Mapping Canada: A Look at Map Projections and their Importance
Related Articles: Mapping Canada: A Look at Map Projections and their Importance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping Canada: A Look at Map Projections and their Importance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping Canada: A Look at Map Projections and their Importance

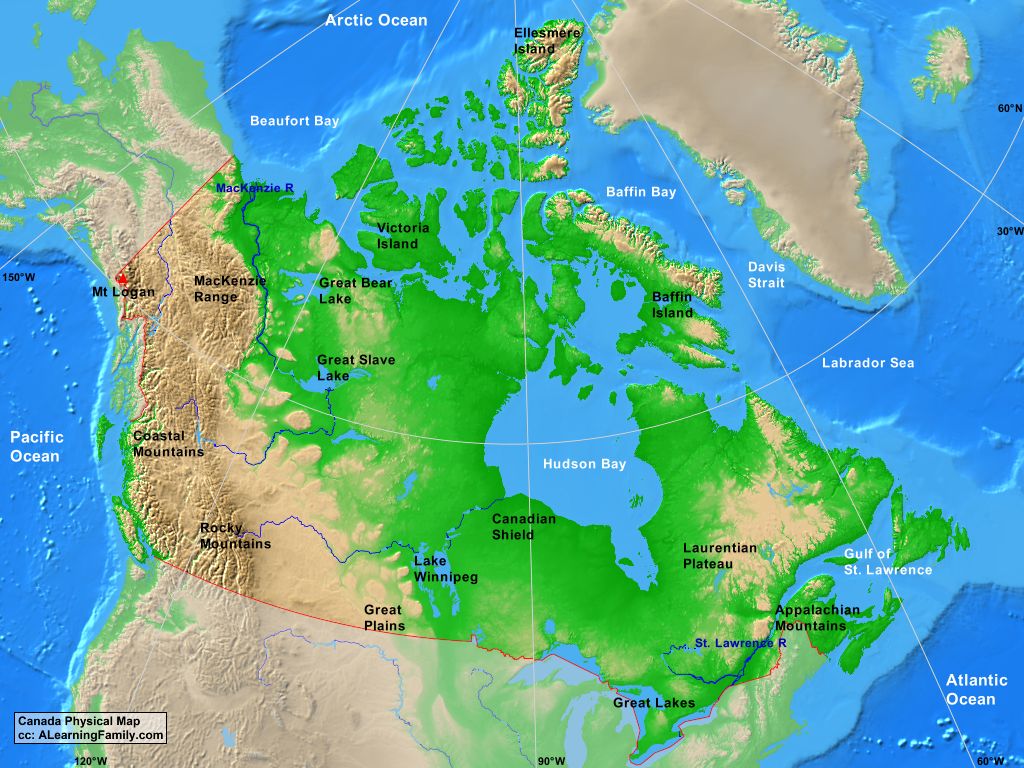
Canada, a vast and geographically diverse nation, presents unique challenges for cartographers. Its immense size, encompassing multiple time zones and diverse landscapes, demands careful consideration of map projections. These projections, mathematical formulas that translate the three-dimensional Earth onto a two-dimensional surface, are crucial for accurately representing Canada’s geography and facilitating a wide range of activities.
Understanding Map Projections
The Earth, being a sphere, cannot be flawlessly flattened onto a map without distortion. Map projections address this by employing different mathematical formulas to minimize specific types of distortion, such as area, shape, distance, or direction. Each projection has its own strengths and weaknesses, making the selection process critical depending on the intended use of the map.
Common Map Projections Used in Canada
Several map projections are commonly used in Canada, each suited for specific purposes:
- Mercator Projection: This cylindrical projection is widely known for its use in nautical charts. It preserves angles, making it ideal for navigation, but it distorts areas significantly, particularly towards the poles. This distortion is evident in maps showing Greenland appearing larger than South America, despite being much smaller in reality.
- Lambert Conformal Conic Projection: This conic projection is widely used for mapping Canada due to its ability to minimize distortion in areas with significant east-west extents. It preserves angles and shapes well, making it suitable for topographic maps and other applications where accurate representation of shapes is crucial.
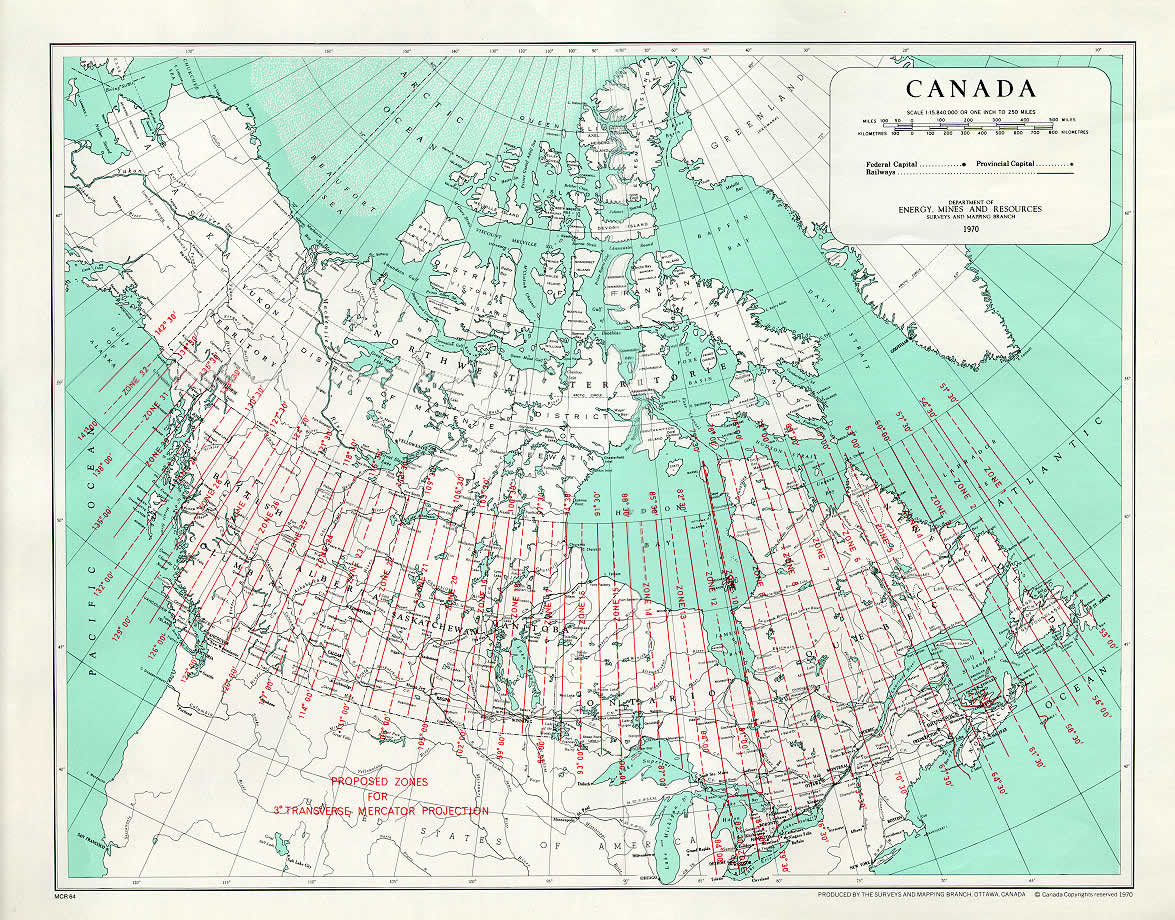
- Transverse Mercator Projection: This projection is particularly useful for mapping regions with a significant north-south extent. It preserves angles and distances along a central meridian, making it ideal for mapping areas along the Canadian coastline.
- Albers Equal-Area Conic Projection: This projection is designed to preserve area, ensuring that the relative sizes of regions on the map accurately represent their actual proportions on Earth. It is commonly used for thematic maps, which focus on displaying spatial patterns and distributions of data, such as population density or resource distribution.
The Importance of Choosing the Right Projection
The selection of an appropriate map projection is crucial for various reasons:
- Accurate Representation of Geographic Features: A projection that minimizes distortion in the desired area ensures that shapes, distances, and areas are depicted as accurately as possible, facilitating understanding and analysis of the landscape.
- Navigation and Travel: Accurate representations of distances and directions are essential for navigation, especially in vast and remote areas like Canada’s north.
- Resource Management and Planning: Maps are essential for resource management, including forestry, mining, and environmental planning. Accurate projections ensure that data is correctly interpreted and decisions are made based on reliable information.
- Research and Analysis: Researchers rely on accurate maps for analyzing spatial patterns and trends in various fields, including geography, climate science, and social sciences.
Beyond the Basics: Considerations for Canadian Mapping
Canada’s unique geographic features necessitate additional considerations for map projections:
- Large Geographic Extent: Canada’s vast size poses challenges for representing the entire country on a single map without significant distortion. Often, multiple projections are employed for different regions, ensuring accuracy for specific areas.
- Diverse Terrain: From the Rocky Mountains to the Arctic tundra, Canada’s varied terrain requires careful selection of projections that minimize distortion in specific areas.
- Political Boundaries: Provincial and territorial boundaries require precise representation, ensuring that maps accurately reflect administrative divisions.
- Indigenous Land Recognition: Map projections play a crucial role in recognizing and representing the territories of Indigenous peoples, acknowledging their historical and cultural connections to the land.
FAQs on Map Projections in Canada
Q: What is the most accurate map projection for Canada?
A: There is no single "most accurate" projection for Canada due to its vast size and diverse terrain. The best projection depends on the specific application and the area being mapped.
Q: Why are some maps distorted?
A: All map projections inherently distort some aspect of the Earth’s surface, whether it’s area, shape, distance, or direction. This distortion is unavoidable because a sphere cannot be perfectly flattened onto a plane.
Q: How can I tell which projection is being used on a map?
A: Most maps will include a projection name or a description of the projection used in the map’s legend or metadata.
Q: Are there any new developments in map projections?
A: Yes, advancements in technology and cartographic techniques continue to refine and improve map projections. New projections are being developed to address specific needs, such as the accurate representation of polar regions or the integration of 3D data.
Tips for Understanding Map Projections
- Examine the map’s legend: Pay attention to the projection name and any notes about the types of distortion present.
- Compare different projections: View the same area on different projections to understand how they vary in their representation of features.
- Use online mapping tools: Many online mapping platforms allow users to switch between different projections, providing a visual comparison of their effects.
- Consult with experts: If you have specific mapping needs, consult with cartographers or GIS specialists for guidance on choosing the most appropriate projection.
Conclusion
Map projections are essential tools for understanding and representing Canada’s vast and diverse geography. Choosing the right projection is crucial for ensuring accuracy, facilitating navigation, supporting resource management, and promoting research and analysis. As technology advances, new and more sophisticated projections will continue to be developed, enhancing our ability to accurately map and understand the complexities of Canada’s landscape.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping Canada: A Look at Map Projections and their Importance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!