Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projection Styles
Related Articles: Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projection Styles
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projection Styles. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projection Styles
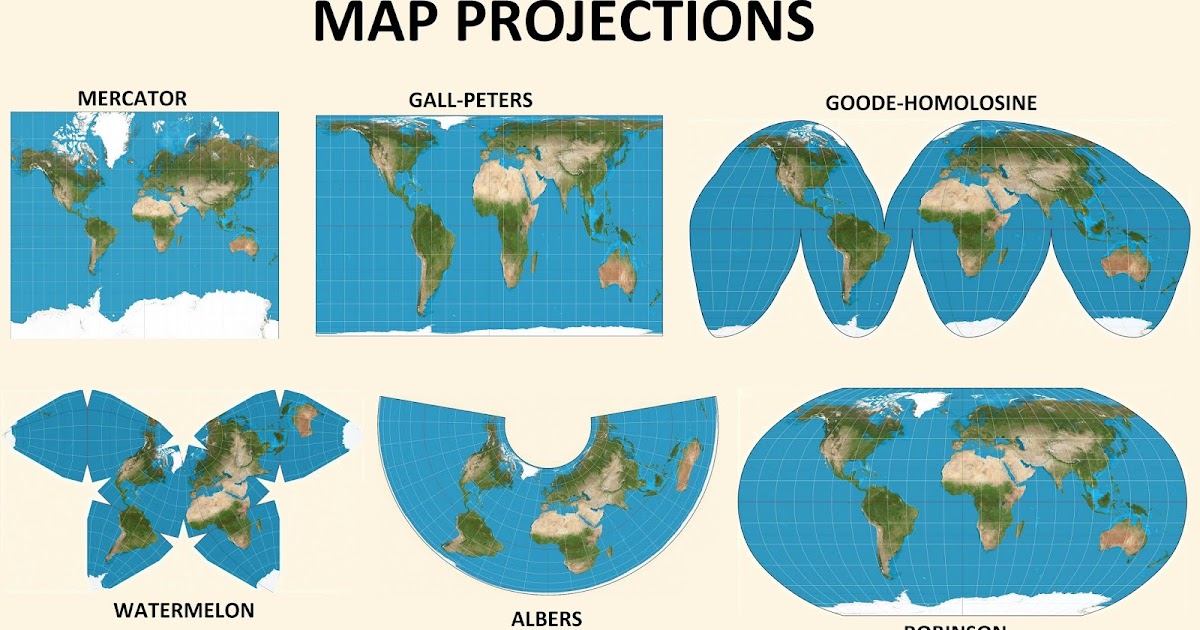
The Earth, a sphere, presents a unique challenge for cartographers: how to accurately represent its three-dimensional surface on a two-dimensional map. This challenge has led to the development of various map projection styles, each offering a specific advantage depending on the intended use. Understanding these projections is crucial for interpreting maps, as they influence the representation of shapes, areas, and distances.
The Essence of Map Projections
Map projections are mathematical transformations that translate the Earth’s curved surface onto a flat plane. This process inevitably introduces distortions, as it is impossible to perfectly preserve all geometric properties simultaneously. Different projections prioritize different aspects, resulting in varying levels of accuracy for shape, area, distance, and direction.
Classifying Map Projections
Map projections can be categorized based on their geometric properties and the resulting distortions they introduce:
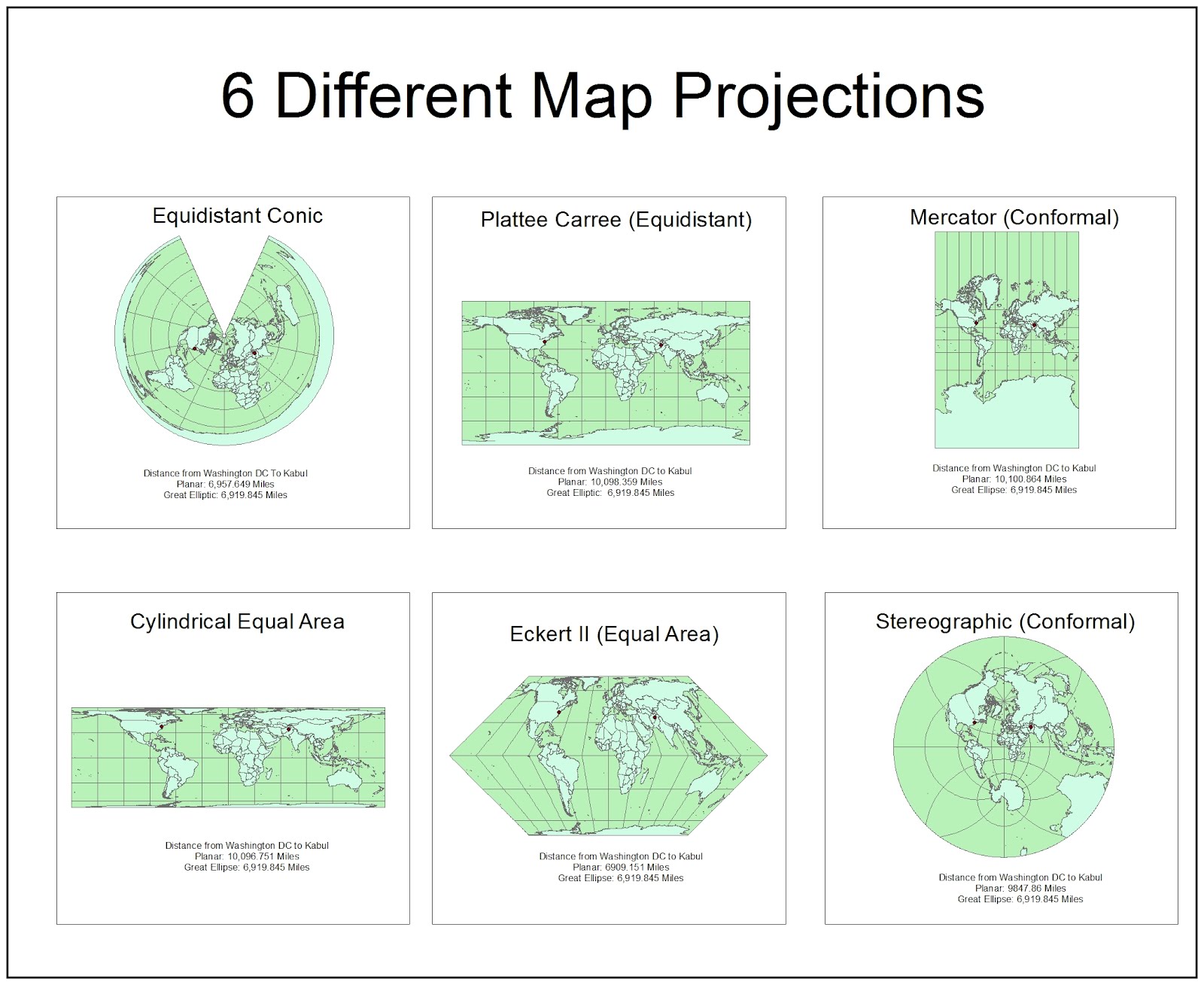
1. Conformal Projections: These projections preserve angles and shapes locally, meaning small shapes on the map are accurately represented. However, they often distort areas, particularly towards the poles. Examples include:
-
Mercator Projection: A cylindrical projection commonly used for navigation, as it preserves angles and shows true directions. It significantly distorts areas, making continents near the poles appear larger than they actually are.
-
Stereographic Projection: A conformal projection that maps the Earth onto a plane tangent to the sphere at a specific point. It preserves angles and shapes but distorts areas, particularly near the point of tangency.
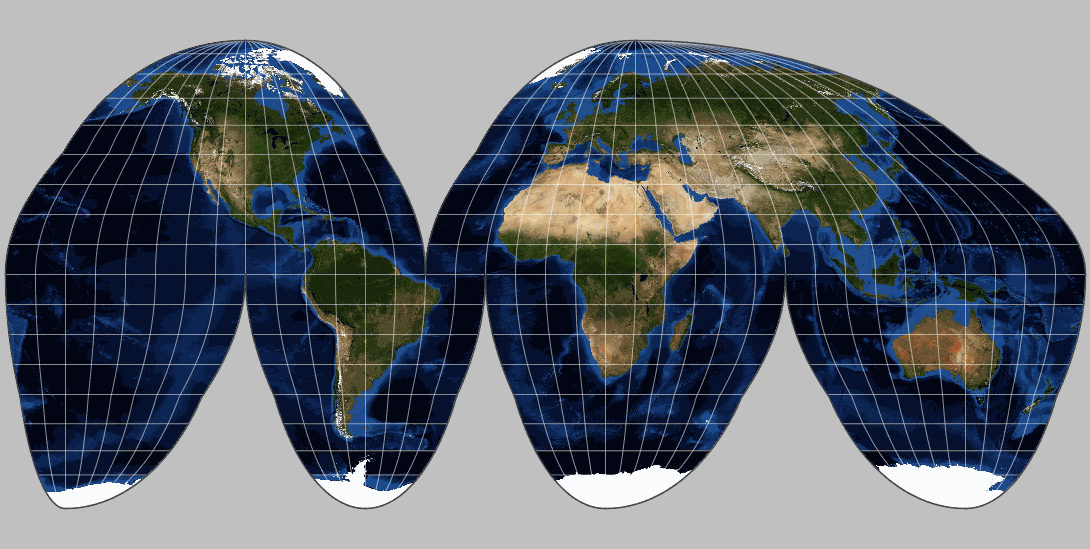
2. Equal-Area Projections: These projections prioritize accurate representation of area. They maintain the relative sizes of continents and countries, even though they distort shapes and angles. Examples include:
-
Albers Equal-Area Conic Projection: A conic projection used for mapping large regions, particularly in the United States. It accurately represents areas but distorts shapes and distances, particularly near the edges of the map.
-
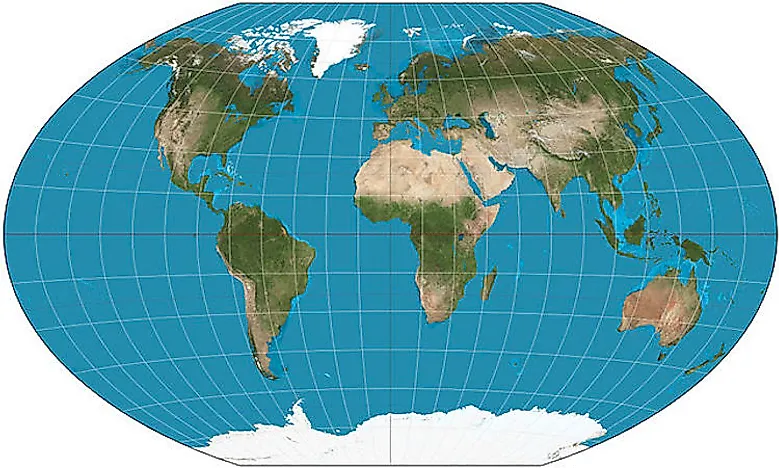
Mollweide Projection: An equal-area projection that portrays the Earth as an ellipse. It accurately represents areas but distorts shapes and distances, particularly near the poles.
3. Equidistant Projections: These projections preserve distances from a central point. They are useful for mapping specific locations and their surrounding areas accurately. Examples include:
-
Azimuthal Equidistant Projection: A planar projection that preserves distances from a central point. It distorts shapes and areas, particularly away from the central point.
-
Gnomonic Projection: A planar projection that maps the Earth onto a plane tangent to the sphere at a specific point. It preserves distances from the central point but distorts shapes and areas.
4. Compromise Projections: These projections seek to minimize distortions across various properties, offering a balance between accuracy and visual appeal. Examples include:
-
Robinson Projection: A compromise projection that attempts to balance area, shape, and distance distortions. It is widely used for world maps.
-
Winkel Tripel Projection: Another compromise projection that minimizes area, shape, and distance distortions. It is often used for world maps and atlases.
The Importance of Understanding Map Projections
Understanding map projections is crucial for accurately interpreting and using maps. For example:
-
Navigation: Navigational maps often use conformal projections, such as the Mercator projection, to ensure accurate directions.
-
Geographic Analysis: Equal-area projections are essential for comparing the sizes of different regions and understanding population density or resource distribution.
-
Cartographic Design: Choosing the appropriate projection is vital for creating visually appealing and informative maps that accurately represent the data being displayed.
FAQs about Map Projections
Q: What is the most accurate map projection?
A: There is no single "most accurate" projection, as each projection introduces distortions in different ways. The best projection for a particular application depends on the intended use and the geographic area being mapped.
Q: How do I choose the right map projection?
A: Consider the purpose of the map, the geographic area being mapped, and the specific properties you need to preserve (e.g., shape, area, distance).
Q: Can I use a single map projection for all purposes?
A: No, different projections are suitable for different purposes. Using an inappropriate projection can lead to misinterpretations and inaccurate conclusions.
Tips for Using Map Projections
-
Consult a cartographer or GIS specialist: They can help you choose the most appropriate projection for your specific needs.
-
Pay attention to the projection used: Always check the map legend to understand the projection and its potential distortions.
-
Use multiple projections: Compare different projections to gain a comprehensive understanding of the data and its spatial relationships.
Conclusion
Map projections are essential tools for representing the Earth’s surface on a flat plane. Understanding their strengths and limitations is crucial for accurate interpretation and analysis of geographic data. By carefully considering the intended use and the specific properties to be preserved, cartographers can select the most appropriate projection to create informative and visually appealing maps.

![50 Map Projections Types: A Visual Reference Guide [BIG LIST] - GIS Geography](https://gisgeography.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/fuller.png)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Projection Styles. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!