Navigating the Terrain: Exploring the Best Map Projections for the USA
Related Articles: Navigating the Terrain: Exploring the Best Map Projections for the USA
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Terrain: Exploring the Best Map Projections for the USA. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Terrain: Exploring the Best Map Projections for the USA

The United States, a vast and diverse nation, presents unique challenges for cartographers seeking to accurately represent its geography on a flat surface. The Earth, being a sphere, cannot be perfectly flattened without introducing distortions. Map projections, mathematical formulas that translate the Earth’s curved surface onto a plane, are crucial for navigating these distortions and achieving desired outcomes. Understanding the strengths and limitations of various projections is essential for selecting the most suitable one for specific applications.
A Deep Dive into Projections:
Map projections are classified based on their properties and the type of distortions they introduce. Common categories include:
- Conformal Projections: Preserve angles and shapes locally, making them suitable for navigation and applications requiring accurate representation of relative sizes. Examples include the Mercator and Lambert Conformal Conic projections.
- Equal-Area Projections: Preserve area ratios, ensuring that the relative sizes of features on the map accurately reflect their real-world counterparts. Examples include the Albers Equal-Area Conic and the Mollweide projection.
- Equidistant Projections: Preserve distances from a central point, useful for depicting distances from a specific location. Examples include the Azimuthal Equidistant and the Gnomonic projection.
The Quest for the Ideal Projection:
Choosing the best map projection for the USA depends on the intended purpose and the specific characteristics that need to be emphasized. While no single projection can perfectly represent all aspects of the country, several options excel in specific applications.
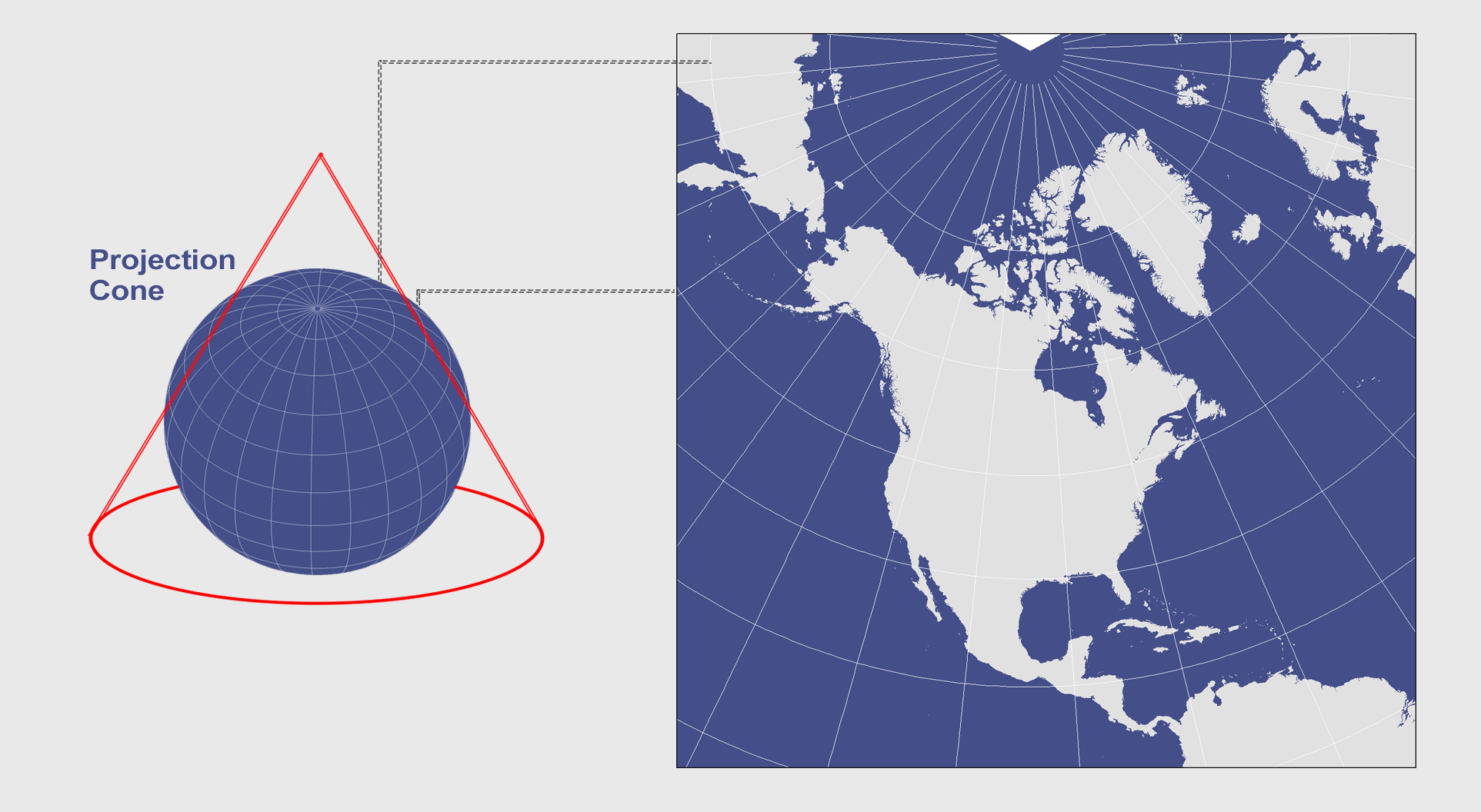
1. The Lambert Conformal Conic Projection:
Widely used for mapping the contiguous United States, the Lambert Conformal Conic projection offers a balance between shape and area preservation. Its conic shape minimizes distortion along the central meridian, making it suitable for representing the country’s longitudinal extent. The projection is widely used for official maps, including those published by the US Geological Survey (USGS).
Benefits:
- Preserves shapes and angles, making it ideal for navigation and mapping infrastructure.
- Maintains area accuracy relatively well, ensuring the relative sizes of states and regions are represented correctly.
- Widely adopted for official maps, ensuring consistency and familiarity.
Limitations:
- Introduces distortions at the edges, particularly in the eastern and western regions.
- Can exaggerate the distances between locations, especially towards the north and south.
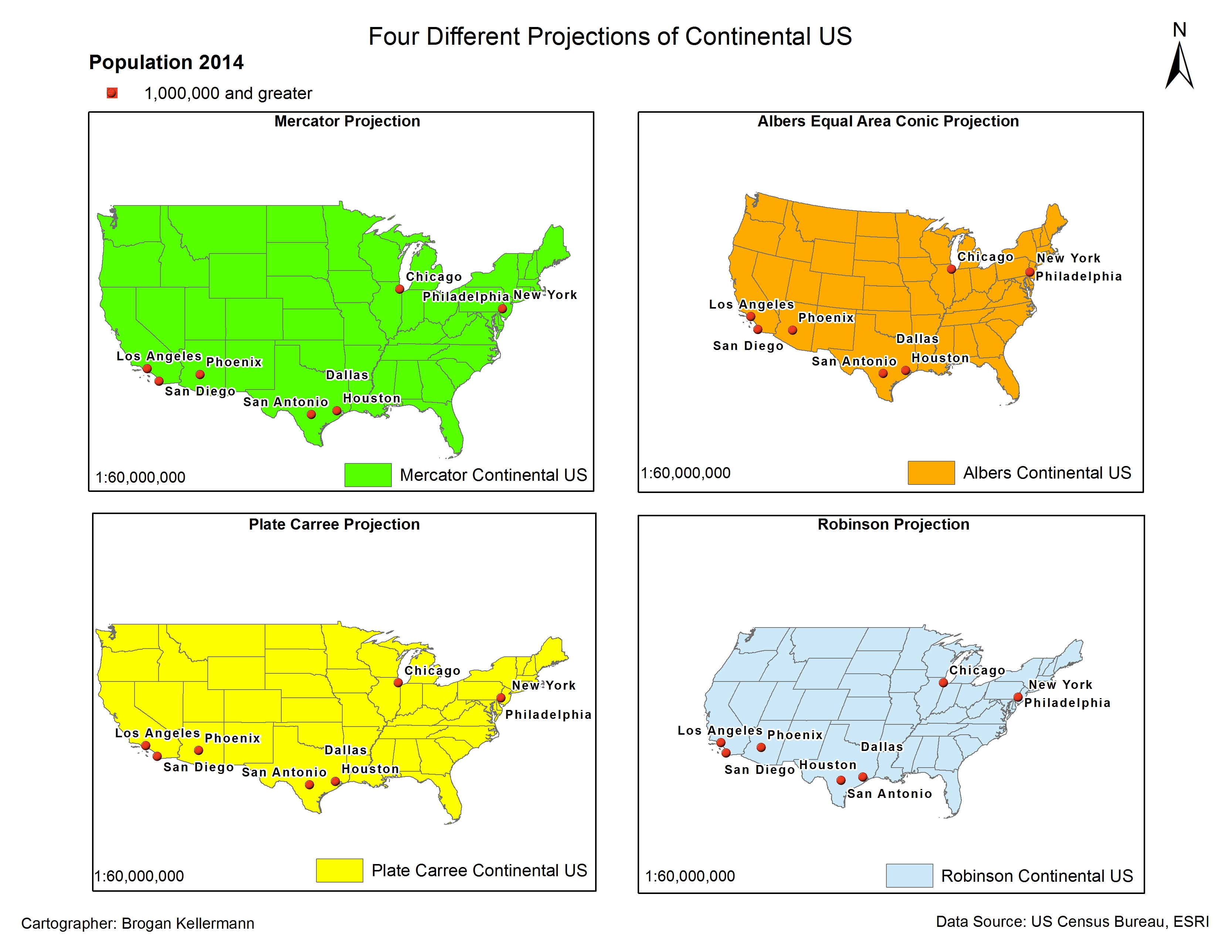
2. The Albers Equal-Area Conic Projection:
The Albers Equal-Area Conic projection prioritizes area preservation, ensuring that the relative sizes of geographic features are accurately represented. This projection is often used for thematic mapping, such as population density or resource distribution, where accurate representation of area is crucial.
Benefits:
- Preserves area ratios, providing an accurate representation of the relative sizes of states and regions.
- Minimizes distortion in area measurements, making it suitable for thematic mapping and statistical analysis.
- Widely used for representing the contiguous United States in geographic information systems (GIS).
Limitations:
- Introduces shape distortions, especially towards the edges of the map.
- May not be ideal for navigation or applications requiring accurate representation of angles.
3. The Mercator Projection:
Despite its widespread use, the Mercator projection is not ideal for mapping the entire USA due to its significant distortion towards the poles. However, its ability to preserve shapes and angles locally makes it valuable for navigation and nautical charts.
Benefits:
- Preserves shapes and angles, making it suitable for navigation and seafaring.
- Provides a consistent scale, ensuring that distances are represented accurately along lines of longitude.
Limitations:
- Severely distorts areas, particularly towards the poles, making it unsuitable for representing the entire USA.
- Exaggerates the size of landmasses at higher latitudes, leading to a distorted perception of the world.
4. The Robinson Projection:
The Robinson projection is a compromise projection that aims to minimize distortions in both area and shape. While not perfect, it offers a more balanced representation of the world than the Mercator projection.
Benefits:
- Provides a visually appealing and balanced representation of the Earth.
- Minimizes distortions in both area and shape, offering a more accurate portrayal of the globe.
Limitations:
- Does not preserve area or shape perfectly, leading to some distortions.
- May not be suitable for specific applications requiring accurate area or shape representation.
Beyond the Basics: Choosing the Right Projection for Your Needs
Selecting the best map projection for the USA involves considering the specific application and the desired characteristics. For instance:
- Navigation and Infrastructure Mapping: Conformal projections like the Lambert Conformal Conic excel in preserving shapes and angles, ensuring accurate representation of roads, waterways, and other infrastructure.
- Thematic Mapping: Equal-area projections like the Albers Equal-Area Conic are ideal for representing data related to population density, resource distribution, or other phenomena where area accuracy is paramount.
- Global Context: Projections like the Robinson or Winkel Tripel offer a balanced representation of the Earth, suitable for maps that emphasize global context.
FAQs:
Q: What is the most accurate map projection for the USA?
A: No single projection is perfectly accurate. Each projection introduces distortions, and the best choice depends on the specific application and the characteristics that need to be prioritized.
Q: Why does the Mercator projection distort the size of Greenland?
A: The Mercator projection exaggerates areas at higher latitudes, making Greenland appear larger than it actually is. This is because the projection preserves angles and shapes locally, but it stretches distances at higher latitudes.
Q: What are some tips for choosing the right map projection?
A:
- Define your purpose: Consider what you want to achieve with the map.
- Understand the distortions: Each projection introduces distortions, so weigh the trade-offs between area, shape, and distance preservation.
- Consult experts: If you are unsure, consult cartographers or GIS professionals for guidance.
Conclusion:
The choice of map projection for the USA is not a one-size-fits-all solution. By understanding the strengths and limitations of various projections, users can select the most suitable option for their specific needs. Whether for navigation, thematic mapping, or global representation, careful consideration of projection properties ensures accurate and informative map representations.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Terrain: Exploring the Best Map Projections for the USA. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!