Navigating the Crossroads: A Comprehensive Look at the Poland-Germany Border
Related Articles: Navigating the Crossroads: A Comprehensive Look at the Poland-Germany Border
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Crossroads: A Comprehensive Look at the Poland-Germany Border. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Crossroads: A Comprehensive Look at the Poland-Germany Border

The Poland-Germany border, a dynamic and ever-evolving frontier, holds a complex history and significant contemporary relevance. Understanding its geographical, historical, and political dimensions provides crucial insights into the intricate relationship between these two European neighbors. This article delves into the intricacies of the Poland-Germany border, exploring its geographical features, historical evolution, political significance, and economic implications.
A Border Shaped by History:
The Poland-Germany border, spanning over 450 kilometers, is a testament to the intertwined destinies of these two nations. Its current configuration, established in 1945 after World War II, reflects the tumultuous history of the region. The border has shifted multiple times throughout history, influenced by wars, political upheavals, and changing power dynamics.
Tracing the Border’s Evolution:
- Medieval Period: During the Middle Ages, the border between Poland and Germany was fluid, marked by shifting territories and allegiances. The region witnessed numerous conflicts, with both nations vying for control over strategic areas.
- Partitions of Poland: In the 18th century, Poland was partitioned by Prussia, Austria, and Russia. This period saw significant territorial losses for Poland, and the border with Prussia became a symbol of oppression and division.
- Post-World War I: After World War I, the Treaty of Versailles established a new border between Germany and Poland, granting Poland access to the Baltic Sea. This border, however, proved unstable and sparked tensions in the region.
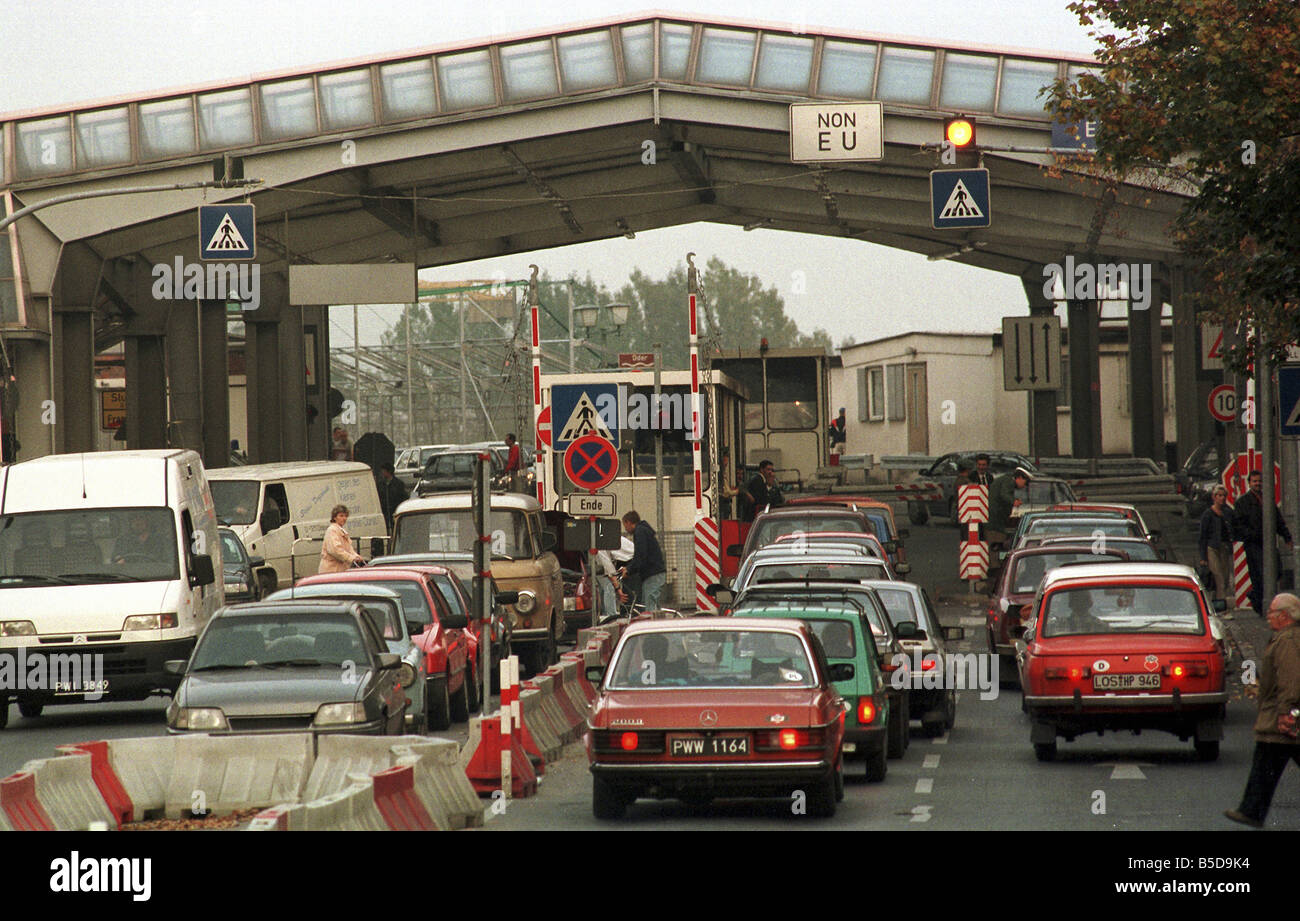
- World War II and the Post-War Settlement: The outbreak of World War II saw Germany’s invasion of Poland, leading to the tragic destruction and displacement of millions. The war’s aftermath saw the establishment of the current border, with Germany losing significant territory in the east, including East Prussia. The Oder-Neisse line, which forms the eastern boundary of Germany, became the defining feature of the post-war border.
The Geography of the Border:
The Poland-Germany border traverses diverse landscapes, ranging from the rolling hills of the Sudeten Mountains to the flat plains of the Oder River valley. The border follows natural features like rivers, mountains, and forests, but it also cuts through settlements and agricultural lands, creating a complex mosaic of shared and divided spaces.
The Oder-Neisse Line: A Symbol of Division and Unity:
The Oder-Neisse line, established as the eastern border of Germany after World War II, remains a significant symbol of the region’s history. While it initially represented a division between East and West Germany, it also became a symbol of unity after the reunification of Germany in 1990.
Political Significance and Cross-Border Cooperation:
The Poland-Germany border is not merely a geographical line; it is a vital link between two powerful and influential nations. The border region has witnessed significant political and economic integration in recent decades, with both countries cooperating on issues of mutual interest, such as environmental protection, infrastructure development, and cultural exchange.
Economic Interdependence and Shared Challenges:
The border region plays a crucial role in the economic development of both Poland and Germany. It is home to numerous industrial centers, transportation hubs, and agricultural areas, creating a vibrant and interconnected economic landscape. However, the region also faces challenges related to environmental sustainability, infrastructure development, and social inequality.
Benefits of Cross-Border Cooperation:
- Economic Growth: Cross-border cooperation facilitates trade, investment, and employment opportunities, boosting economic growth in both countries.
- Infrastructure Development: Joint infrastructure projects, such as road and rail networks, improve connectivity and facilitate trade and travel.
- Environmental Protection: Collaborative efforts on environmental issues like air and water pollution contribute to a cleaner and healthier environment.
- Cultural Exchange: Cross-border initiatives promote cultural understanding and cooperation, fostering stronger bonds between the two nations.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While the Poland-Germany border has witnessed significant progress in terms of cooperation, challenges remain. These include:
- Historical Legacy: The legacy of the past, including territorial disputes and historical grievances, continues to influence the relationship between the two countries.
- Economic Disparities: The economic disparities between Poland and Germany can create challenges for equitable cross-border cooperation.
- Migration and Security: The border region is a focal point for migration and security concerns, requiring close coordination between the two countries.
FAQs about the Poland-Germany Border:
1. What is the current status of the Poland-Germany border?
The current border, established in 1945, is recognized by both Poland and Germany. It is a stable and well-defined border, with no significant territorial disputes.
2. What is the historical significance of the Oder-Neisse line?
The Oder-Neisse line, established as the eastern border of Germany after World War II, is a symbol of both division and unity. It marked the loss of significant territory for Germany and the re-establishment of Poland’s eastern borders. However, it also became a symbol of unity after the reunification of Germany in 1990.
3. What are the major economic activities in the border region?
The border region is home to a diverse range of economic activities, including manufacturing, agriculture, transportation, and tourism. It is a hub for trade and investment, benefiting from the strong economic ties between Poland and Germany.
4. What are the main challenges facing the border region?
The border region faces challenges related to historical legacy, economic disparities, migration, and security. Addressing these challenges requires continued cooperation between Poland and Germany.
5. What is the future outlook for the Poland-Germany border?
The future of the Poland-Germany border is likely to be characterized by continued cooperation and integration. Both countries have a vested interest in maintaining strong ties and working together to address common challenges.
Tips for Understanding the Poland-Germany Border:
- Study the history of the border region: Understanding the historical context is crucial for grasping the current dynamics of the border.
- Explore the geography of the region: Examining the physical features of the border helps to understand its influence on economic activities, cultural exchange, and environmental issues.
- Follow the latest developments in cross-border cooperation: Staying informed about current initiatives and challenges facing the border region provides insights into its future trajectory.
Conclusion:
The Poland-Germany border is a dynamic and evolving frontier, reflecting a complex and intertwined history. While the border has been a source of conflict and division in the past, it has also served as a catalyst for cooperation and integration in recent decades. Understanding the geographical, historical, and political dimensions of the border provides a valuable lens for comprehending the intricate relationship between Poland and Germany. By fostering continued cooperation and addressing shared challenges, both countries can build a brighter future for the border region and its inhabitants.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Crossroads: A Comprehensive Look at the Poland-Germany Border. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!