The Imperfect Picture: Understanding Distortions in Map Projections
Related Articles: The Imperfect Picture: Understanding Distortions in Map Projections
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Imperfect Picture: Understanding Distortions in Map Projections. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Imperfect Picture: Understanding Distortions in Map Projections

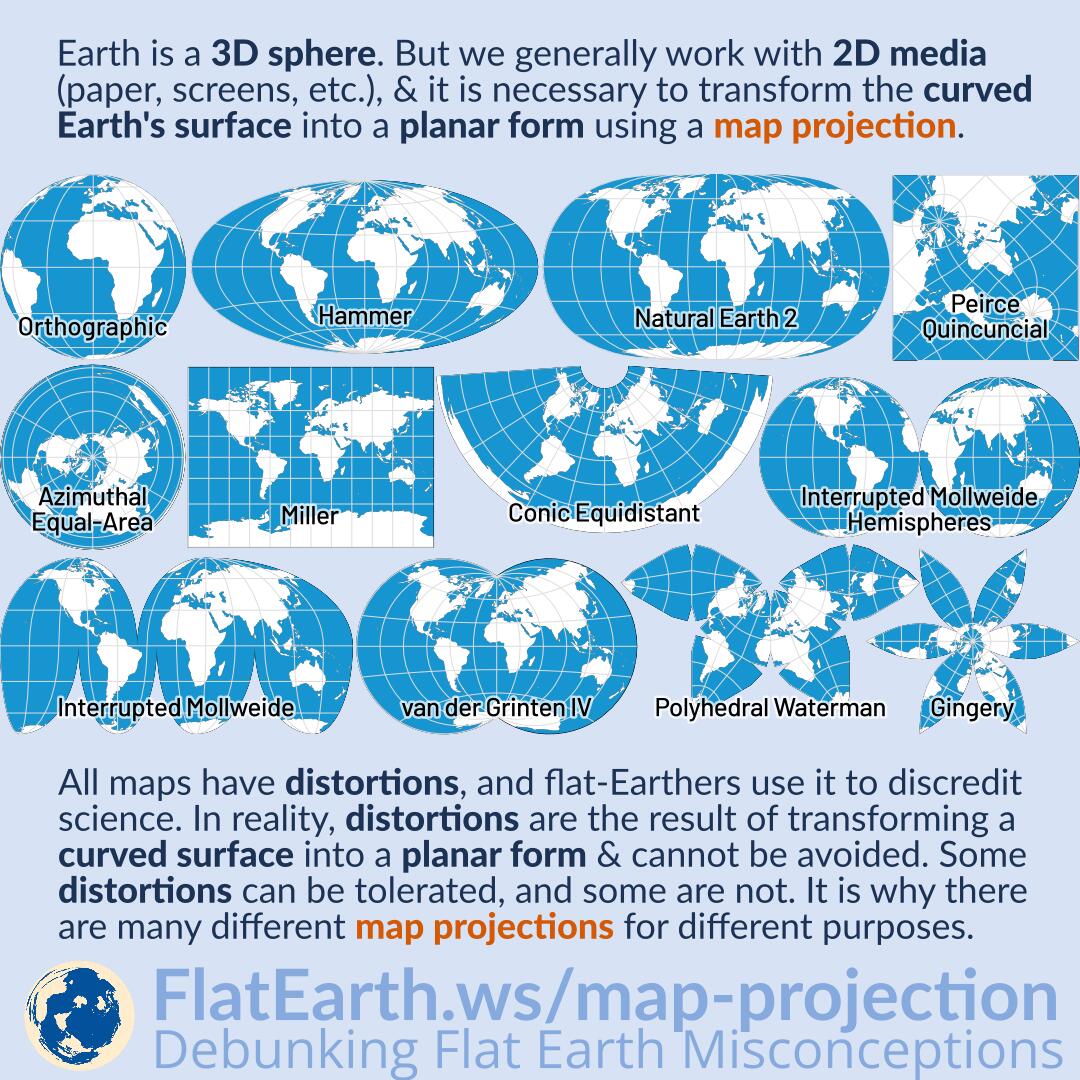
Maps, at their core, are simplified representations of the Earth’s complex three-dimensional surface onto a two-dimensional plane. This inherent transformation inevitably introduces distortions, altering the shapes, sizes, distances, and directions of geographical features. While striving for accuracy, map projections inherently involve compromises, each seeking to prioritize certain aspects at the expense of others. Recognizing and understanding these distortions is crucial for interpreting maps accurately and appreciating the limitations of their representations.
This article delves into four fundamental distortions inherent in map projections: area, shape, distance, and direction. Examining these distortions provides insight into the complexities of mapmaking and the trade-offs involved in presenting a comprehensive picture of our planet.
1. Area Distortion
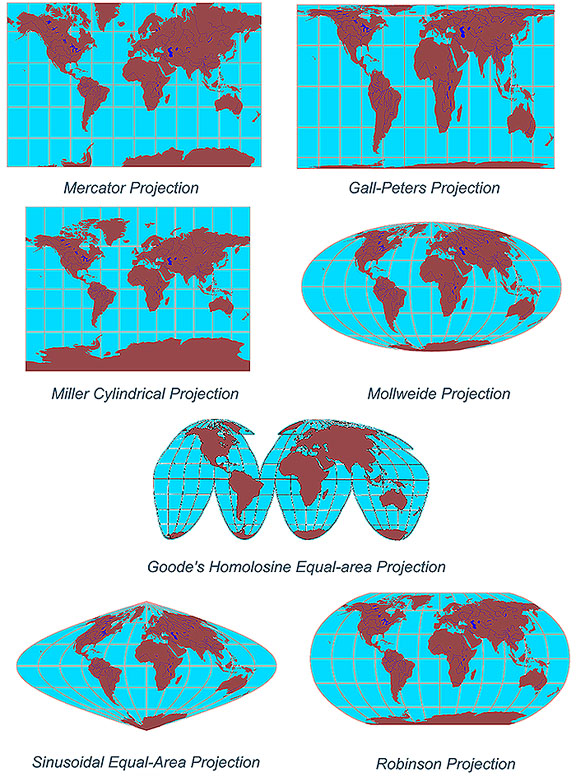
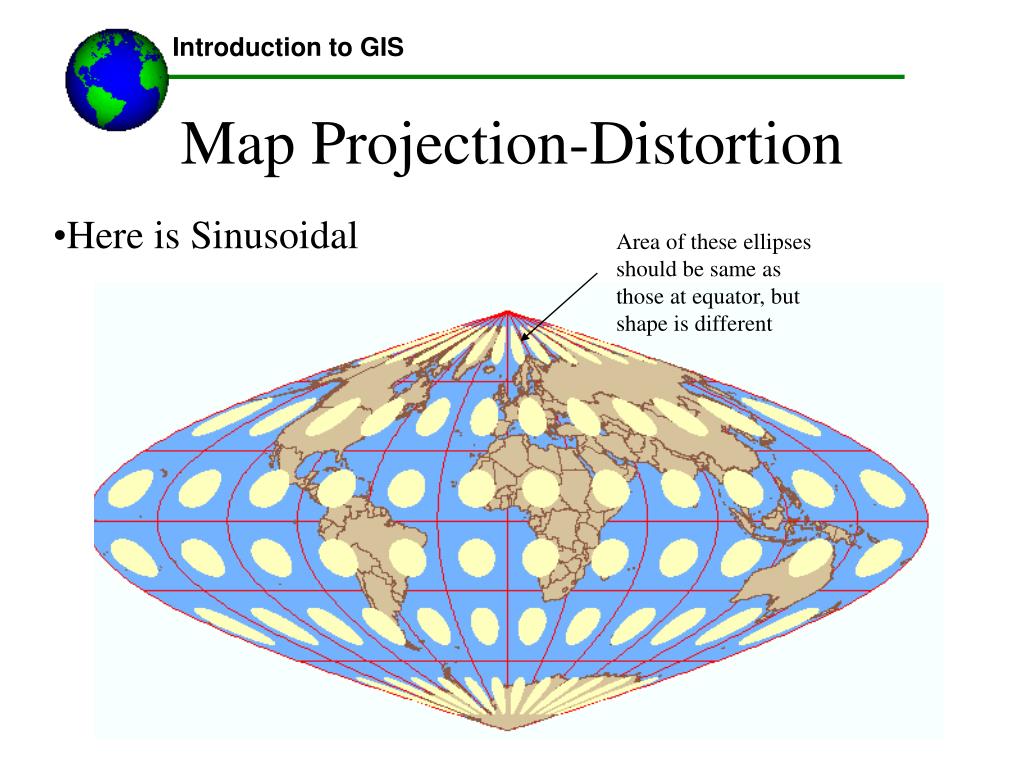
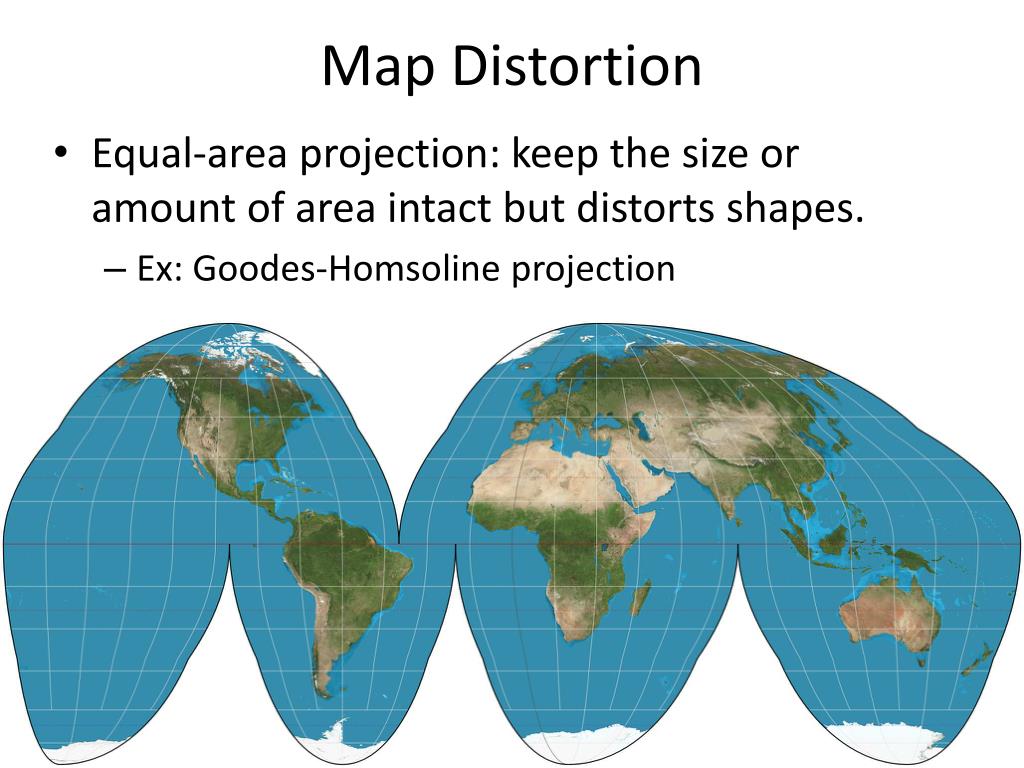
Area distortion refers to the change in the relative size of geographical features on a map compared to their actual size on the Earth. This distortion arises from the need to flatten the Earth’s curved surface onto a flat plane. Maps with significant area distortion can exaggerate the size of landmasses in certain regions while shrinking others.
For instance, the Mercator projection, widely used for navigation, dramatically exaggerates the size of landmasses at higher latitudes, particularly Greenland and Antarctica, making them appear significantly larger than their actual proportions. Conversely, areas closer to the equator are compressed, underrepresenting their true size.
Importance and Benefits:
While area distortion may seem like a drawback, it can be beneficial in specific applications. For example, maps focusing on navigation or emphasizing political boundaries may prioritize accurate representation of shapes and directions, even if it means sacrificing accurate area representation.
FAQs:
- Why does area distortion occur? Area distortion arises from the inherent challenge of transforming a curved surface (Earth) onto a flat plane (map).
- What are some examples of maps with significant area distortion? The Mercator projection, commonly used for navigation, exhibits significant area distortion, particularly at higher latitudes.
- Is area distortion always a negative aspect? Not necessarily. In some applications, such as navigation, prioritizing shape and direction over accurate area representation can be beneficial.
Tips:
- Be aware of the type of map projection used and its inherent distortions.
- When analyzing geographical data, consider the potential impact of area distortion on the results.
- Use multiple maps with different projections to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the geographical relationships.
2. Shape Distortion
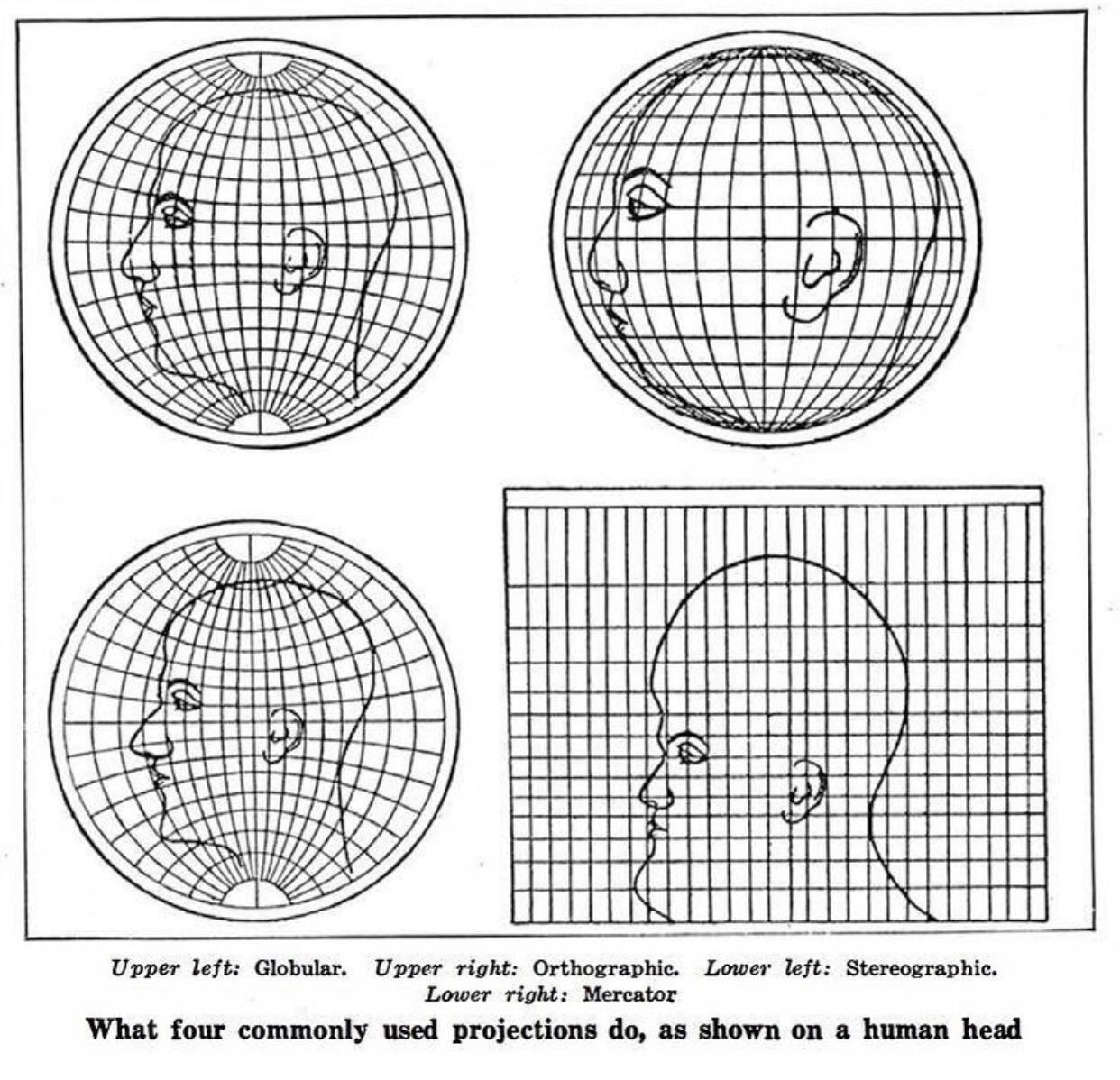
Shape distortion, also known as conformal distortion, refers to the alteration of the shapes of geographical features on a map compared to their actual shapes on the Earth. This distortion arises from the need to preserve angles, leading to stretching or shrinking of shapes along different directions.
For example, the Mercator projection, despite its area distortion, maintains accurate angles, making it ideal for navigation. However, this preservation of angles comes at the cost of distorting shapes, especially at higher latitudes. Greenland, for instance, appears elongated and distorted in the Mercator projection, while its actual shape is more compact.
Importance and Benefits:
Shape distortion, although altering the visual representation of shapes, can be beneficial in specific applications. For example, maps used for navigation prioritize accurate angles and directions, even if it means sacrificing accurate shape representation. This allows for precise plotting of courses and maintaining accurate bearings.
FAQs:
- What is the relationship between shape distortion and angle preservation? Shape distortion is a consequence of preserving angles on a map, which requires stretching or shrinking of shapes along different directions.
- How does shape distortion affect the representation of landmasses? Shape distortion can make landmasses appear elongated, compressed, or distorted, especially at higher latitudes.
- Is shape distortion always a negative aspect? Not necessarily. In applications like navigation, preserving angles outweighs the importance of accurate shape representation.
Tips:
- Recognize the inherent shape distortions of different map projections.
- Use multiple maps with different projections to compare and analyze the shapes of geographical features.
- Consider the specific application of the map and the importance of accurate shape representation.
3. Distance Distortion
Distance distortion refers to the difference between the distances measured on a map and the actual distances on the Earth. This distortion arises from the inherent challenge of representing a curved surface on a flat plane, leading to stretching or shrinking of distances in different directions.
For instance, the Mercator projection, while preserving angles and directions, significantly distorts distances at higher latitudes. A straight line drawn between two points on a Mercator projection map does not represent the shortest distance between those points on the Earth’s surface.
Importance and Benefits:
Distance distortion, while altering the representation of distances, can be beneficial in specific applications. For example, maps used for navigation may prioritize accurate representation of directions and shapes, even if it means sacrificing accurate distance representation. This allows for plotting courses and maintaining accurate bearings, even if the actual distance travelled is different.
FAQs:
- Why does distance distortion occur? Distance distortion arises from the need to flatten the Earth’s curved surface onto a flat plane, leading to stretching or shrinking of distances.
- How does distance distortion affect the representation of distances? Distance distortion can make distances appear longer or shorter than their actual values, especially at higher latitudes.
- Is distance distortion always a negative aspect? Not necessarily. In applications like navigation, prioritizing directions and shapes may outweigh the importance of accurate distance representation.
Tips:
- Be aware of the inherent distance distortions of different map projections.
- Use a scale bar or other distance measurement tools to interpret distances accurately.
- Consider the specific application of the map and the importance of accurate distance representation.
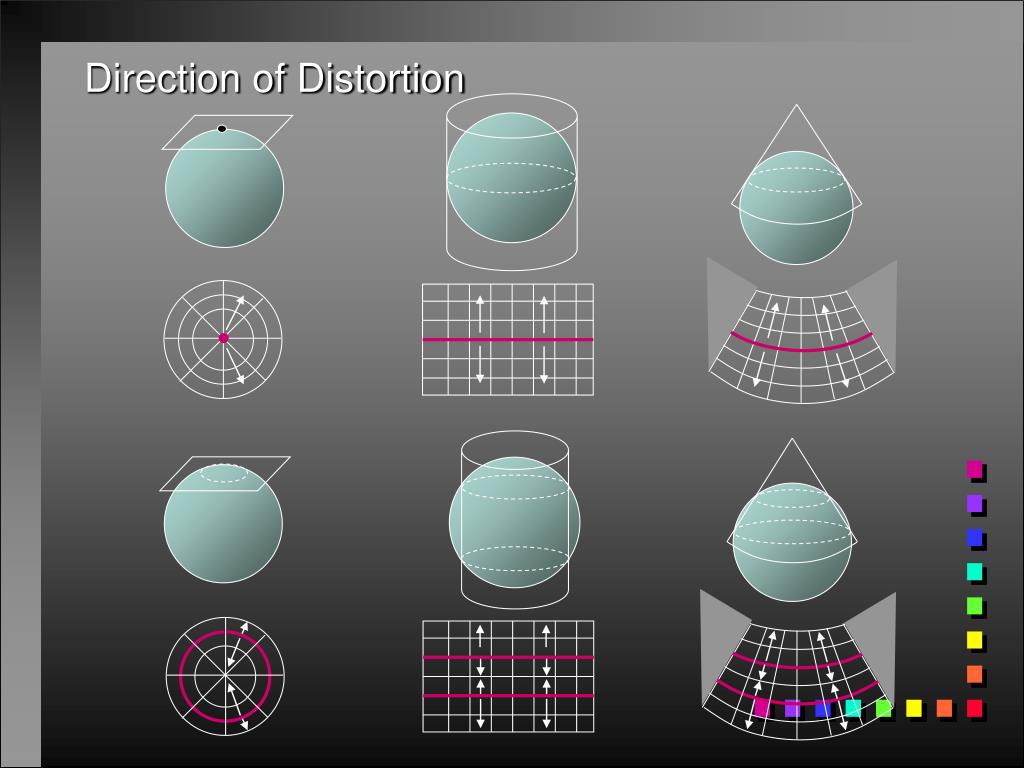
4. Direction Distortion
Direction distortion refers to the difference between the directions shown on a map and the actual directions on the Earth. This distortion arises from the need to represent a curved surface on a flat plane, leading to deviations in the angles between lines on the map compared to the angles on the Earth’s surface.
For example, the Mercator projection, while preserving angles at the point of tangency, distorts directions away from the point of tangency. This means that a straight line drawn on a Mercator projection map does not represent the true direction between two points on the Earth’s surface, especially at higher latitudes.
Importance and Benefits:
Direction distortion, while altering the representation of directions, can be beneficial in specific applications. For example, maps used for navigation may prioritize accurate representation of shapes and distances, even if it means sacrificing accurate direction representation. This allows for plotting courses and maintaining accurate bearings, even if the true direction travelled is different.
FAQs:
- Why does direction distortion occur? Direction distortion arises from the need to flatten the Earth’s curved surface onto a flat plane, leading to deviations in angles between lines on the map compared to the Earth’s surface.
- How does direction distortion affect the representation of directions? Direction distortion can make directions appear different from their actual values, especially at higher latitudes.
- Is direction distortion always a negative aspect? Not necessarily. In applications like navigation, prioritizing shapes and distances may outweigh the importance of accurate direction representation.
Tips:
- Be aware of the inherent direction distortions of different map projections.
- Use a compass or other direction-finding tools to interpret directions accurately.
- Consider the specific application of the map and the importance of accurate direction representation.
Conclusion:
Understanding the distortions inherent in map projections is crucial for interpreting maps accurately and appreciating the limitations of their representations. Each projection prioritizes certain aspects, sacrificing others to achieve a balance between accuracy and practicality. By recognizing these distortions, users can make informed decisions about the appropriate map projection for their specific needs and avoid misinterpretations.
Ultimately, maps are powerful tools for understanding our world, but their effectiveness depends on recognizing their inherent limitations. By acknowledging the distortions inherent in map projections, users can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of mapmaking and the trade-offs involved in presenting a comprehensive picture of our planet.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Imperfect Picture: Understanding Distortions in Map Projections. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!