Navigating Data Transformations with Python’s map Function: Exploring Dictionaries
Related Articles: Navigating Data Transformations with Python’s map Function: Exploring Dictionaries
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating Data Transformations with Python’s map Function: Exploring Dictionaries. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating Data Transformations with Python’s map Function: Exploring Dictionaries
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating Data Transformations with Python’s map Function: Exploring Dictionaries
- 3.1 Understanding the Fundamentals: map in Action
- 3.2 Applying map to Dictionaries: A Deeper Dive
- 3.3 Beyond Simple Transformations: Leveraging map for Complex Operations
- 3.4 Benefits of Using map with Dictionaries
- 3.5 FAQs Regarding map and Dictionaries
- 3.6 Tips for Effective map Usage with Dictionaries
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating Data Transformations with Python’s map Function: Exploring Dictionaries

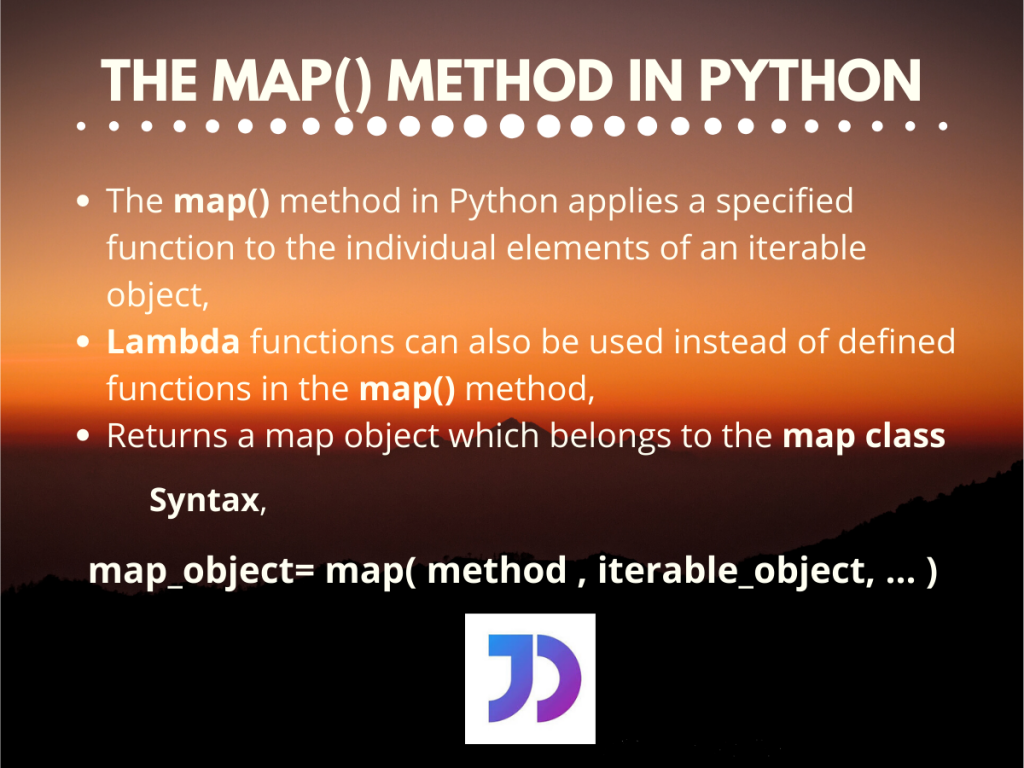
The map function in Python is a powerful tool for applying a function to each element of an iterable, such as a list or a tuple. While map is commonly used with lists, its application extends to dictionaries, providing a streamlined approach to data manipulation and transformation. This article delves into the intricacies of using map with dictionaries, highlighting its versatility and benefits in diverse scenarios.
Understanding the Fundamentals: map in Action
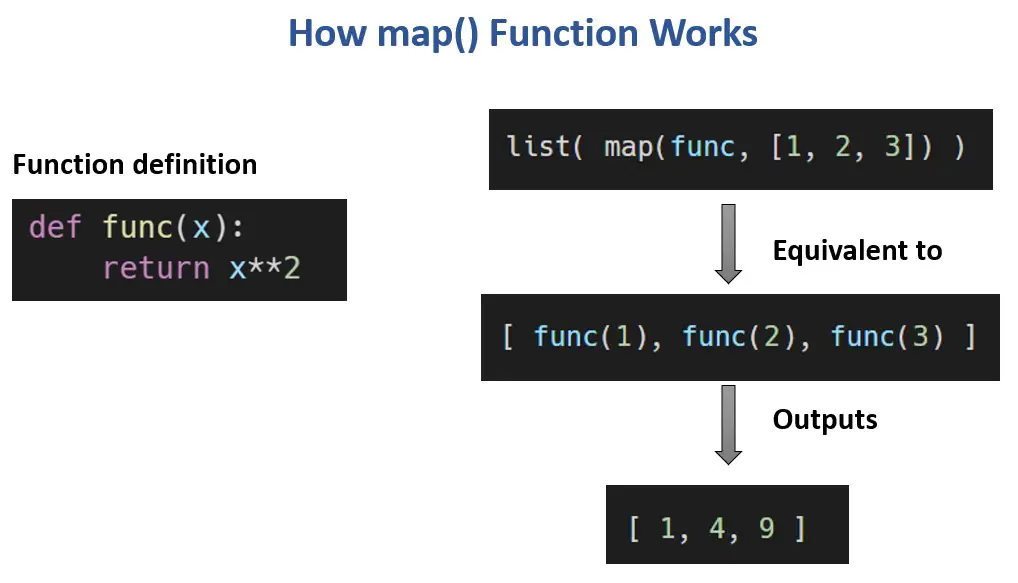
At its core, the map function takes two arguments: a function and an iterable. It iterates through each element of the iterable, applies the specified function to each element, and returns an iterator containing the results.
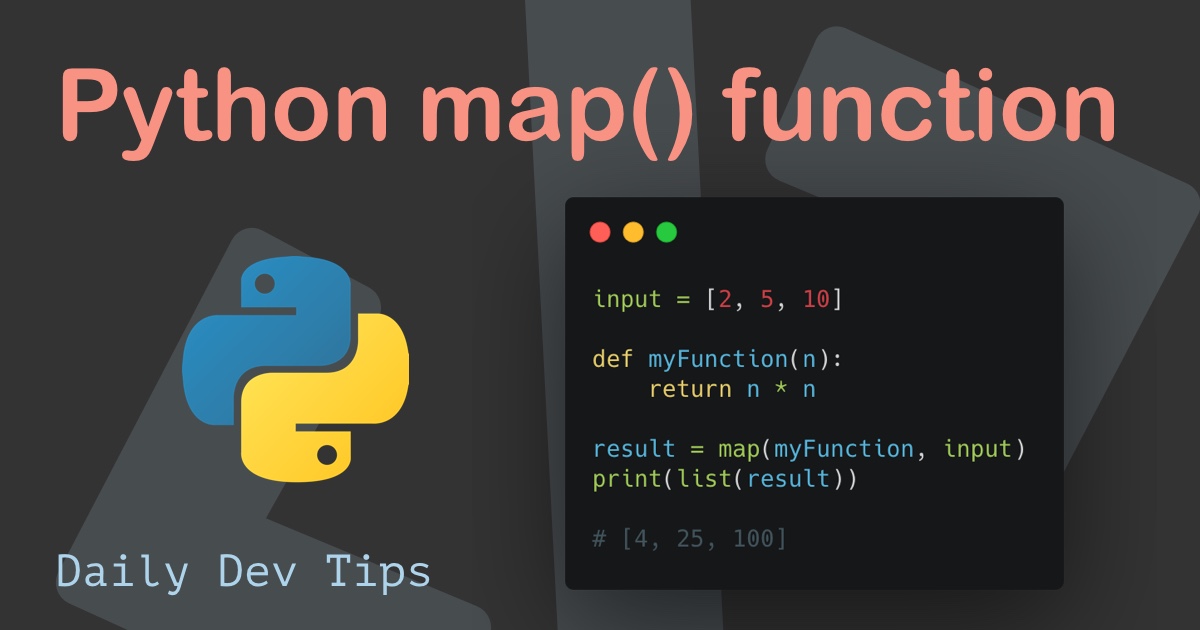
Let’s consider a simple example:
def square(x):
return x * x
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
squared_numbers = map(square, numbers)
print(list(squared_numbers)) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]In this example, the square function squares its input. The map function applies square to each element in the numbers list, yielding an iterator containing the squared values. Converting this iterator to a list using list() displays the results.
Applying map to Dictionaries: A Deeper Dive
Dictionaries, unlike lists, are composed of key-value pairs. Applying map to a dictionary requires a different approach, as it operates on individual elements rather than key-value pairs. There are two primary methods for utilizing map with dictionaries:
-
Transforming Keys:
To apply a function to the keys of a dictionary, you can use
mapin conjunction with thedict.keys()method. This method returns a view object containing the keys of the dictionary.def uppercase(key): return key.upper() my_dict = 'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3 new_dict = dict(zip(map(uppercase, my_dict.keys()), my_dict.values())) print(new_dict) # Output: 'A': 1, 'B': 2, 'C': 3Here, the
uppercasefunction converts a string to uppercase.mapappliesuppercaseto each key in the dictionary. Thezipfunction combines the transformed keys with the original values, creating a new dictionary with uppercase keys. -
Transforming Values:
Similarly, you can transform values by applying
mapto thedict.values()method. This method returns a view object containing the values of the dictionary.def double(value): return value * 2 my_dict = 'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3 new_dict = dict(zip(my_dict.keys(), map(double, my_dict.values()))) print(new_dict) # Output: 'a': 2, 'b': 4, 'c': 6In this example, the
doublefunction multiplies its input by 2.mapappliesdoubleto each value in the dictionary. Thezipfunction combines the original keys with the transformed values, creating a new dictionary with doubled values.
Beyond Simple Transformations: Leveraging map for Complex Operations
While map is effective for basic transformations, its true potential lies in its ability to handle more intricate operations. By combining map with lambda functions, you can perform various manipulations on dictionaries, including:
-
Conditional Transformations: Applying different transformations based on specific conditions.
my_dict = 'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3 new_dict = dict(zip(my_dict.keys(), map(lambda x: x * 2 if x > 1 else x, my_dict.values()))) print(new_dict) # Output: 'a': 1, 'b': 4, 'c': 6This example uses a lambda function to double values greater than 1, leaving others unchanged.
-
Data Aggregation: Combining multiple values into a single result.
my_dict = 'a': [1, 2], 'b': [3, 4], 'c': [5, 6] new_dict = dict(zip(my_dict.keys(), map(sum, my_dict.values()))) print(new_dict) # Output: 'a': 3, 'b': 7, 'c': 11This example uses a lambda function to sum the elements of each value list, effectively aggregating the data within each key.
-
Complex Data Structures: Handling nested dictionaries and lists within dictionaries.
my_dict = 'a': 'x': 1, 'y': 2, 'b': 'x': 3, 'y': 4 new_dict = dict(zip(my_dict.keys(), map(lambda x: x['x'] * 2, my_dict.values()))) print(new_dict) # Output: 'a': 2, 'b': 6This example uses a lambda function to access and double the ‘x’ value within nested dictionaries, demonstrating the ability to handle complex data structures.
Benefits of Using map with Dictionaries
Employing map with dictionaries offers several advantages:
-
Conciseness:
mapprovides a compact and readable way to perform transformations, enhancing code clarity. -
Efficiency:
mapoften improves performance compared to manual looping, especially for large datasets. -
Flexibility:
mapcan be combined with various functions and lambda expressions, enabling complex manipulations. -
Readability:
mappromotes a more declarative style, focusing on what needs to be done rather than how.
FAQs Regarding map and Dictionaries
Q: Can I modify the original dictionary using map?
A: No, map returns a new iterator. To modify the original dictionary, you need to iterate through it directly and modify the values in place.
Q: Is map always the most efficient way to transform a dictionary?
A: While map is generally efficient, for simple transformations, list comprehensions can sometimes be more readable and performant.
Q: Can I use map with multiple arguments?
A: Yes, you can use map with multiple arguments by providing multiple iterables. The function applied will receive corresponding elements from each iterable.
Q: How do I handle errors when using map?
A: You can use a try-except block to handle errors within the function applied by map. Alternatively, you can use the itertools.zip_longest function to handle cases where iterables have different lengths.
Tips for Effective map Usage with Dictionaries
- Choose the right function: Select a function that aligns with the desired transformation.
- Leverage lambda functions: Use lambda functions for concise and efficient operations.
-
Consider performance: For large datasets,
mapoften offers better performance than manual looping. - Prioritize readability: Aim for clear and concise code that reflects the intended transformation.
- Handle errors gracefully: Implement error handling to ensure robust code.
Conclusion
Python’s map function empowers developers to efficiently transform dictionaries, streamlining data manipulation and enhancing code readability. By understanding the principles of applying map to dictionaries, combined with the use of lambda functions and error handling, developers can harness the full potential of this versatile tool for various data processing tasks. Whether performing simple transformations or handling complex data structures, map provides a powerful and efficient approach to working with dictionaries in Python.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Data Transformations with Python’s map Function: Exploring Dictionaries. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!