Poland’s Position in Europe: A Geographic and Historical Perspective
Related Articles: Poland’s Position in Europe: A Geographic and Historical Perspective
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Poland’s Position in Europe: A Geographic and Historical Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Poland’s Position in Europe: A Geographic and Historical Perspective

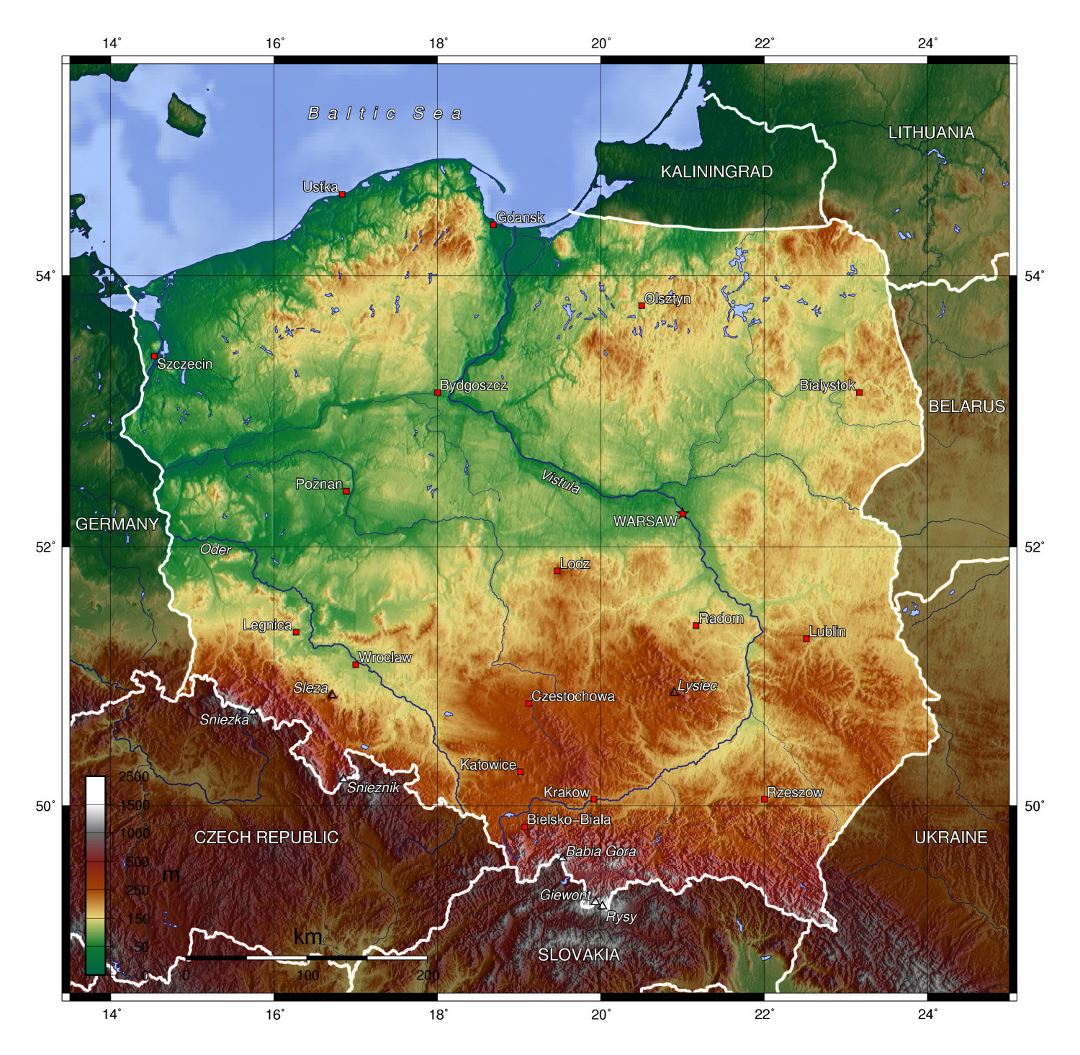
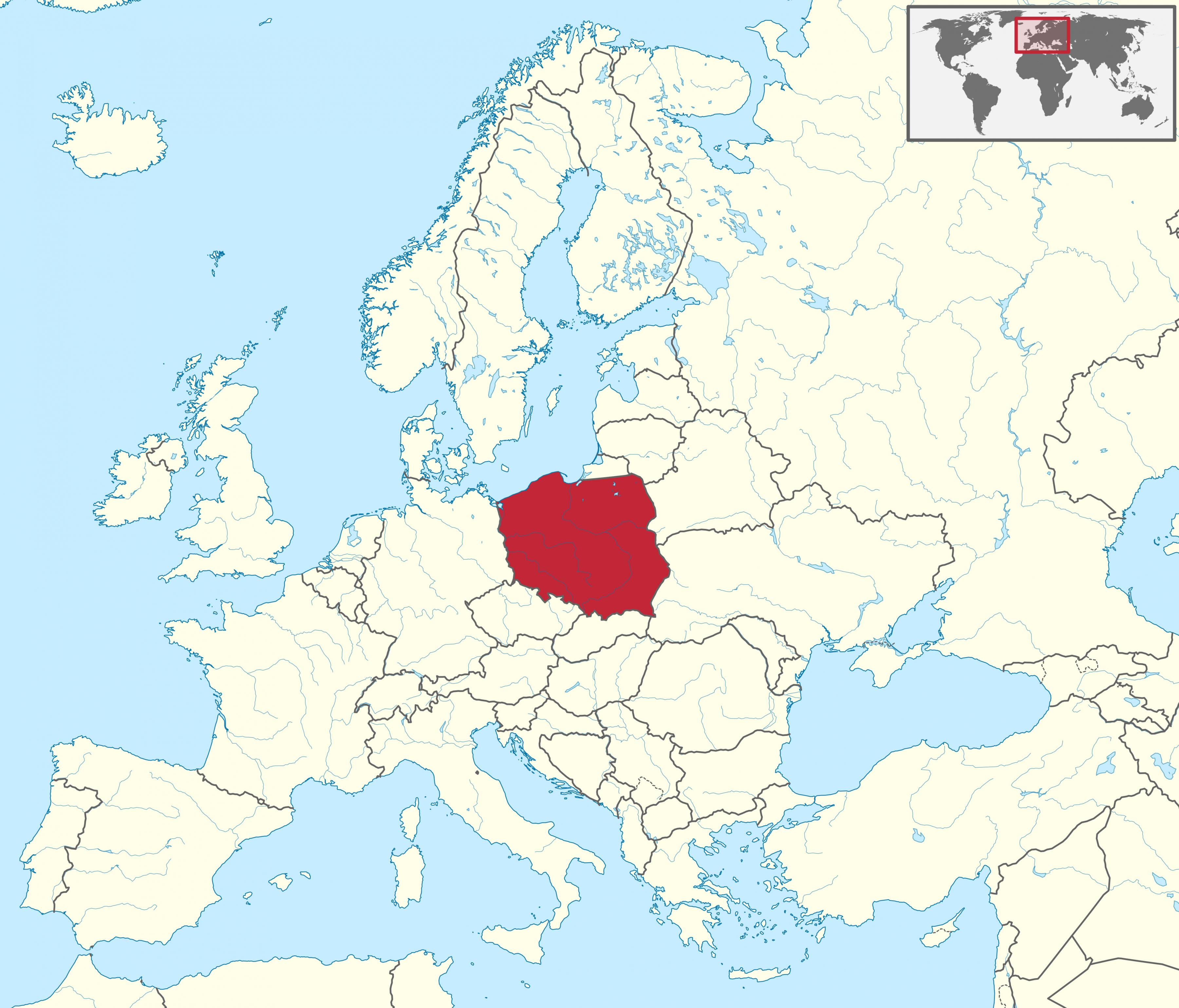
Poland, a nation of vibrant culture and rich history, occupies a pivotal position in the heart of Europe. Its geography, bordering seven countries, has shaped its destiny, influencing its political, economic, and cultural development. Understanding Poland’s location within the European map offers crucial insight into the nation’s past, present, and future.
A Strategic Location:
Poland’s geographic position at the crossroads of Central and Eastern Europe makes it a strategic location. It borders Germany, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Ukraine, Belarus, Lithuania, and Russia (Kaliningrad Oblast). This proximity to major European powers has historically made Poland a focal point of political and military conflicts, with its borders shifting over the centuries.
The Baltic Sea Connection:
Poland’s access to the Baltic Sea, through its coastline stretching over 500 kilometers, provides vital economic advantages. This connection facilitates trade with Scandinavian countries and the rest of Europe, contributing to Poland’s economic growth and international trade. The port of Gdynia, located on the Baltic coast, is a major hub for shipping and logistics.
The Vistula River:
The Vistula River, Poland’s longest river, flows through the heart of the country, serving as a vital transportation route and a source of water for agriculture and industry. The river basin encompasses a significant portion of Poland’s territory, fostering economic activity and connecting different regions.
The Carpathian Mountains:
The Carpathian Mountains, which run along Poland’s southern border, provide natural barriers and a diverse landscape. This region is known for its stunning scenery, rich biodiversity, and traditional culture. The mountains also play a crucial role in water management, regulating water flow and providing a source of hydropower.
Historical Significance:
Poland’s geographic location has profoundly influenced its history. Situated on the Eastern European Plain, a region historically subject to migrations and invasions, Poland has faced numerous challenges throughout its history. It has been invaded, divided, and occupied by various powers, shaping its national identity and resilience.
The Importance of Understanding Poland’s Geography:
Analyzing Poland’s position within Europe allows for a deeper understanding of its history, culture, and contemporary challenges. It reveals the nation’s strategic importance, its connection to the Baltic Sea, and the influence of its diverse landscape. Furthermore, it highlights the importance of understanding the historical context that has shaped Poland’s present and its future aspirations.
FAQs
Q: What are the major geographic features of Poland?
A: Poland is characterized by its diverse landscape, including the Baltic Sea coastline, the Vistula River, the Carpathian Mountains, and the Eastern European Plain.
Q: How does Poland’s geography influence its economy?
A: Poland’s access to the Baltic Sea facilitates trade and economic growth. The Vistula River provides a transportation route and water resources for agriculture and industry. The Carpathian Mountains offer opportunities for tourism and hydropower.
Q: What are some of the challenges Poland faces due to its geographic location?
A: Poland’s location has historically made it vulnerable to invasions and political instability. Its proximity to Russia and Ukraine also presents challenges in terms of security and geopolitical tensions.
Q: How has Poland’s geography shaped its culture?
A: Poland’s diverse landscape has influenced its cultural traditions and folklore. Its historical experiences have also shaped its national identity and resilience.
Tips
1. Study a map of Europe and focus on Poland’s location within the continent.
2. Research the historical events that have shaped Poland’s borders and its relationship with neighboring countries.
3. Explore the economic and cultural significance of Poland’s access to the Baltic Sea, the Vistula River, and the Carpathian Mountains.
4. Consider the geopolitical challenges that Poland faces due to its location in Central Europe.
Conclusion
Poland’s position within the European map is a testament to its historical significance, cultural richness, and economic potential. Understanding its strategic location, diverse landscape, and historical experiences provides crucial insight into the nation’s past, present, and future. As a key player in the European Union, Poland continues to contribute to the continent’s growth and development, demonstrating its enduring importance in the global landscape.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Poland’s Position in Europe: A Geographic and Historical Perspective. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!