Mapping Florida: Choosing the Right Projection for Accuracy and Clarity
Related Articles: Mapping Florida: Choosing the Right Projection for Accuracy and Clarity
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping Florida: Choosing the Right Projection for Accuracy and Clarity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping Florida: Choosing the Right Projection for Accuracy and Clarity
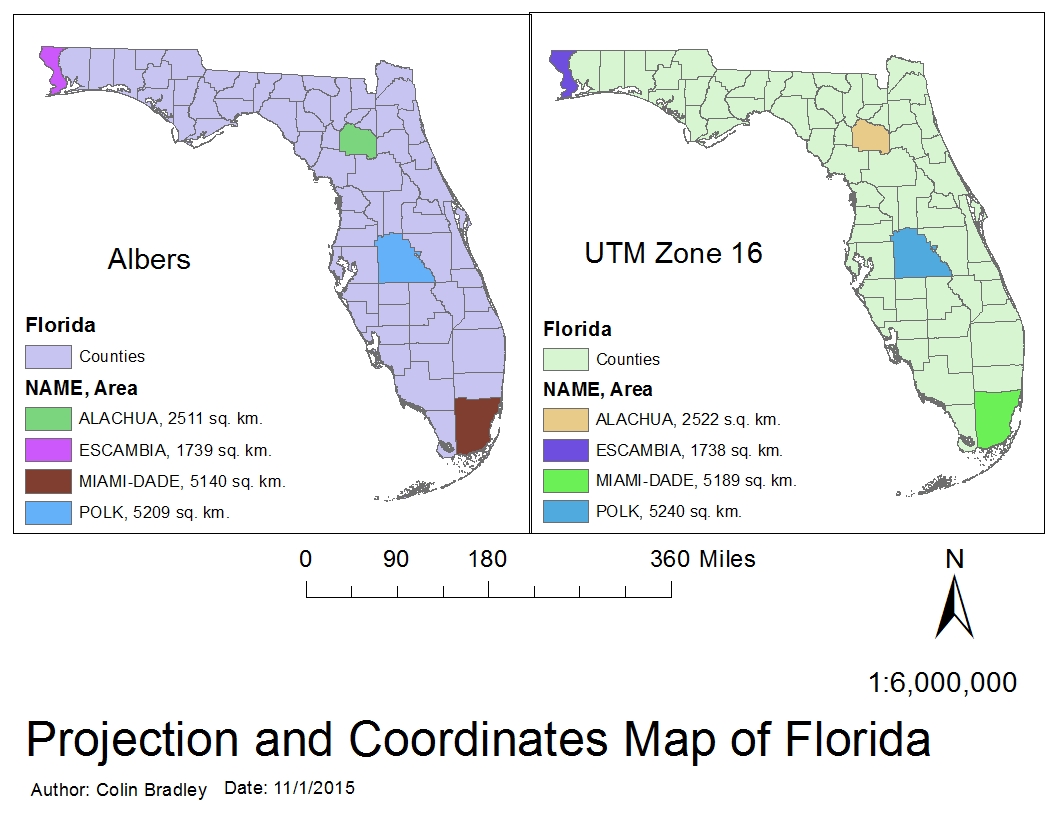
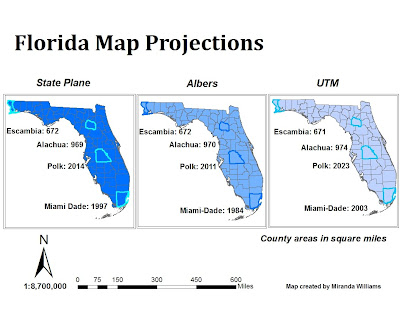
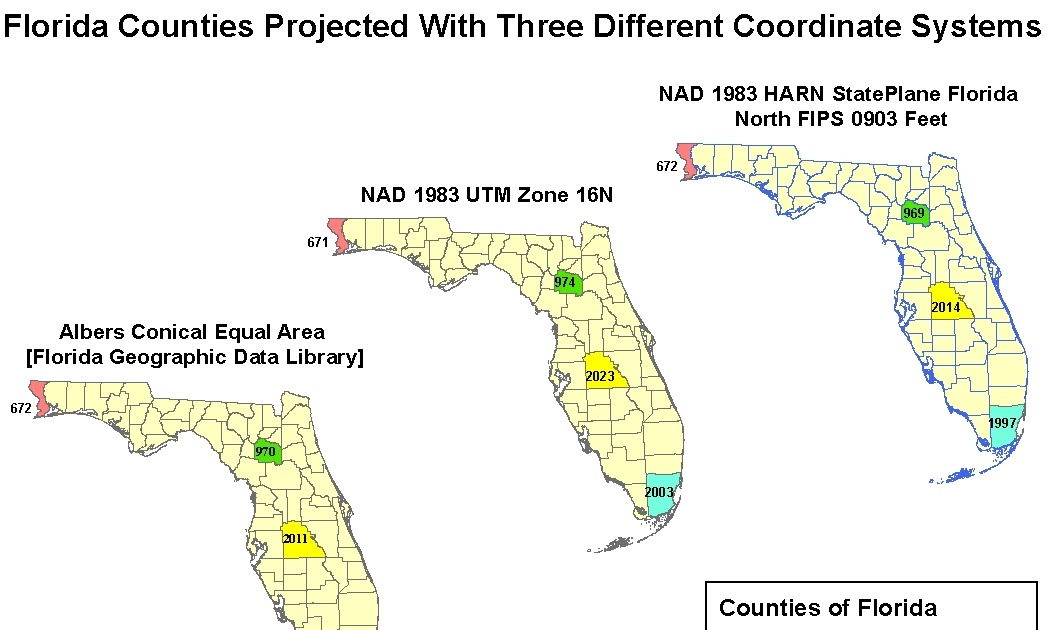
Florida, with its unique shape and geographic position, presents a challenge for cartographers seeking to accurately represent its features on a map. The choice of map projection, a method of transforming the Earth’s curved surface onto a flat plane, significantly influences how the state’s geography is depicted. This article explores the optimal map projections for Florida, considering factors such as shape, area, and distance preservation, ultimately aiming to provide a clear understanding of the best projection for specific applications.
Understanding Map Projections and Their Limitations
All map projections inherently involve distortions. The Earth, a sphere, cannot be flattened without altering its geometric properties. Projections introduce compromises, prioritizing some aspects of representation while sacrificing others. Key considerations include:
- Shape Preservation: Maintaining the correct shape of geographic features is crucial for accurate representation. Some projections excel in this aspect, while others introduce significant distortions, especially in areas with high curvature, like Florida’s coastline.
- Area Preservation: Ensuring that the relative sizes of areas remain true to reality is critical for applications involving population density, land use, or resource distribution. Projections that preserve area may distort shapes to achieve this balance.
- Distance Preservation: Maintaining accurate distances between points is essential for navigation and measuring geographic distances. Some projections preserve distances along specific lines, while others distort distances across the entire map.
Optimal Projections for Florida
Given Florida’s elongated shape and proximity to the equator, specific projections offer superior accuracy for various applications. Here are some prominent contenders:
1. The Transverse Mercator Projection:
This projection, commonly used for topographic maps and large-scale mapping, is particularly well-suited for Florida. It maintains accurate distances and shapes along the central meridian, which runs vertically through the state. This characteristic is crucial for applications requiring precise measurements of distances and angles, such as surveying, navigation, and engineering.
However, the Transverse Mercator projection introduces distortions in areas further away from the central meridian. This is less problematic for Florida due to its relatively narrow width.
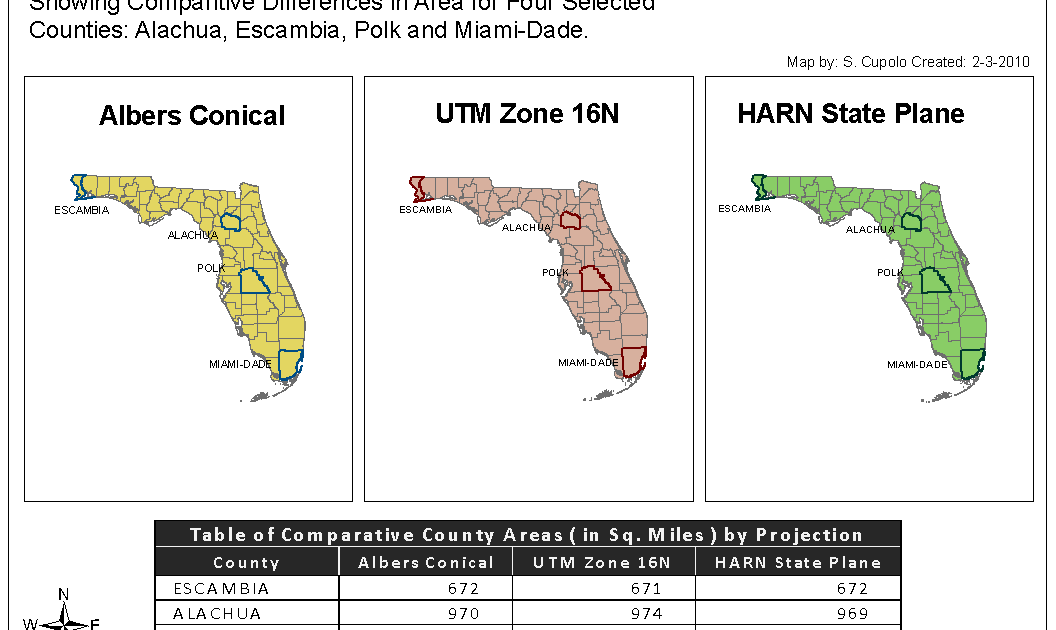
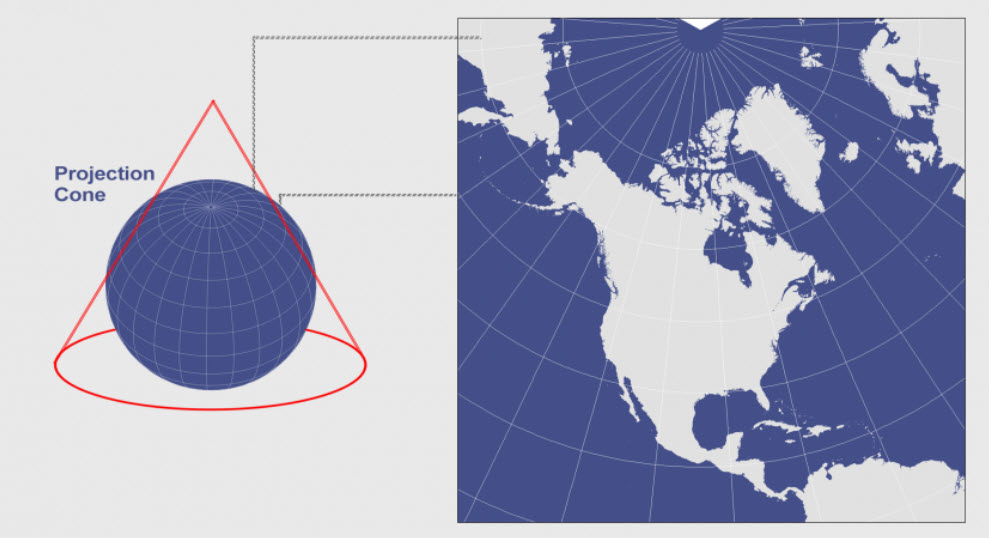
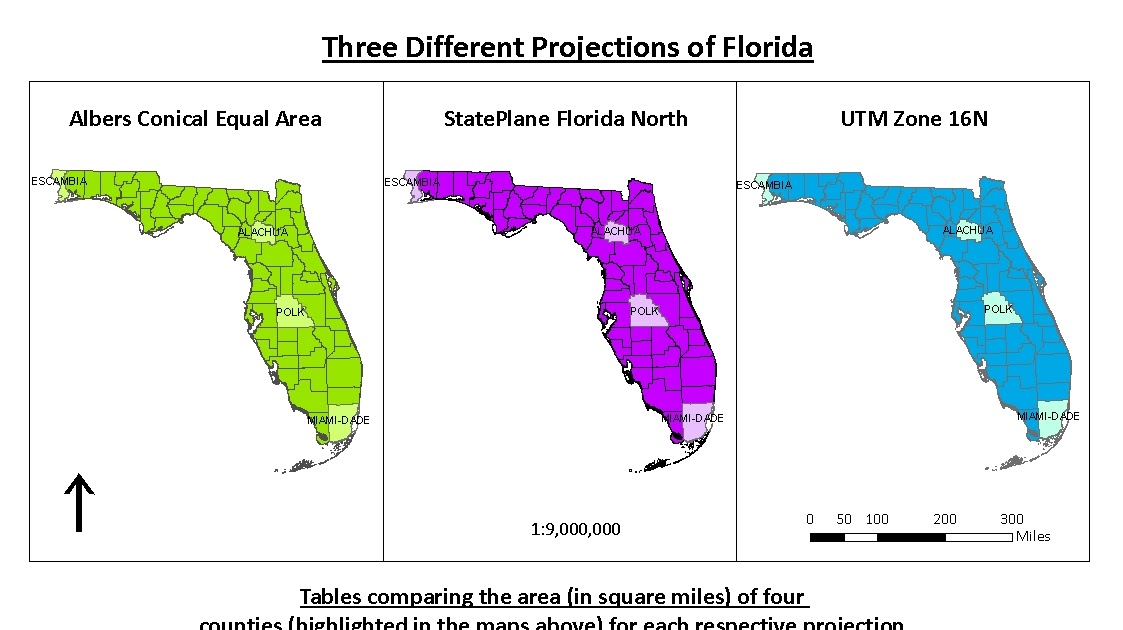
2. The Albers Equal-Area Conic Projection:
This projection excels in preserving area, ensuring that the relative sizes of regions on the map accurately reflect their real-world counterparts. It is particularly useful for applications involving population density, land use analysis, and resource management.
While the Albers projection preserves area, it introduces shape distortions, particularly towards the edges of the map. However, these distortions are minimal for Florida, as the state’s elongated shape minimizes the distance between its edges and the central meridian.
3. The Lambert Conformal Conic Projection:
This projection offers a balance between shape and area preservation, making it a versatile option for general-purpose mapping. It maintains accurate angles and shapes, particularly near the central meridian, while introducing minimal area distortions.
The Lambert Conformal Conic projection is well-suited for applications requiring accurate representations of both shape and area, such as thematic mapping, environmental studies, and geographic information systems (GIS).
4. The Robinson Projection:
While not as accurate as the previous projections, the Robinson projection offers a visually appealing compromise. It minimizes distortions in both shape and area, making it a popular choice for world maps and general-purpose mapping.
While the Robinson projection may not be the most accurate choice for Florida, its balanced distortions and aesthetically pleasing appearance make it suitable for educational purposes and general understanding of the state’s geography.
Choosing the Right Projection: A Practical Guide
The optimal projection for Florida depends on the specific application and the desired level of accuracy.
- For accurate measurements and precise representation of shapes, the Transverse Mercator projection is the most suitable.
- For applications involving area analysis and maintaining relative sizes of regions, the Albers Equal-Area Conic projection is the preferred choice.
- For general-purpose mapping and a balance between shape and area preservation, the Lambert Conformal Conic projection is a versatile option.
- For visually appealing maps and a general understanding of Florida’s geography, the Robinson projection offers a compromise between accuracy and aesthetics.
FAQ: Best Map Projection for Florida
Q: What is the most accurate map projection for Florida?
A: The Transverse Mercator projection is generally considered the most accurate for Florida, particularly for applications requiring precise measurements of distances and shapes.
Q: Which projection is best for showing Florida’s population density?
A: The Albers Equal-Area Conic projection is best suited for representing population density, as it accurately preserves the relative sizes of regions.
Q: Is there a single best projection for all applications?
A: No, the best projection depends on the specific application and the desired level of accuracy. Each projection has its strengths and weaknesses, and choosing the most appropriate one is crucial for achieving accurate and meaningful representations of Florida’s geography.
Tips for Choosing the Right Projection for Florida:
- Identify the specific purpose of the map. What information do you want to convey?
- Consider the level of accuracy required. Do you need precise measurements or a general overview?
- Understand the strengths and weaknesses of each projection. Choose the projection that best aligns with your needs.
- Consult with a cartographer or GIS specialist for guidance. They can provide expert advice on selecting the most appropriate projection for your specific application.
Conclusion
Choosing the right map projection for Florida is crucial for achieving accurate and meaningful representations of its geography. The Transverse Mercator, Albers Equal-Area Conic, Lambert Conformal Conic, and Robinson projections offer varying levels of accuracy and distortion, catering to different applications. By carefully considering the purpose of the map, the desired level of accuracy, and the strengths and weaknesses of each projection, users can select the optimal projection for their specific needs, ensuring that their maps accurately and effectively convey the unique features of Florida’s landscape.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping Florida: Choosing the Right Projection for Accuracy and Clarity. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!