Navigating the City in Three Dimensions: Exploring the Potential of 3D City Models
Related Articles: Navigating the City in Three Dimensions: Exploring the Potential of 3D City Models
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the City in Three Dimensions: Exploring the Potential of 3D City Models. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the City in Three Dimensions: Exploring the Potential of 3D City Models
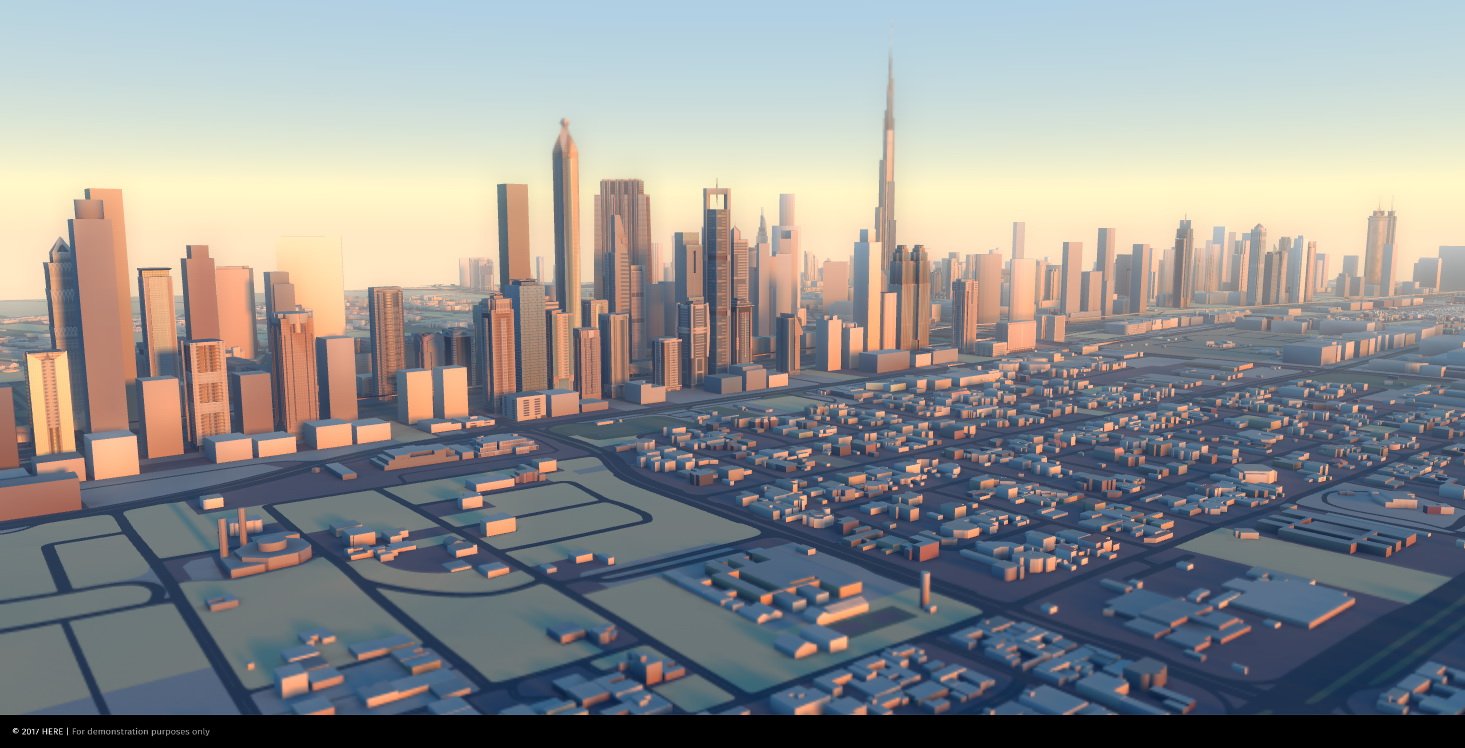

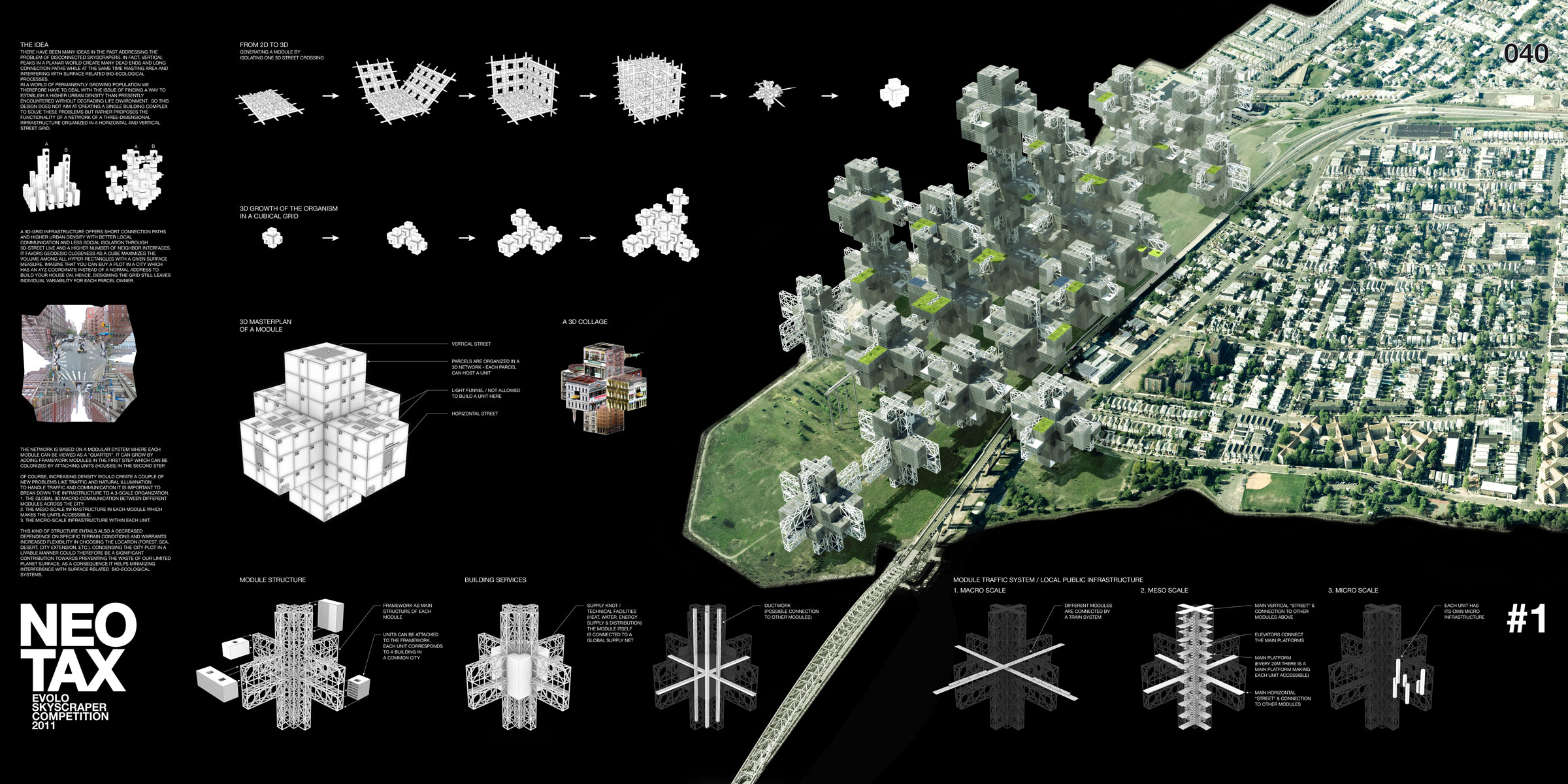
The rapid evolution of technology has transformed the way we interact with our surroundings. This transformation is particularly evident in the realm of urban planning and design, where advancements in 3D modeling and visualization are revolutionizing how we understand and engage with our cities. One notable example of this shift is the emergence of 3D city models, which are becoming increasingly valuable tools for various stakeholders, from urban planners and architects to citizens and businesses.
A Digital Twin of the Urban Landscape:
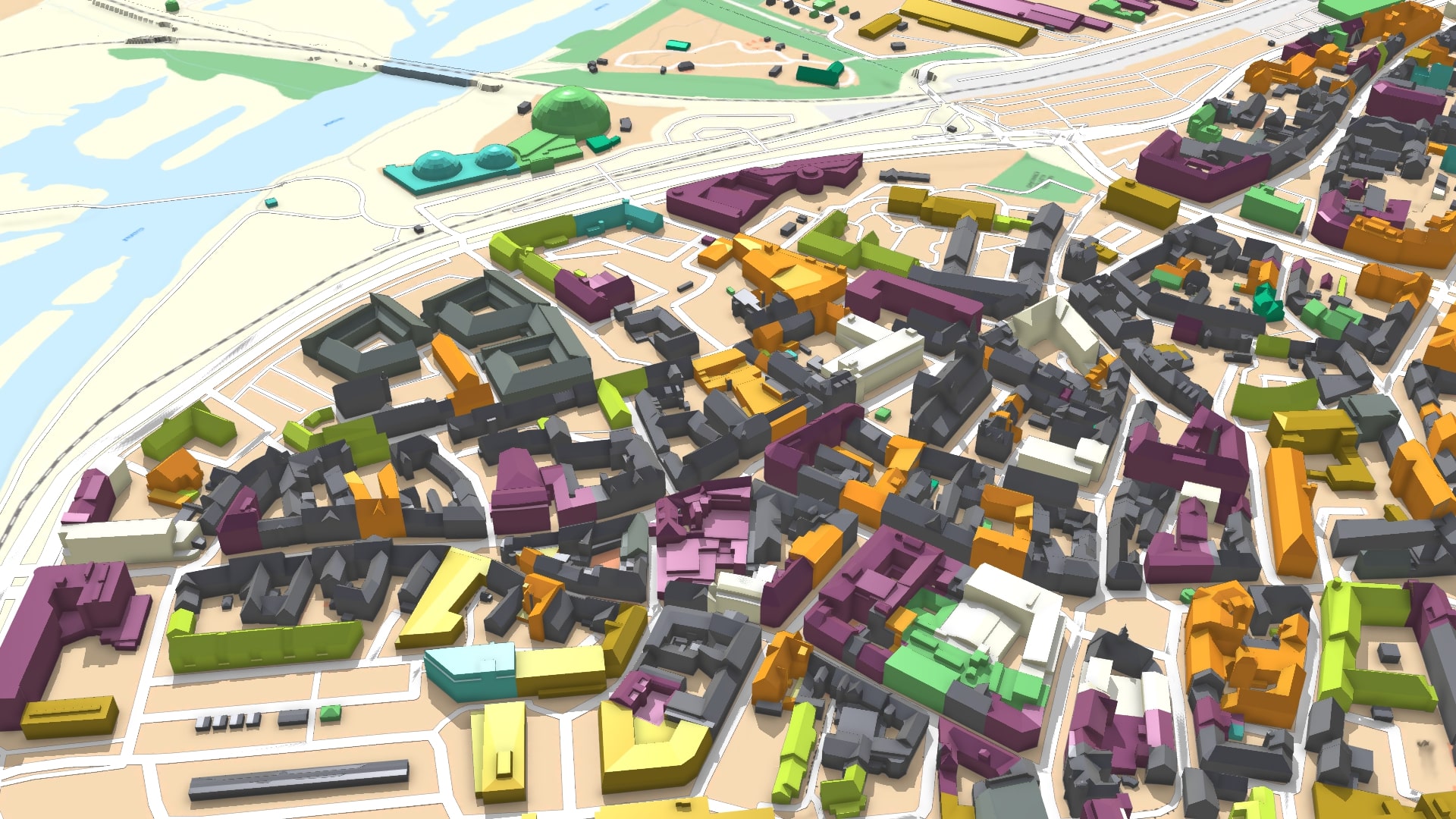
3D city models are digital representations of a city, capturing its physical features, infrastructure, and even its dynamic aspects, such as traffic flow and population density. These models are built using data from a variety of sources, including aerial photography, LiDAR scans, and building information models (BIM). The result is a comprehensive and interactive representation of the urban environment that can be accessed and manipulated digitally.
Benefits Beyond the Visual:
The benefits of 3D city models extend far beyond their visual appeal. They offer a powerful platform for:
- Urban Planning and Design: 3D models provide a realistic and interactive environment for testing different planning scenarios. Planners can explore the impact of new infrastructure projects, evaluate the effectiveness of traffic management strategies, and assess the potential for urban renewal initiatives.
- Infrastructure Management: By visualizing underground infrastructure, 3D models facilitate efficient maintenance and repair operations. They enable engineers to identify potential conflicts between utilities, optimize resource allocation, and plan for future infrastructure expansion.
- Emergency Response: In the event of natural disasters or other emergencies, 3D models provide a crucial tool for first responders. They offer real-time information on affected areas, enabling better coordination of rescue efforts and resource deployment.
- Citizen Engagement: 3D models can empower citizens to participate in urban planning processes. Interactive platforms allow residents to explore proposed projects, provide feedback, and understand the potential impact of development on their neighborhoods.
- Tourism and Marketing: 3D city models offer a compelling way to showcase a city’s attractions and promote tourism. Interactive tours and virtual reality experiences can engage visitors and provide a unique perspective of the urban landscape.
Beyond Static Representations:
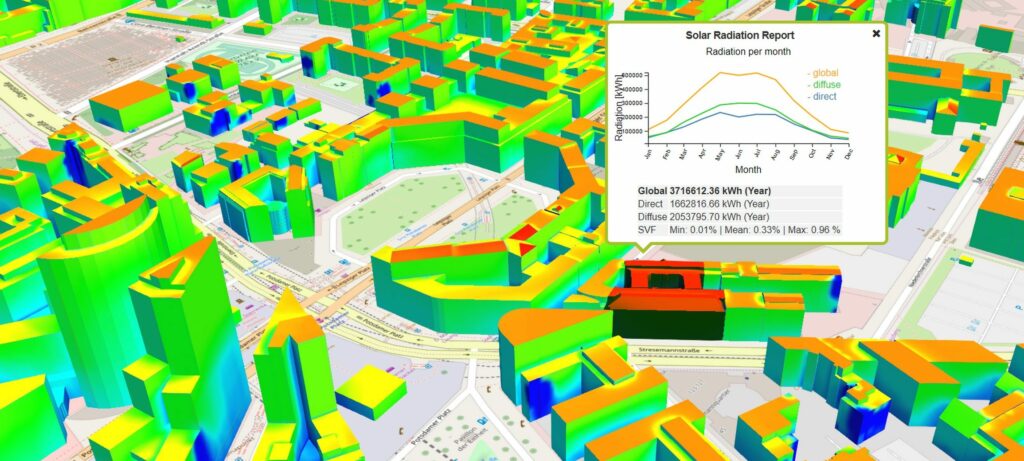
The value of 3D city models is further enhanced by the integration of dynamic data. This includes real-time information on traffic conditions, air quality, and other environmental factors. This dynamic data layer allows for a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the city’s functioning and provides valuable insights for decision-making.
Challenges and Considerations:
While the potential of 3D city models is vast, there are also challenges associated with their development and implementation. These include:
- Data Acquisition and Integration: Obtaining accurate and up-to-date data from various sources can be a complex and resource-intensive process. Integrating data from different formats and ensuring consistency across the model is also a significant challenge.
- Model Accuracy and Detail: The accuracy and level of detail in a 3D model are crucial for its effectiveness. Maintaining a balance between complexity and usability is essential to ensure that the model is both informative and user-friendly.
- Data Privacy and Security: As 3D city models often contain sensitive information about individuals and infrastructure, ensuring data privacy and security is paramount.
- Accessibility and Collaboration: Making 3D models accessible to a wide range of stakeholders, including citizens, requires user-friendly interfaces and collaborative platforms.
Looking Ahead: A Collaborative Future:
Overcoming these challenges requires collaboration between various stakeholders, including government agencies, research institutions, technology companies, and citizens. Open data initiatives and standardized formats can facilitate data sharing and collaboration, while advancements in cloud computing and data visualization technologies can enhance the accessibility and usability of 3D city models.
FAQs:
1. What are the different types of 3D city models?
3D city models can be categorized based on their level of detail, purpose, and data sources. Common types include:
- Conceptual Models: These models focus on general urban form and are often used for planning and design purposes.
- Detailed Models: These models capture a high level of detail, including buildings, infrastructure, and even vegetation. They are used for a wider range of applications, including infrastructure management and emergency response.
- Dynamic Models: These models incorporate real-time data, such as traffic flow and air quality, to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the city’s functioning.
2. How are 3D city models created?
3D city models are typically created using a combination of data sources, including:
- Aerial Photography: Aerial images provide a bird’s-eye view of the city, capturing its overall layout and features.
- LiDAR Scans: LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology uses laser beams to measure distances and create highly detailed 3D representations of the city.
- Building Information Models (BIM): BIM data provides detailed information about individual buildings, including their structural elements and internal layout.
- Geo-spatial Data: Data sources such as cadastral maps and street networks provide information on property boundaries and infrastructure.
3. What are the applications of 3D city models in urban planning?
3D city models are invaluable tools for urban planners, enabling them to:
- Simulate Development Scenarios: Test different development proposals and assess their impact on the city’s infrastructure, traffic flow, and overall livability.
- Visualize Infrastructure Projects: Plan and design new infrastructure projects, including roads, bridges, and public transportation systems, in a realistic 3D environment.
- Evaluate Urban Renewal Initiatives: Analyze the effectiveness of urban renewal projects and identify areas for improvement.
- Promote Citizen Engagement: Create interactive platforms for citizens to explore proposed projects, provide feedback, and participate in planning decisions.
4. What are the challenges associated with data privacy in 3D city models?
Ensuring data privacy is a crucial consideration in the development and use of 3D city models, as they often contain sensitive information about individuals and infrastructure. Key challenges include:
- Anonymization of Personal Data: Protecting the privacy of individuals depicted in the model by anonymizing or removing identifiable information.
- Security of Sensitive Infrastructure Data: Safeguarding information about critical infrastructure, such as power grids and water systems, from unauthorized access.
- Transparency and Accountability: Establishing clear guidelines and procedures for data collection, use, and disclosure to ensure transparency and accountability.
Tips for Using 3D City Models Effectively:
- Define Clear Objectives: Determine the specific goals and applications for the 3D model to ensure it is tailored to the desired outcomes.
- Involve Stakeholders: Engage with relevant stakeholders, including government agencies, businesses, and citizens, to gather input and ensure the model meets their needs.
- Prioritize Data Accuracy and Consistency: Ensure the data used to build the model is accurate, up-to-date, and consistent across different sources.
- Focus on User Experience: Develop user-friendly interfaces and tools to make the model accessible and engaging for a wide range of users.
- Continuously Update and Improve: Regularly update the model with new data and advancements in technology to ensure its relevance and accuracy.
Conclusion:
3D city models are emerging as a powerful tool for navigating and understanding the urban environment. Their ability to visualize complex urban systems, simulate planning scenarios, and facilitate citizen engagement makes them invaluable assets for urban planning, infrastructure management, and emergency response. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect 3D city models to play an increasingly prominent role in shaping the future of our cities, fostering sustainable development, and enhancing the quality of life for all citizens.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the City in Three Dimensions: Exploring the Potential of 3D City Models. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!