The Geopolitical Landscape of Poland and Russia: A Historical and Contemporary Perspective
Related Articles: The Geopolitical Landscape of Poland and Russia: A Historical and Contemporary Perspective
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Geopolitical Landscape of Poland and Russia: A Historical and Contemporary Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Geopolitical Landscape of Poland and Russia: A Historical and Contemporary Perspective
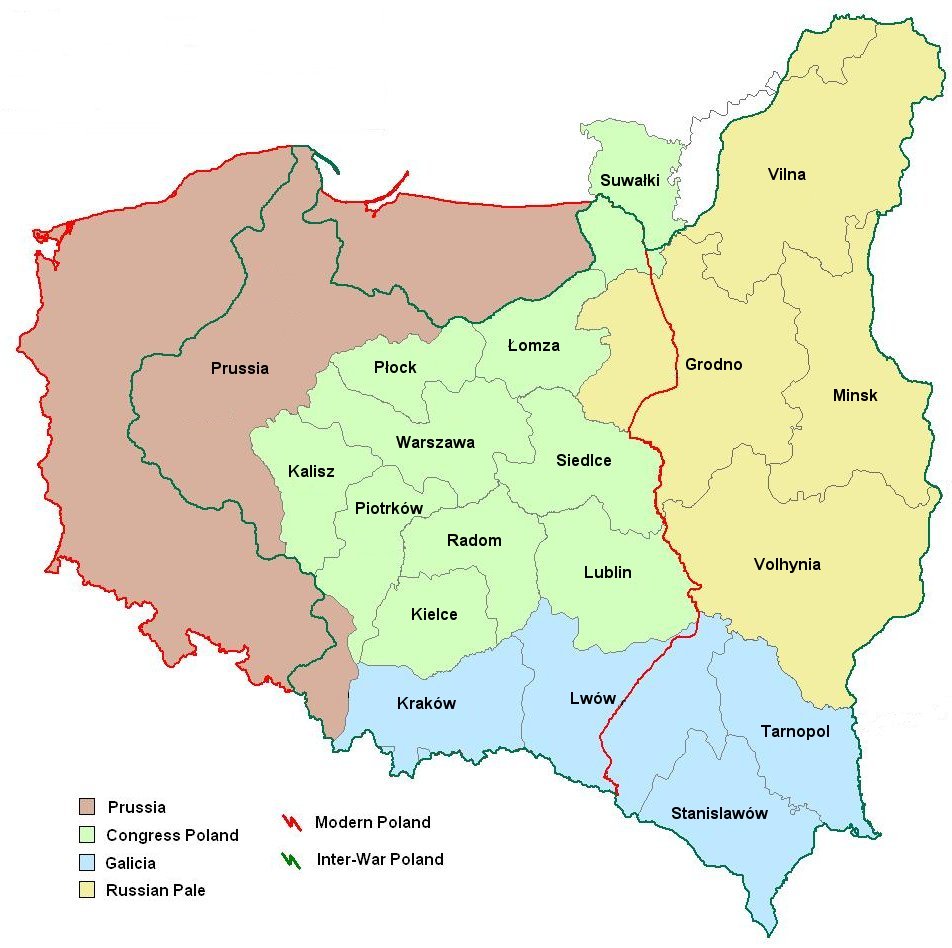
The relationship between Poland and Russia has been a complex and dynamic one, shaped by centuries of intertwined history, shared borders, and contrasting ideologies. This essay examines the geopolitical landscape of these two nations, exploring their historical interactions, current challenges, and future prospects.
Historical Intertwining: From Shared Origins to Bitter Conflict
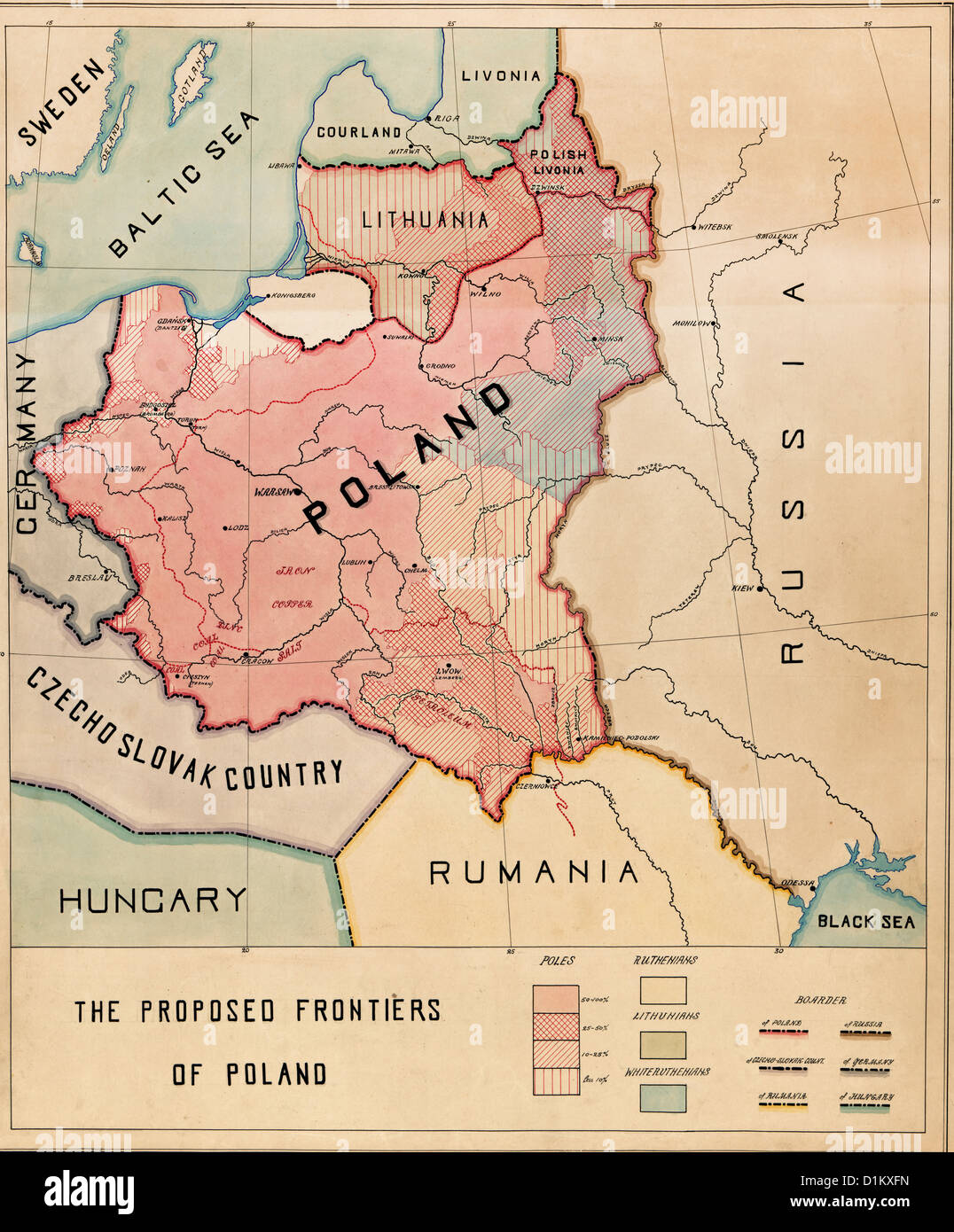
Poland and Russia share a long and intricate history, marked by periods of cooperation, conflict, and cultural exchange. Both nations emerged from the Slavic civilization, with their territories overlapping and shifting throughout the centuries. The Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, a powerful entity in Eastern Europe during the 16th and 17th centuries, encompassed vast swathes of modern-day Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus.
However, this shared heritage gave way to a complex and often antagonistic relationship. The rise of the Russian Empire in the 18th century led to the partitioning of Poland, a tragic event that erased the Polish state for over a century. This period was characterized by oppression, cultural suppression, and the struggle for national independence.
The 20th century witnessed further turmoil. Poland emerged as an independent nation after World War I, but its sovereignty was short-lived. The Nazi-Soviet Pact in 1939 led to the joint invasion and occupation of Poland, marking the beginning of World War II. After the war, Poland became a satellite state within the Soviet bloc, subject to Moscow’s political and economic influence.
The Post-Cold War Era: New Challenges and Opportunities
The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 brought about a new chapter in Polish-Russian relations. Poland embraced democracy and market reforms, seeking closer integration with the West through NATO and the European Union. This shift in alignment created a sense of unease in Moscow, as it perceived the expansion of Western influence as a threat to its own security interests.
The annexation of Crimea by Russia in 2014 and the ongoing conflict in eastern Ukraine further exacerbated tensions. Poland, alongside other NATO members, condemned Russia’s actions, viewing them as a violation of international law and a threat to European security. The conflict also highlighted the fragility of the post-Cold War order and the resurgence of geopolitical competition.
Economic Ties and Strategic Interests
Despite political tensions, Poland and Russia maintain significant economic ties. Poland is a major importer of Russian energy resources, particularly natural gas, while Russia sees Poland as a potential market for its manufactured goods. However, these economic relations are subject to geopolitical constraints, with sanctions imposed by the West on Russia impacting trade flows.
Strategically, both countries hold important positions in the European security architecture. Poland, a member of NATO, plays a crucial role in the alliance’s eastern flank, contributing to collective defense and deterring potential aggression. Russia, meanwhile, views Poland’s membership in NATO as a threat to its national security, leading to a cycle of mistrust and military posturing.
The Future: Navigating Challenges and Seeking Stability
The future of Polish-Russian relations remains uncertain. While dialogue and cooperation on specific issues, such as energy security and regional stability, are possible, overcoming deep-seated historical grievances and political mistrust will be a challenging endeavor.
Several factors will shape the trajectory of this relationship:
- The evolving security environment in Europe: The ongoing conflict in Ukraine, the rise of China, and the increasing assertiveness of Russia will continue to influence regional dynamics.
- The strength of the European Union and NATO: The unity and resolve of these institutions will be crucial in deterring Russian aggression and ensuring the security of Poland and other Eastern European states.
- Economic interdependence and energy security: The dependence of Poland on Russian energy resources creates vulnerabilities, while Russia’s need for European markets presents opportunities for economic cooperation.
- Historical reconciliation and cultural exchange: Fostering dialogue and understanding between the two societies, particularly among younger generations, is essential for building trust and promoting long-term stability.
FAQs
Q: What are the main reasons for the historical tensions between Poland and Russia?
A: The main reasons for historical tensions include the partitions of Poland in the 18th century, the suppression of Polish culture under Russian rule, and the Soviet occupation of Poland after World War II.
Q: How has the annexation of Crimea by Russia impacted Polish-Russian relations?
A: The annexation of Crimea was seen by Poland as a violation of international law and a threat to European security. It further exacerbated tensions and led to increased military cooperation between Poland and NATO.
Q: What are the main economic ties between Poland and Russia?
A: Poland is a major importer of Russian natural gas, while Russia sees Poland as a potential market for its manufactured goods. However, these economic relations are subject to geopolitical constraints.
Q: What are the prospects for future cooperation between Poland and Russia?
A: While dialogue and cooperation on specific issues are possible, overcoming deep-seated historical grievances and political mistrust will be a challenging endeavor. The future of Polish-Russian relations will depend on the evolving security environment in Europe, the strength of the European Union and NATO, and the level of economic interdependence between the two countries.
Tips
- Stay informed: Follow developments in Polish-Russian relations through reputable news sources and analytical reports.
- Engage in constructive dialogue: Encourage discussions and debates on the complexities of this relationship, promoting understanding and empathy.
- Support initiatives for cultural exchange: Encourage programs that foster cultural understanding and build bridges between the two societies.
Conclusion
The relationship between Poland and Russia is a complex and multifaceted one, shaped by historical legacies, shared borders, and diverging political interests. While the current environment is characterized by tensions and mistrust, the future of this relationship will depend on the ability of both countries to address their shared challenges and find common ground for cooperation. This will require a commitment to dialogue, mutual respect, and a shared vision for a stable and secure European order.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Geopolitical Landscape of Poland and Russia: A Historical and Contemporary Perspective. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!