Mapping the Globe: An Exploration of Map Projections in Geography
Related Articles: Mapping the Globe: An Exploration of Map Projections in Geography
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Globe: An Exploration of Map Projections in Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Globe: An Exploration of Map Projections in Geography
The Earth, a sphere with intricate contours and diverse landscapes, presents a challenge when attempting to represent it on a flat surface. This is where the concept of map projections comes into play. A map projection is a systematic transformation of the Earth’s spherical surface onto a plane, enabling us to visualize and analyze geographical information.
Understanding the Challenge: The Spherical Earth and the Flat Map
The Earth’s spherical shape poses a fundamental obstacle in cartography. A flat map, by its nature, cannot accurately represent all the features of a curved surface without distortions. These distortions can manifest in various ways, affecting the shape, size, distance, and direction of geographical features.
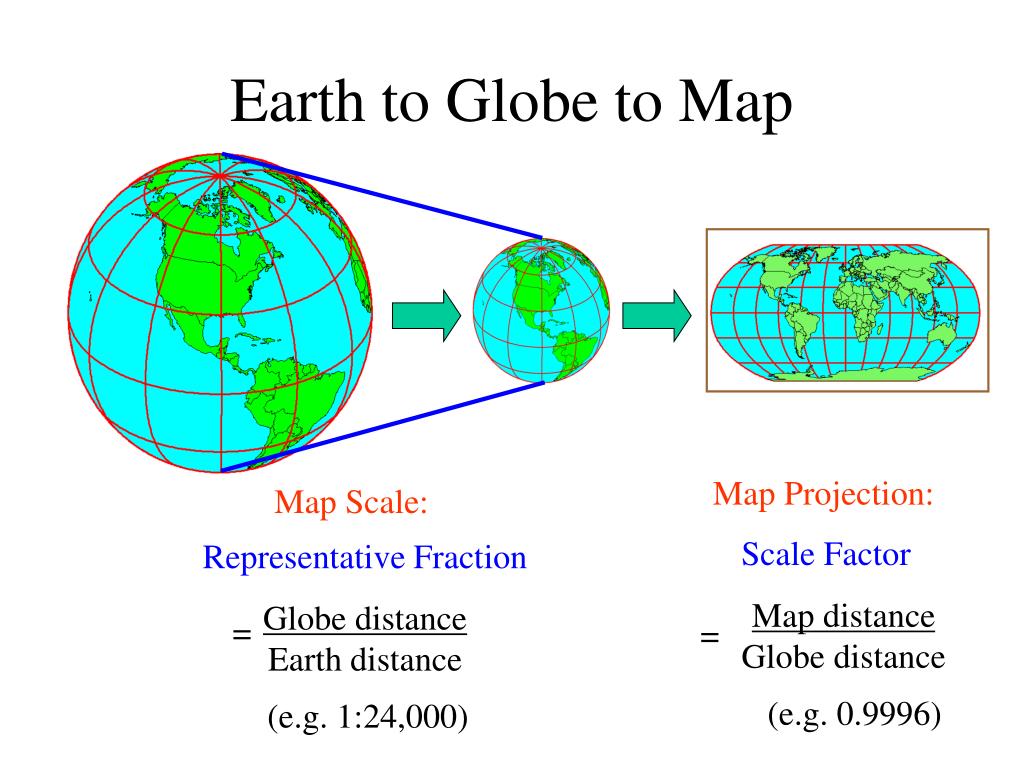
The Mechanics of Map Projections
Map projections employ mathematical formulas to translate the coordinates of points on the Earth’s surface onto a flat plane. This process involves choosing a specific point of reference, known as the projection point, and a specific surface, called the projection surface. The choice of projection point and surface determines the type of projection and the resulting distortions.
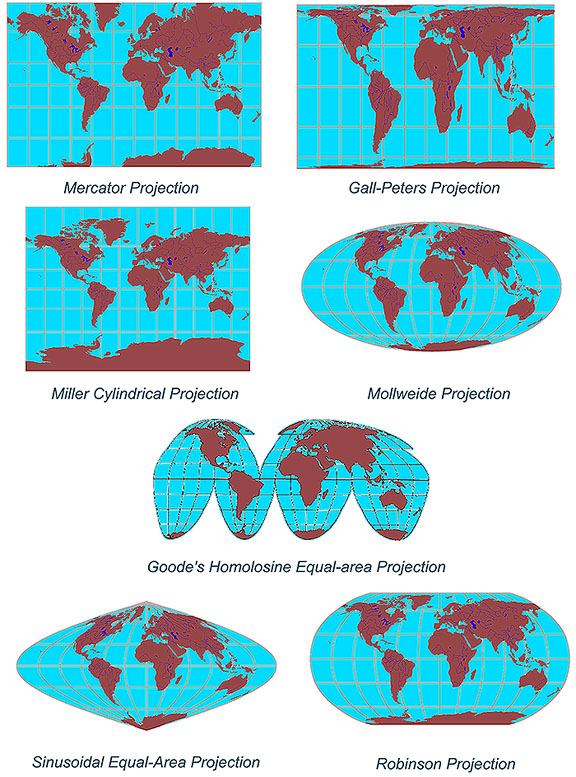
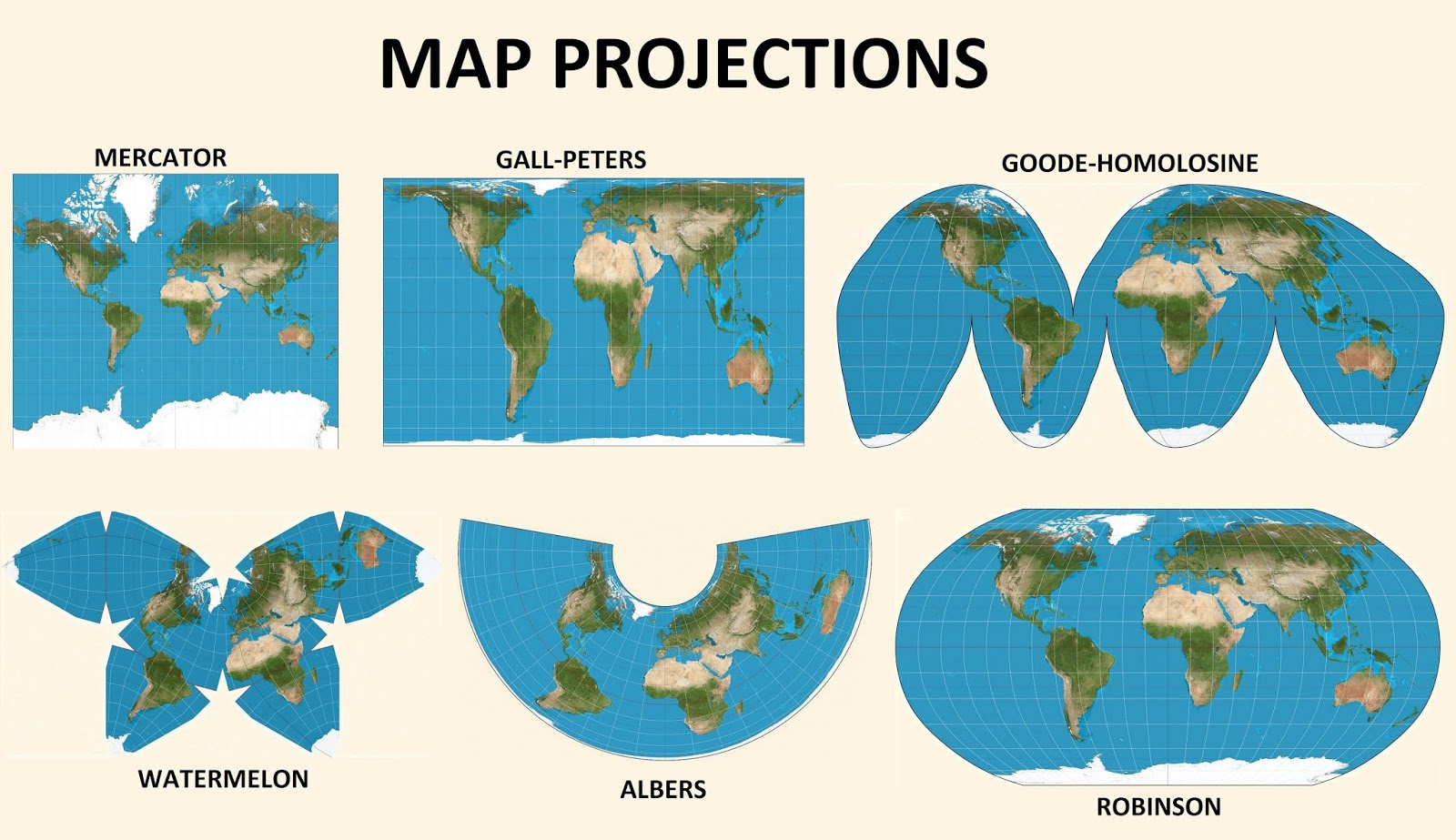
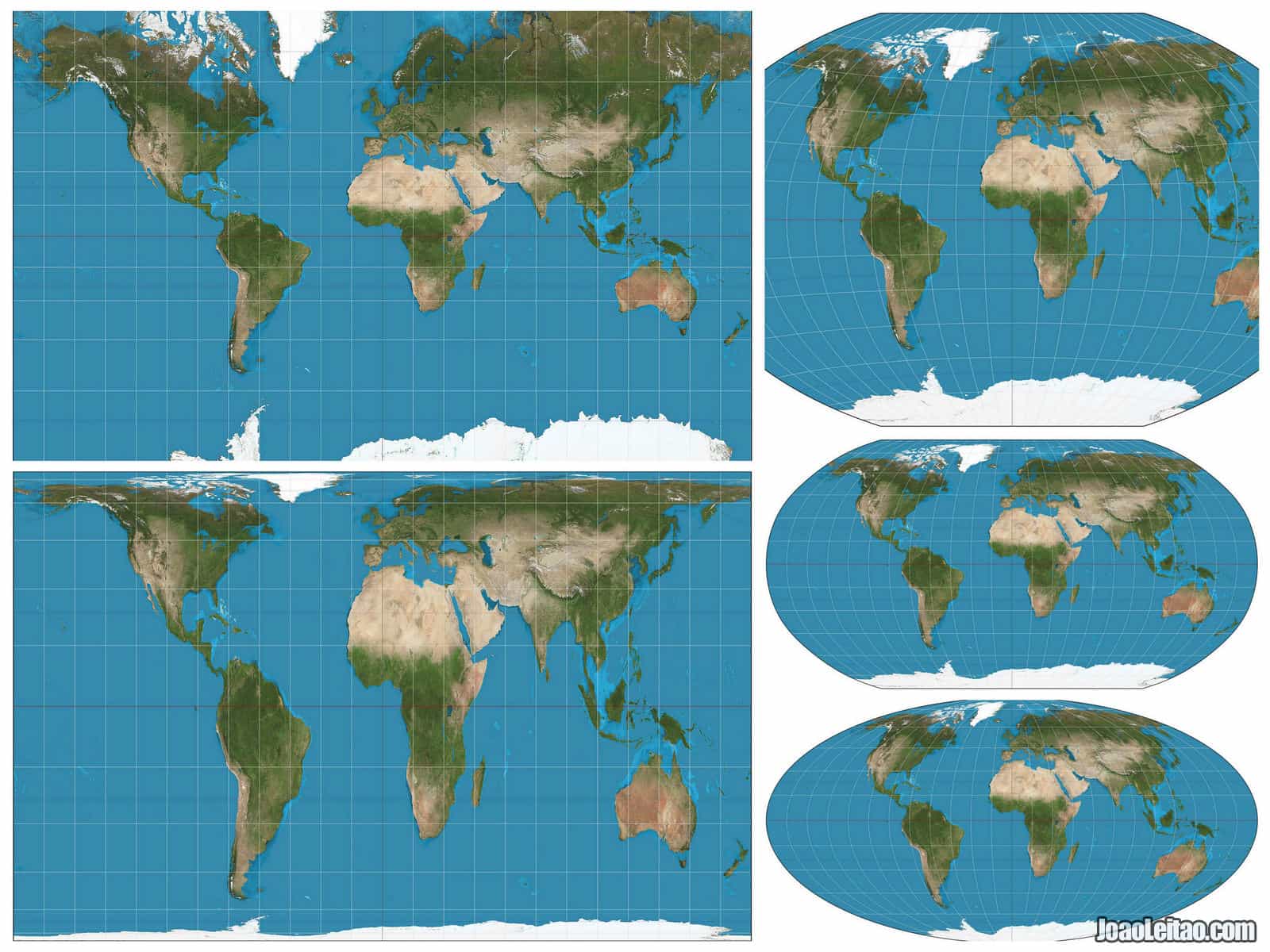
Types of Map Projections
There are numerous types of map projections, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Some of the most common types include:
-
Cylindrical Projections: These projections wrap a cylinder around the globe, projecting the Earth’s features onto the cylinder’s surface. Examples include the Mercator projection, commonly used for nautical charts, and the Transverse Mercator projection, utilized in national mapping systems.
-
Conic Projections: Conic projections use a cone intersecting the globe, projecting the Earth’s features onto the cone’s surface. They are often used for mid-latitude regions, such as the United States, and are known for their good representation of areas close to the standard parallel.
-
Azimuthal Projections: These projections use a plane tangent to the globe, projecting the Earth’s features onto the plane. They are particularly useful for representing polar regions and are often used in aeronautical charts.
-
Other Projections: There are other less common projection types, including the pseudo-cylindrical projections and the polyconic projections. Each type is designed to minimize specific distortions and optimize the representation of certain geographical features.
The Impact of Distortions
The choice of map projection significantly influences the representation of geographical features. Understanding the types of distortions introduced by different projections is crucial for accurate interpretation and analysis. Common distortions include:
-
Shape Distortion: This refers to the distortion of the shape of geographical features, particularly noticeable in areas with significant latitude differences.
-
Area Distortion: This distortion affects the size of geographical features, with some areas appearing larger or smaller than their actual size.
-
Distance Distortion: This distortion affects the representation of distances between geographical features, with some distances being exaggerated or minimized.
-
Direction Distortion: This distortion affects the representation of directions, particularly noticeable near the poles.
Choosing the Right Projection
The choice of map projection depends on the specific application and the geographical region being represented. For example, a Mercator projection is suitable for navigation, but it exaggerates areas near the poles. A conic projection is well-suited for mid-latitude regions but introduces significant distortions near the poles.
Beyond Distortions: The Importance of Map Projections
Despite the inherent distortions, map projections are essential tools for geographers, cartographers, and other professionals. They enable us to:
-
Visualize and analyze geographical data: Projections allow us to represent complex geographical information in a comprehensible format.
-
Communicate spatial relationships: Maps based on projections help us understand the relative positions and distances between different locations.
-
Support navigation and exploration: Projections are crucial for navigation, particularly for maritime and aerial travel.
-
Facilitate planning and decision-making: Maps based on projections are essential for planning infrastructure projects, managing natural resources, and addressing environmental challenges.
FAQs about Map Projections
Q: What is the most accurate map projection?
A: There is no single "most accurate" projection. All projections introduce distortions, and the best choice depends on the specific application and geographical region.
Q: Why are there so many different map projections?
A: Different projections are designed to minimize specific distortions and optimize the representation of certain geographical features.
Q: How can I tell which projection is being used on a map?
A: The map’s legend or metadata should specify the projection used.
Q: Are there any projections that are completely distortion-free?
A: No, all map projections introduce some level of distortion.
Tips for Understanding Map Projections
-
Examine the projection used: Pay attention to the projection used on a map and understand its associated distortions.
-
Consider the purpose of the map: The choice of projection should align with the purpose of the map.
-
Compare different projections: Analyze maps using different projections to understand how they affect the representation of geographical features.
Conclusion
Map projections are fundamental tools in geography, allowing us to represent the Earth’s spherical surface on a flat plane. While they introduce unavoidable distortions, they enable us to visualize, analyze, and communicate geographical information effectively. Understanding the principles of map projections is crucial for interpreting maps accurately and making informed decisions based on geographical data. By carefully considering the purpose of a map and the associated distortions, we can effectively utilize these powerful tools to explore and understand our world.
![]()



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Globe: An Exploration of Map Projections in Geography. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!