Navigating the Globe: A Comprehensive Guide to Common Map Projections
Related Articles: Navigating the Globe: A Comprehensive Guide to Common Map Projections
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Globe: A Comprehensive Guide to Common Map Projections. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Globe: A Comprehensive Guide to Common Map Projections
![]()
The Earth, a three-dimensional sphere, presents a significant challenge when attempting to represent it on a two-dimensional surface. This challenge has driven cartographers to develop various map projections, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these projections is crucial for accurately interpreting maps and appreciating the complexities of representing our planet.
The Fundamentals of Map Projections
A map projection is a systematic transformation of the Earth’s curved surface onto a flat plane. This process inevitably introduces distortions, as it is impossible to perfectly represent a sphere on a flat surface without altering the shapes, sizes, distances, or angles of geographical features.
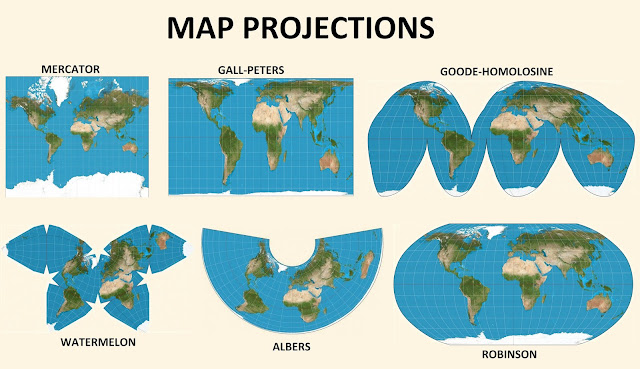
Common Types of Map Projections
The choice of map projection depends on the intended purpose of the map. Different projections excel in specific areas, such as preserving area, shape, distance, or direction. Common types of map projections include:
1. Cylindrical Projections:
- Mercator Projection: This projection is widely known for its use in nautical charts. It preserves angles, making it ideal for navigation. However, it significantly distorts areas, particularly towards the poles, where landmasses appear exaggerated.
- Transverse Mercator Projection: Similar to the Mercator projection, but rotated 90 degrees. It is commonly used for large-scale maps of countries or regions, as it minimizes distortion within a specific zone.
- Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) Projection: This projection divides the Earth into 60 zones, each spanning six degrees of longitude. It is highly accurate for specific regions and is often used for mapping and surveying.
2. Conic Projections:
- Albers Equal-Area Conic Projection: This projection preserves areas, making it suitable for mapping population distributions or resource management. However, it distorts shapes, particularly towards the edges of the map.
- Lambert Conformal Conic Projection: This projection preserves angles and shapes, making it useful for mapping large areas with minimal distortion. It is often used for topographic maps and regional planning.
3. Azimuthal Projections:
- Stereographic Projection: This projection preserves angles and is often used for mapping polar regions. It distorts distances and areas, especially towards the edges of the map.
- Orthographic Projection: This projection depicts the Earth as seen from a distant point in space. It provides a realistic view but distorts areas and shapes, particularly near the edges.
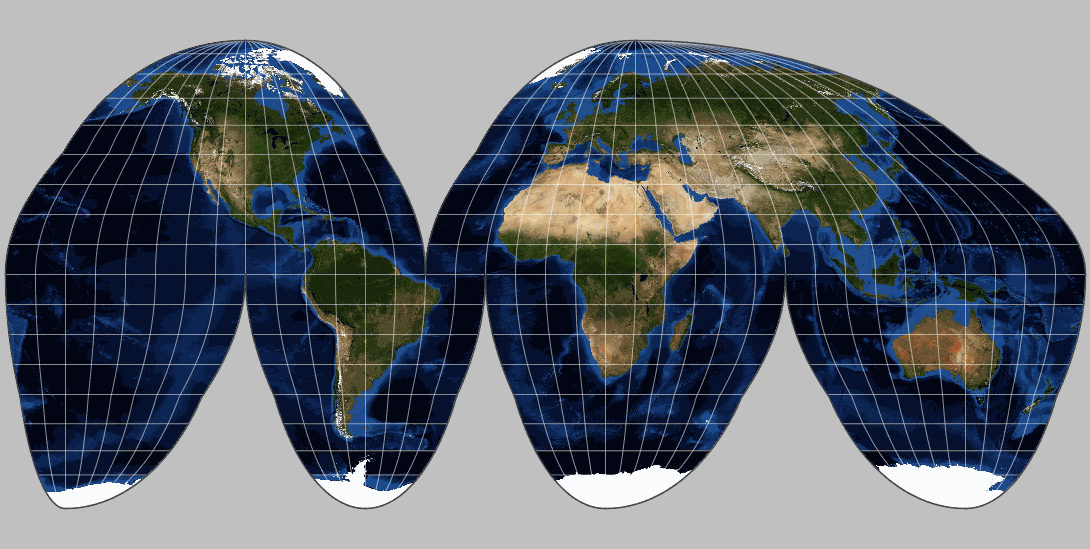
4. Other Projections:
- Mollweide Projection: This projection preserves areas and is commonly used for world maps. It distorts shapes and distances, particularly towards the poles.
- Robinson Projection: This projection is a compromise projection, aiming to minimize distortions in area, shape, and distance. It is often used for general-purpose world maps.
Importance and Benefits of Map Projections
Map projections play a crucial role in various fields, including:
- Navigation: Projections like the Mercator and UTM are essential for accurate navigation, ensuring safe travel on land, sea, and air.
- Mapping and Surveying: Projections are used to create accurate maps and surveys for various purposes, including urban planning, resource management, and disaster response.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Projections are fundamental to GIS, enabling the analysis and visualization of spatial data, facilitating informed decision-making.
- Education: Understanding map projections helps individuals interpret maps accurately and develop a deeper understanding of the Earth’s geography.
FAQs on Common Map Projections:
Q: What is the most accurate map projection?
A: There is no single "most accurate" projection, as each projection introduces different types of distortions. The best projection depends on the intended purpose of the map and the specific region being mapped.
Q: Why do maps distort the Earth’s shape?
A: It is impossible to perfectly represent a sphere on a flat surface without introducing distortions. This is due to the fundamental difference in geometry between a sphere and a plane.
Q: What is the difference between a cylindrical and a conic projection?
A: Cylindrical projections wrap the Earth’s surface around a cylinder, while conic projections project the Earth’s surface onto a cone. Each type has different characteristics and suitability for specific purposes.
Q: How can I tell what projection a map is using?
A: Most maps include a projection description or a projection symbol. Additionally, the map’s scale and the extent of the mapped area can provide clues about the projection used.
Tips for Understanding and Using Map Projections:
- Understand the Purpose of the Map: Consider why the map was created and what information it is intended to convey. This will help you determine the most appropriate projection for the task.
- Be Aware of Distortions: Understand that all projections introduce distortions, and be aware of the specific types of distortions associated with each projection.
- Compare Multiple Projections: When analyzing spatial data, consider using multiple projections to assess the impact of distortions on the results.
- Consult with Experts: If you are unsure about the best projection for a particular task, consult with a cartographer or GIS specialist.
Conclusion
Map projections are essential tools for understanding and representing the Earth’s surface. Each projection offers a unique perspective, with varying strengths and weaknesses. By understanding the different types of projections and their limitations, individuals can interpret maps accurately and make informed decisions based on the information they provide. As technology advances, new projections and techniques continue to emerge, further enhancing our ability to navigate and understand our complex planet.
![]()




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Globe: A Comprehensive Guide to Common Map Projections. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!