Navigating the World: The Importance of Distance-Preserving Map Projections
Related Articles: Navigating the World: The Importance of Distance-Preserving Map Projections
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: The Importance of Distance-Preserving Map Projections. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: The Importance of Distance-Preserving Map Projections

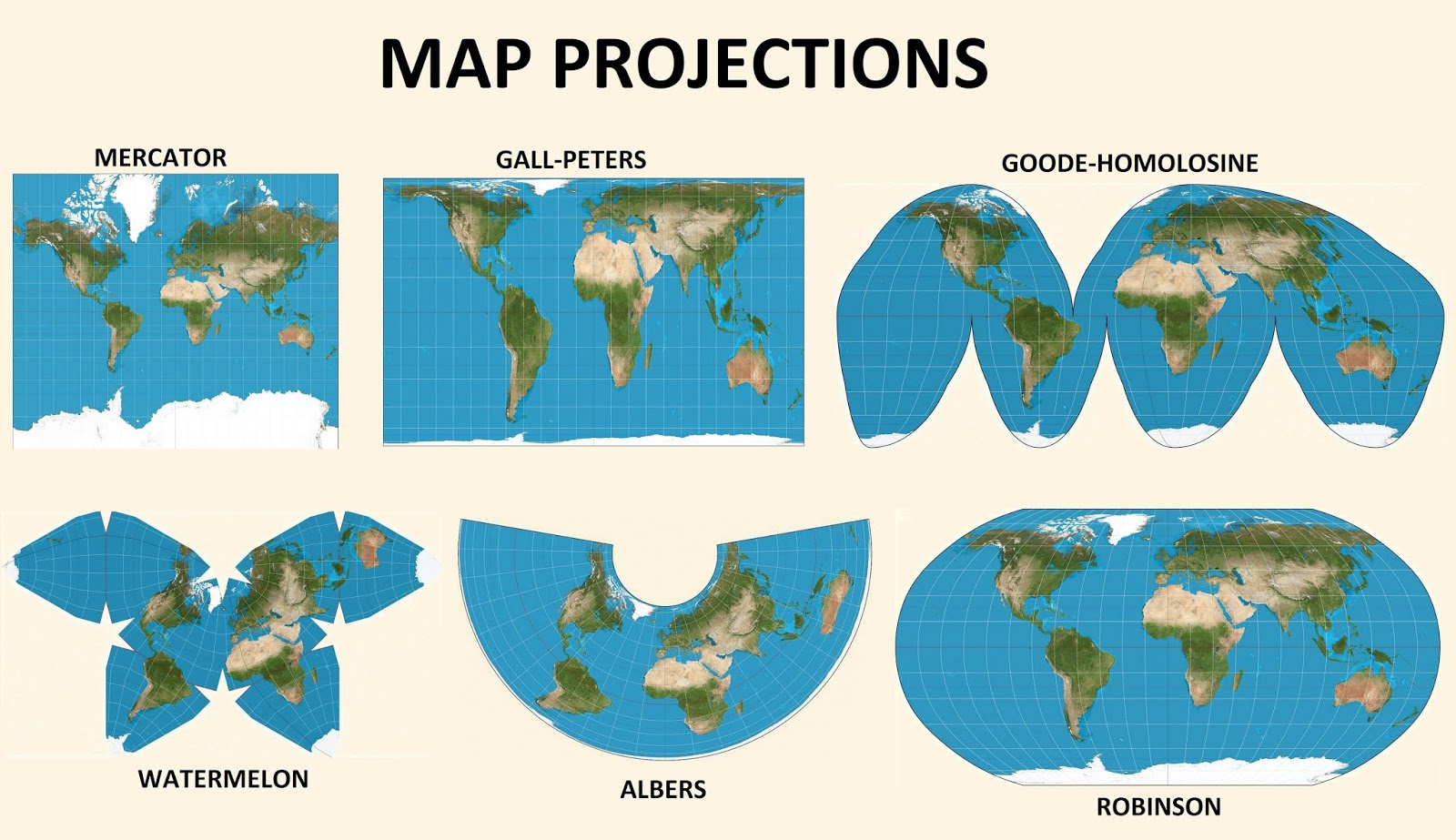
The world, a sphere, is inherently difficult to represent accurately on a flat surface. Map projections, the mathematical transformations that translate spherical coordinates onto a plane, inevitably introduce distortions. These distortions can affect various aspects of a map, including shapes, areas, distances, and directions. While some projections prioritize preserving specific features like shape (conformal projections) or area (equal-area projections), others focus on maintaining accurate distances. These projections, known as equidistant projections, are crucial for applications where precise distance measurement is paramount.
Understanding Equidistant Projections
Equidistant projections are designed to accurately represent distances from a specific point on the map, often referred to as the center of projection. This point, typically a city or a geographical feature, serves as the reference point for all distance calculations. Lines radiating outwards from this center represent true distances, while lines parallel to the center represent distorted distances.
Types of Equidistant Projections
Several equidistant projections exist, each with its unique characteristics and applications:
-
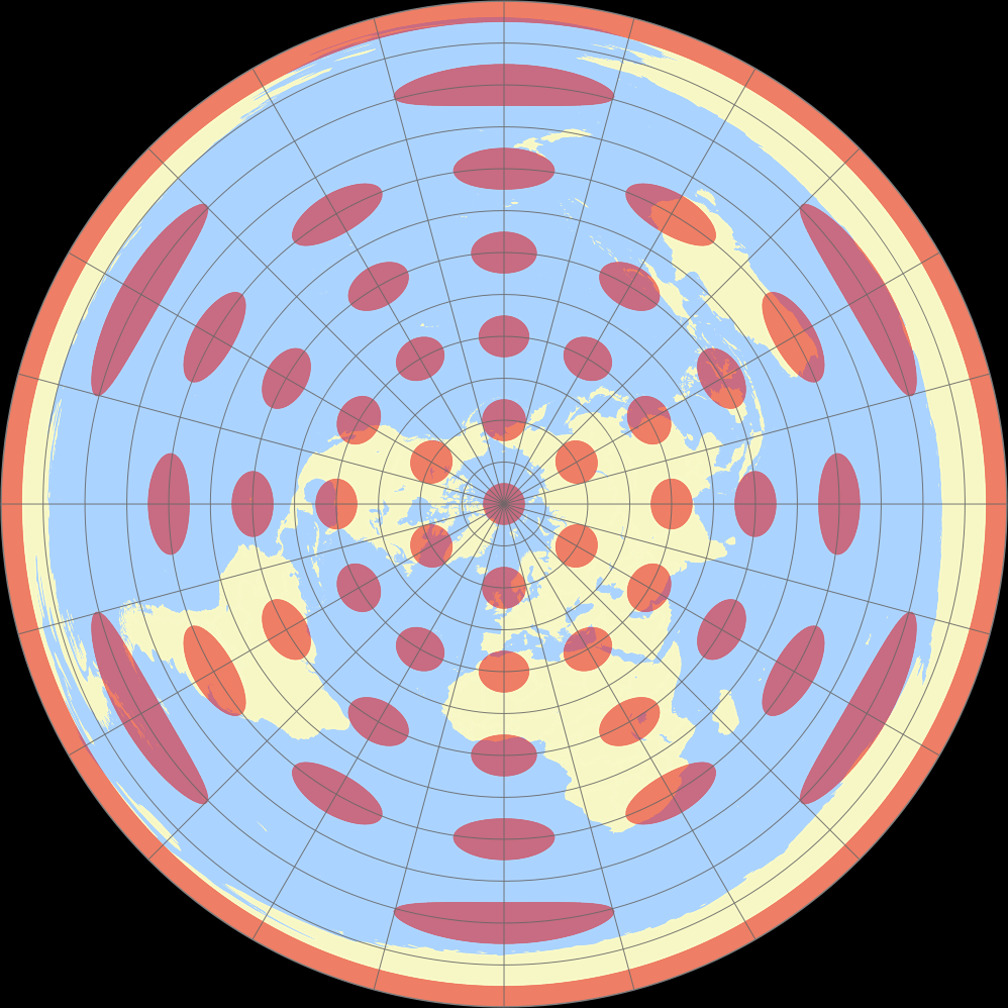
Azimuthal Equidistant Projection: This projection preserves distances from a central point in all directions. It is often used for maps centered on a specific location, such as a city or a country, providing accurate distance measurements from that point. The projection distorts shapes and areas as you move away from the center, with increasing distortion towards the edges.
-
Equidistant Conic Projection: This projection preserves distances along lines of longitude and preserves true directions from the center point. It is frequently used for maps of regions that extend longitudinally, like continents or countries with significant north-south extent. The projection introduces some distortion in areas away from the central meridian, but it is generally considered a good compromise for representing large areas with accurate distances.
-
Equidistant Cylindrical Projection: This projection preserves distances along the equator, effectively representing a rectangular grid. It is often used for world maps, where it preserves distances along the equator but distorts areas and shapes at higher latitudes. The distortion increases significantly towards the poles, making it less suitable for maps focused on polar regions.
Applications of Equidistant Projections
The importance of equidistant projections lies in their ability to accurately represent distances, making them indispensable for various applications:
-
Navigation: Equidistant projections are crucial for navigation, particularly in air and sea travel. They allow pilots and mariners to calculate accurate distances between locations, facilitating efficient route planning and navigation.
-
Cartography: Equidistant projections are commonly used in cartographic applications where accurate distance measurement is essential, such as in mapping for resource management, transportation planning, and environmental monitoring.
-
Military Applications: Equidistant projections are vital in military operations, enabling accurate targeting and distance estimations for artillery and missile strikes.
-
Emergency Response: In emergency situations, accurate distance measurements are crucial for coordinating rescue efforts and delivering aid effectively. Equidistant projections play a vital role in disaster response and emergency management.
-
Geographical Research: Equidistant projections are valuable tools for researchers studying geographical phenomena, allowing them to analyze spatial patterns and relationships based on accurate distance measurements.
Limitations of Equidistant Projections
While equidistant projections excel at representing distances, they come with certain limitations:
-
Distortion of Shapes and Areas: Equidistant projections, like most other map projections, introduce distortions in shapes and areas. The degree of distortion increases as you move away from the center of projection.
-
Limited Applicability: Equidistant projections are best suited for maps centered on a specific location. Their accuracy diminishes significantly when representing areas far from the center point.
-
Complexity: Some equidistant projections, particularly those designed for specific purposes, can be complex to understand and use.
Choosing the Right Projection
The choice of an appropriate equidistant projection depends on the specific application and the area being represented. Factors to consider include:
-
The Area of Interest: The size and location of the region being mapped are crucial.
-
The Purpose of the Map: The intended use of the map will dictate the required level of accuracy in distance measurements.
-
The Level of Distortion Acceptable: The projection should be chosen based on the acceptable level of distortion in shapes and areas.
FAQs about Equidistant Projections
Q: What is the most accurate map projection?
A: There is no single "most accurate" map projection. Each projection introduces distortions in different ways. Equidistant projections are accurate for distances from the center point but distort shapes and areas. The best projection depends on the specific application and the desired level of accuracy.
Q: Can equidistant projections be used for global maps?
A: Equidistant projections can be used for global maps, but they will introduce significant distortions in areas far from the center point. Other projections, like the Winkel Tripel or Robinson projection, are better suited for representing the entire globe with minimal distortion.
Q: Are equidistant projections always better than other projections?
A: Equidistant projections are not always the best choice. If accurate representation of shapes or areas is more important than accurate distance measurement, other projections might be more appropriate.
Tips for Using Equidistant Projections
-
Understand the limitations of the projection: Be aware of the distortions introduced by the chosen projection, particularly in areas away from the center point.
-
Use appropriate tools for distance measurement: Use specialized software or tools designed for accurate distance measurements on maps.
-
Consult with experts: If you are unsure about the best projection for your needs, consult with a cartographer or other expert in map projections.
Conclusion
Equidistant projections play a vital role in various fields, enabling accurate distance measurement for navigation, cartography, military operations, and emergency response. While they introduce distortions in shapes and areas, their ability to preserve distances from a specific point makes them indispensable for applications where precise distance measurement is paramount. By understanding the characteristics and limitations of different equidistant projections, users can select the most appropriate projection for their specific needs, ensuring accurate distance measurements and effective map interpretation.


![]()

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: The Importance of Distance-Preserving Map Projections. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!