Navigating the Globe: Understanding Map Projections in ArcGIS Online
Related Articles: Navigating the Globe: Understanding Map Projections in ArcGIS Online
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Globe: Understanding Map Projections in ArcGIS Online. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Globe: Understanding Map Projections in ArcGIS Online
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Globe: Understanding Map Projections in ArcGIS Online
- 3.1 The Essence of Map Projections
- 3.2 Types of Map Projections
- 3.3 Choosing the Right Projection in ArcGIS Online
- 3.4 The Importance of Understanding Projections
- 3.5 Working with Projections in ArcGIS Online
- 3.6 FAQs on Map Projections in ArcGIS Online
- 3.7 Tips for Using Map Projections in ArcGIS Online
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Globe: Understanding Map Projections in ArcGIS Online
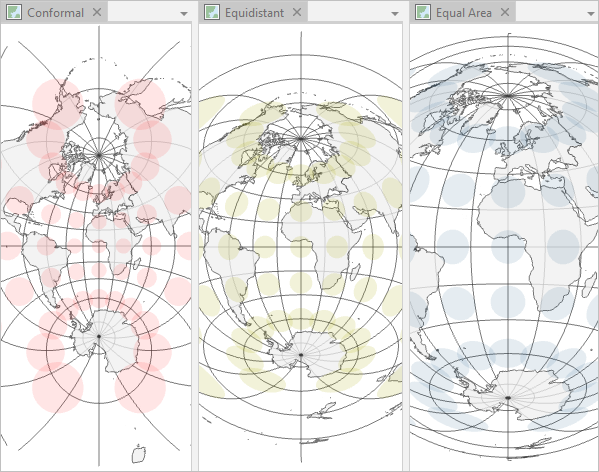
The Earth, a sphere, presents a unique challenge when attempting to represent it on a flat surface. This challenge lies at the heart of map projections, a fundamental concept in cartography that involves transforming the Earth’s three-dimensional surface onto a two-dimensional plane. ArcGIS Online, a powerful platform for creating and sharing maps, offers a wide range of map projections, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these projections is crucial for accurately representing geographic data and ensuring that maps communicate information effectively.
The Essence of Map Projections
The very act of creating a map necessitates a projection. The Earth’s curved surface cannot be flattened without distortion. Map projections address this by using mathematical formulas to project the Earth’s spherical surface onto a plane. This process inevitably introduces distortion, affecting properties like distance, area, shape, and direction.
Types of Map Projections
Numerous map projections exist, each designed to minimize distortion in specific aspects of the Earth’s surface. Common projection types include:
- Conic Projections: These projections are created by wrapping a cone around the globe. They are particularly useful for representing regions that extend longitudinally, such as the United States. Examples include the Albers Equal Area Conic and the Lambert Conformal Conic projections.
- Cylindrical Projections: Imagine wrapping a cylinder around the globe – this is the basis for cylindrical projections. They are well-suited for representing regions that span latitudinally, like the equator. The Mercator projection, commonly used for nautical charts, falls under this category.
- Azimuthal Projections: These projections are created by projecting the Earth’s surface onto a plane tangent to the globe at a specific point. They are often used for representing polar regions and are known for their ability to preserve direction from the center point. The Stereographic projection is an example.
Choosing the Right Projection in ArcGIS Online
ArcGIS Online provides a comprehensive library of map projections, empowering users to select the most appropriate projection for their specific needs. Several factors influence this decision:
- Geographic Area: The geographic extent of the data significantly impacts the choice of projection. For example, a conic projection is suitable for representing a large region of the United States, while an azimuthal projection might be better for mapping Greenland.
- Purpose of the Map: The intended use of the map dictates the projection. A map used for navigation might prioritize direction preservation, while a map showcasing population density would benefit from an equal-area projection.
- Level of Detail: The scale and detail of the data influence projection selection. Fine-scale maps often require projections that minimize distortion in specific areas.
The Importance of Understanding Projections
Choosing the right map projection is crucial for several reasons:
- Accurate Representation: A well-chosen projection ensures that geographic data is represented accurately, minimizing distortion and preserving the intended spatial relationships.
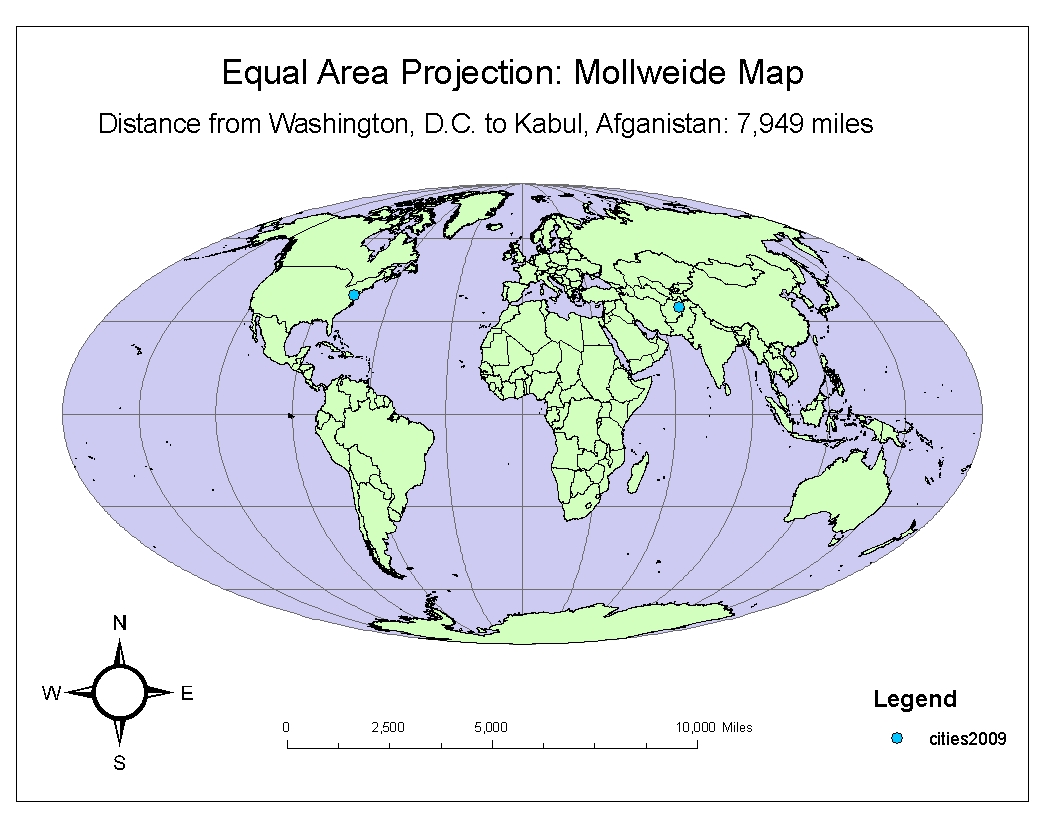
- Effective Communication: Maps communicate information effectively when the chosen projection reflects the intended purpose. For instance, a map showing distances between cities should employ a projection that preserves distances accurately.
- Avoid Misinterpretation: Misinterpreting distorted information on a map can lead to incorrect conclusions. Understanding the inherent distortion of a projection helps users interpret data correctly.
Working with Projections in ArcGIS Online
ArcGIS Online provides various tools to manage and work with map projections:
- Projecting Data: ArcGIS Online allows users to project data from one coordinate system to another. This process involves transforming the data’s coordinates to match the target projection, ensuring consistency across different datasets.
- Defining Coordinate Systems: ArcGIS Online enables users to define custom coordinate systems, providing flexibility in representing geographic data according to specific requirements.
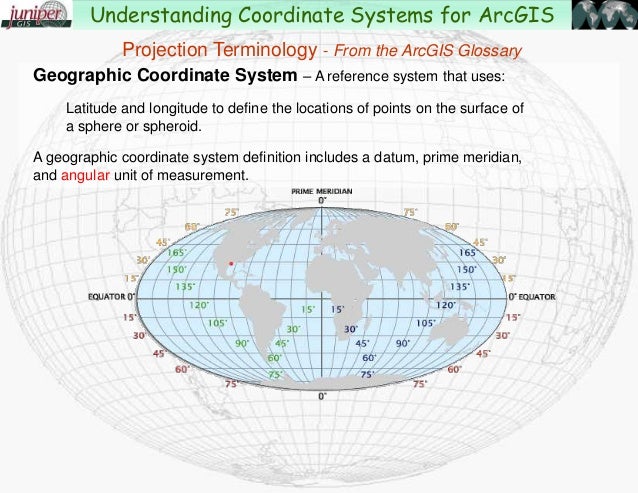
- Using Predefined Projections: The platform offers a vast library of predefined projections, including commonly used ones like UTM, Web Mercator, and Geographic (latitude/longitude).
FAQs on Map Projections in ArcGIS Online
1. Why is it important to project data in ArcGIS Online?
Projecting data ensures that all layers in a map share the same coordinate system, preventing spatial misalignment and ensuring accurate representation of geographic relationships.
2. How do I know which projection to choose for my map?
Consider the geographic extent of your data, the purpose of the map, and the level of detail required. Refer to ArcGIS Online’s documentation and resources for guidance on selecting appropriate projections.
3. Can I change the projection of an existing map in ArcGIS Online?
Yes, ArcGIS Online allows you to re-project existing maps, enabling you to adjust the projection to meet your evolving needs.
4. What are the limitations of map projections?
All map projections introduce some distortion. Understanding the specific distortions associated with a chosen projection is crucial for accurate interpretation of the data.
5. How can I learn more about map projections in ArcGIS Online?
ArcGIS Online offers comprehensive documentation and tutorials on map projections, providing a wealth of information to help users understand and utilize these tools effectively.
Tips for Using Map Projections in ArcGIS Online
- Start with a Common Projection: Use a widely recognized projection like Web Mercator for initial map creation, ensuring compatibility with various online services and applications.
- Consider Your Audience: Choose a projection that is appropriate for your target audience and the intended purpose of the map.
- Explore Different Projections: Experiment with different projections to determine which best meets your needs and effectively communicates the desired information.
- Consult Resources: Leverage ArcGIS Online’s documentation, tutorials, and community forums to gain deeper insights into map projections and their application.
Conclusion
Map projections are a fundamental aspect of cartography, playing a critical role in representing the Earth’s surface on a flat plane. ArcGIS Online empowers users with a rich set of tools for managing and working with map projections, ensuring accurate representation of geographic data and effective communication of spatial information. By understanding the principles of map projections and leveraging the capabilities of ArcGIS Online, users can create insightful and informative maps that accurately depict the complexities of the world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Globe: Understanding Map Projections in ArcGIS Online. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!