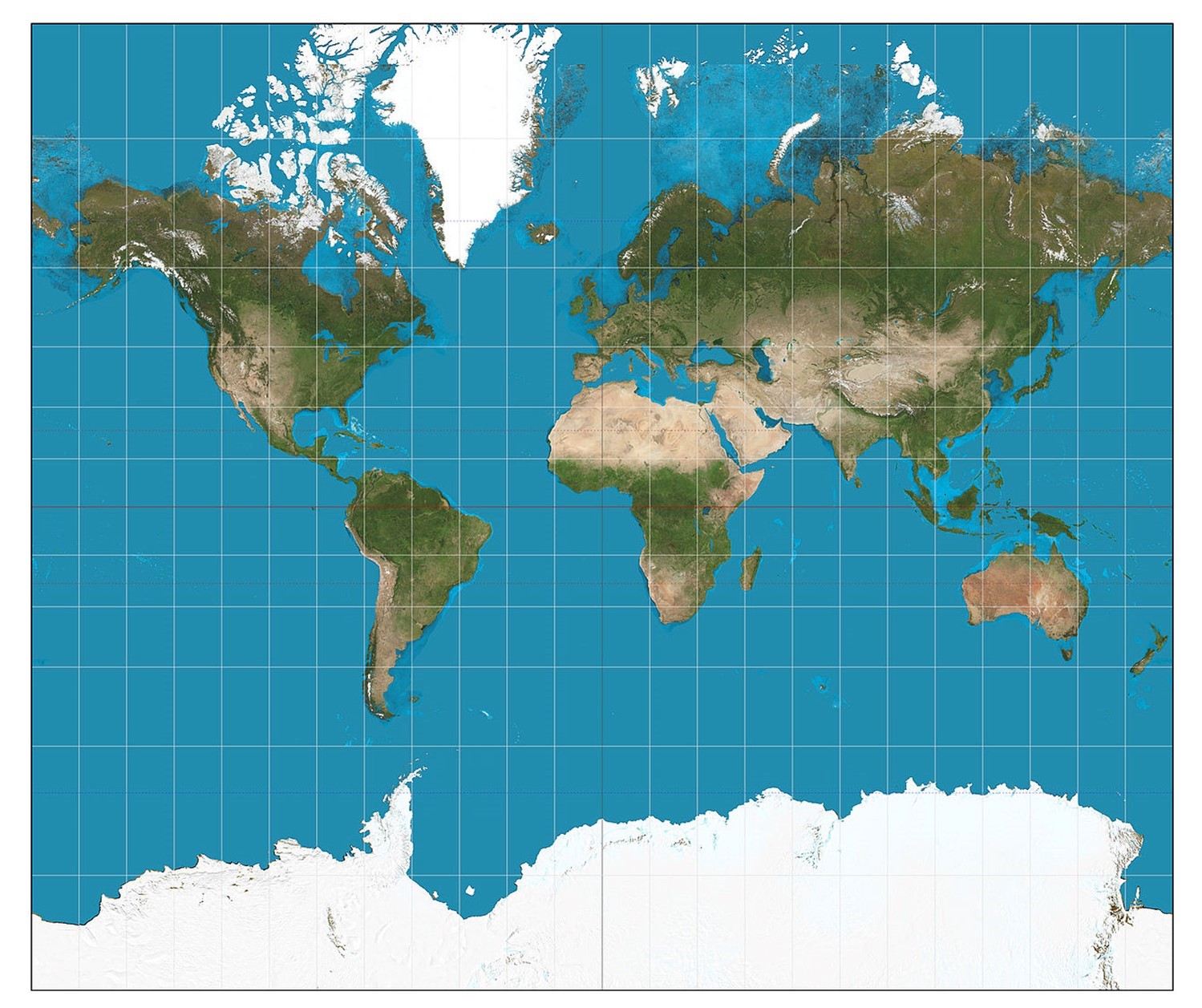
Equal-Area Projections: These projections maintain the relative areas of regions on the map, ensuring that the size of features remains proportional to their actual size on the Earth.
- Albers Equal-Area Conic Projection: Commonly used for large regions, particularly in the United States, this projection preserves area while minimizing shape distortion.
- Lambert Azimuthal Equal-Area Projection: This projection is ideal for representing polar regions, preserving area and providing a visually appealing representation.
- Mollweide Projection: Known for its aesthetically pleasing, oval shape, this projection provides a balanced compromise between area preservation and minimal shape distortion.
-
Cylindrical Equal-Area Projections: These projections project the Earth onto a cylinder, resulting in a rectangular map.
- Gall-Peters Projection: This projection is notable for its emphasis on accurate area representation, but it distorts shapes significantly, particularly near the poles.
- Lambert Cylindrical Equal-Area Projection: This projection offers a balance between area preservation and shape distortion, making it suitable for representing regions along the equator.
Challenges and Limitations
While area-preserving projections offer valuable insights, they are not without limitations:
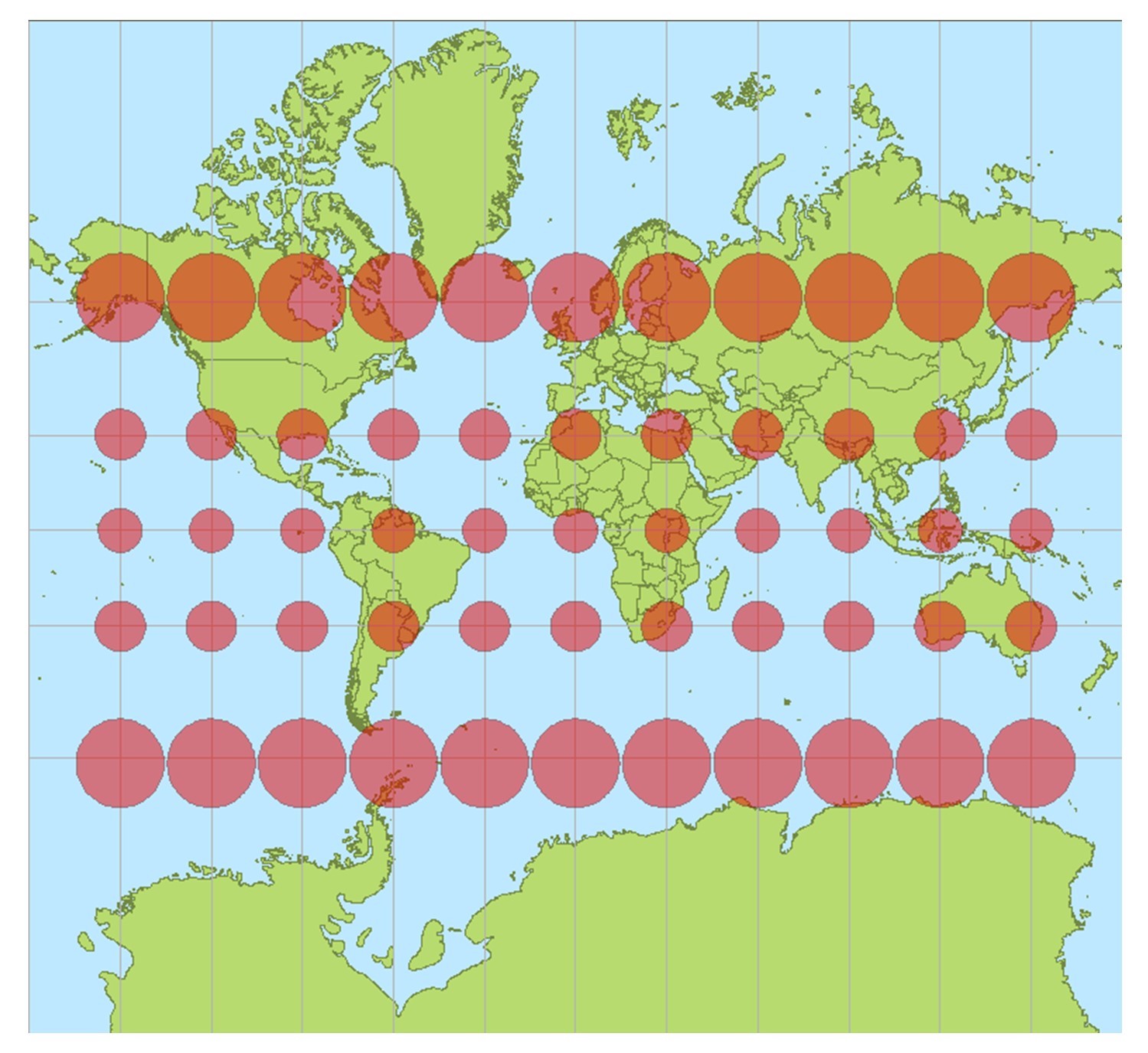
- Shape Distortion: Preserving area often leads to distortions in shape, particularly near the poles or edges of the map.
- Direction Distortion: Area-preserving projections do not typically preserve direction accurately, making them unsuitable for navigation.
- Visual Representation: Some area-preserving projections may result in less visually appealing maps, making it challenging to interpret certain features.
Choosing the Right Projection
The selection of a map projection depends on the specific application and the desired level of accuracy. When area preservation is paramount, consider the following factors:
- Region of Interest: The size and location of the area being mapped will influence the suitability of different projections.
- Desired Properties: Determine the primary properties that need to be preserved, such as area, shape, or distance.
- Intended Use: The purpose of the map will determine the level of accuracy and distortion acceptable for the application.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between an equal-area projection and a conformal projection?
A: Equal-area projections preserve the relative areas of regions, while conformal projections preserve the shapes of small features. Conformal projections are ideal for navigation and mapping coastal areas, while equal-area projections are suitable for analyzing population density or resource distribution.
Q: Why are some maps distorted?
A: Distortion is inevitable when projecting the Earth’s curved surface onto a flat map. Different projections prioritize different properties, leading to varying levels of distortion in area, shape, distance, or direction.
Q: How can I identify an area-preserving projection?
A: Look for projections with "equal-area" or "equivalent" in their names. Additionally, check the projection’s properties and identify if it maintains the relative sizes of regions.
Tips for Using Area-Preserving Projections
- Understand the limitations: Be aware of the distortions introduced by the chosen projection, particularly shape and direction distortion.
- Compare different projections: Experiment with various area-preserving projections to find the one that best suits the specific application.
- Use appropriate software: GIS software allows for selecting and manipulating different projections, enabling accurate area calculations and data analysis.
- Communicate clearly: When presenting maps created using area-preserving projections, clearly communicate the projection used and any associated distortions.
Conclusion
Preserving area in map projections is crucial for accurately representing geographic data and ensuring reliable analysis. By understanding the principles of area preservation, the various projections available, and their limitations, users can choose the most appropriate projection for their specific needs. This ensures accurate representation of the Earth’s surface, enabling informed decision-making across diverse fields, from population analysis and resource management to environmental studies and cartographic design.


![]()

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Importance of Preserving Area in Map Projections. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!