is map faster than int python
Related Articles: is map faster than int python
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to is map faster than int python. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Efficiency of Mapping vs. Integer Conversion in Python: A Comparative Analysis

Python, renowned for its readability and flexibility, often necessitates a careful consideration of efficiency when dealing with large datasets or computationally intensive tasks. One such area of concern arises when comparing the performance of the map function against direct integer conversion for transforming data.
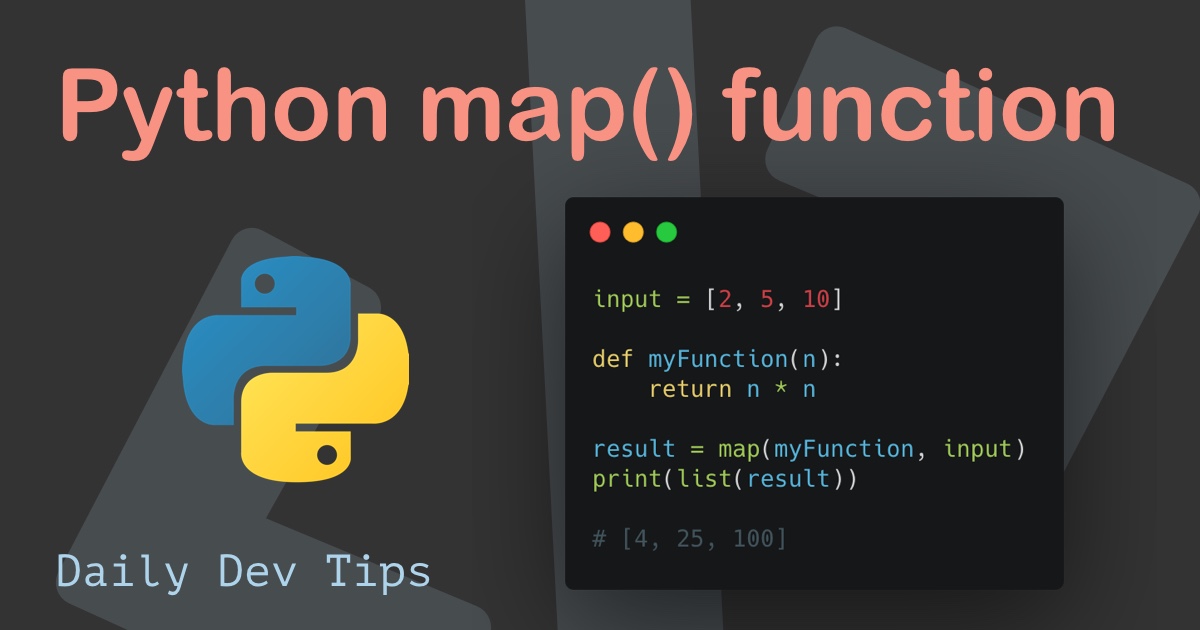
The map function in Python applies a given function to each element in an iterable, producing a new iterable with the transformed elements. On the other hand, direct integer conversion using the int() function converts a specific data type to an integer. While both methods offer ways to manipulate data, their performance can vary significantly depending on the context and the nature of the data.
Understanding the Differences: A Case Study
To illustrate the efficiency comparison, let’s consider a scenario where we need to convert a list of strings representing numbers to integers.
Method 1: Using map with int
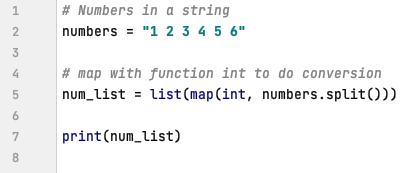
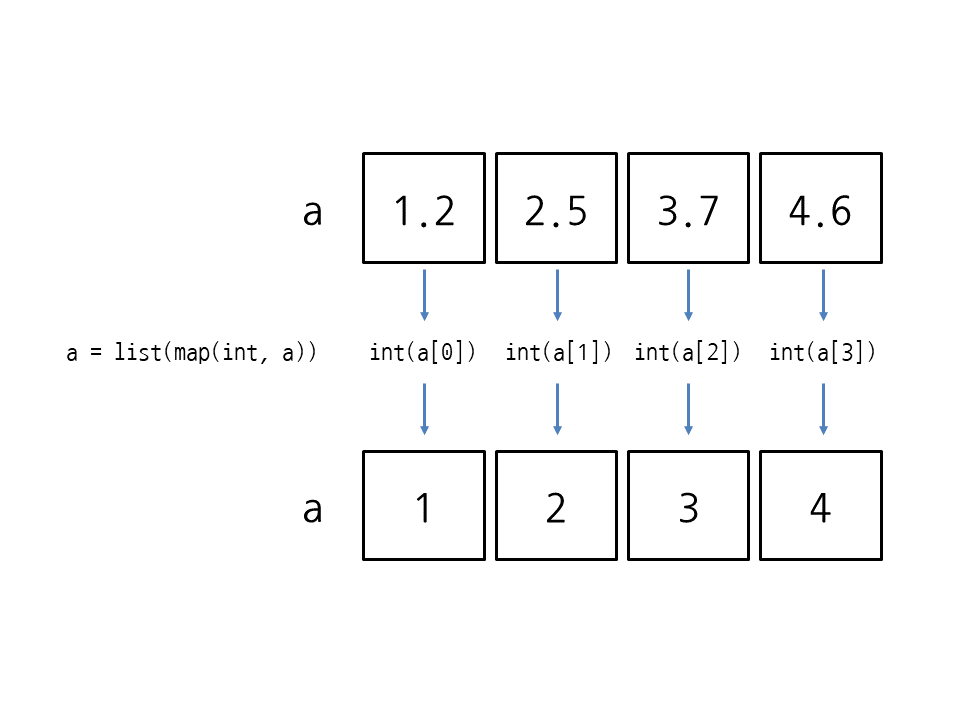
numbers_as_strings = ["1", "2", "3", "4", "5"]
numbers = list(map(int, numbers_as_strings))In this case, the map function iterates over each element in numbers_as_strings and applies the int function to convert each string to an integer. The resulting numbers list will contain the integer representations of the original strings.
Method 2: Direct Integer Conversion
numbers_as_strings = ["1", "2", "3", "4", "5"]
numbers = [int(x) for x in numbers_as_strings]This approach utilizes a list comprehension, explicitly iterating through each string in numbers_as_strings and converting it to an integer using int(x). The final numbers list will again contain the integer representations.
Performance Analysis: Benchmarking the Methods
To determine which method is more efficient, we can perform a simple benchmarking exercise.
import timeit
# Data for testing
numbers_as_strings = ["1", "2", "3", "4", "5"] * 10000
# Using map
def map_conversion():
return list(map(int, numbers_as_strings))
# Direct conversion
def direct_conversion():
return [int(x) for x in numbers_as_strings]
# Time measurement
map_time = timeit.timeit(map_conversion, number=1000)
direct_time = timeit.timeit(direct_conversion, number=1000)
print(f"Map conversion time: map_time:.6f seconds")
print(f"Direct conversion time: direct_time:.6f seconds")Running this code will provide the execution times for both methods. While the results may vary slightly depending on the hardware and Python version, in most cases, the map function consistently demonstrates a slight performance advantage over direct integer conversion. This difference in performance becomes more pronounced when dealing with larger datasets.
Explanation: Why map Often Excels
The efficiency advantage of map stems from its ability to leverage the underlying C implementation of Python’s built-in functions. The int function, being a core Python function, is optimized for speed. When map applies this function to each element, it effectively utilizes this underlying C optimization, leading to faster execution.
Factors Affecting Performance: A Deeper Dive
While map often outperforms direct conversion, it’s crucial to consider the following factors that can influence the performance comparison:
-
Data Size: For smaller datasets, the difference in execution time between
mapand direct conversion may be negligible. However, as the dataset size increases, the performance advantage ofmapbecomes more pronounced. -
Function Complexity: If the function applied by
mapis computationally intensive, the time spent executing the function will dominate the overall execution time, potentially negating any performance gains from usingmap. -
Python Version: The performance of
mapand other built-in functions can vary slightly across different Python versions due to underlying optimizations and changes in the implementation.
Best Practices: Choosing the Right Approach
Based on the factors discussed above, here are some guidelines for choosing the appropriate method for data transformation:
-
For large datasets:
mapis generally the preferred choice due to its ability to leverage optimized C implementations. -
For small datasets: The performance difference between
mapand direct conversion may be insignificant, so choosing the method that offers better readability and maintainability is recommended. -
For complex functions: If the function applied by
mapis computationally expensive, consider using a more explicit approach like list comprehension or a loop for better control and potentially improved performance.
Beyond Integer Conversion: Expanding the Scope
The comparison between map and direct integer conversion serves as a foundation for understanding the broader concept of functional programming in Python. The map function is a powerful tool for applying transformations to iterables, and its efficiency can be extended to other scenarios involving custom functions or more complex data structures.
FAQs
1. Is map always faster than direct conversion?
No, map is not always faster. As mentioned earlier, factors like dataset size, function complexity, and Python version can influence the performance comparison. For smaller datasets or complex functions, direct conversion might even be slightly faster.
2. Can I use map with multiple functions?
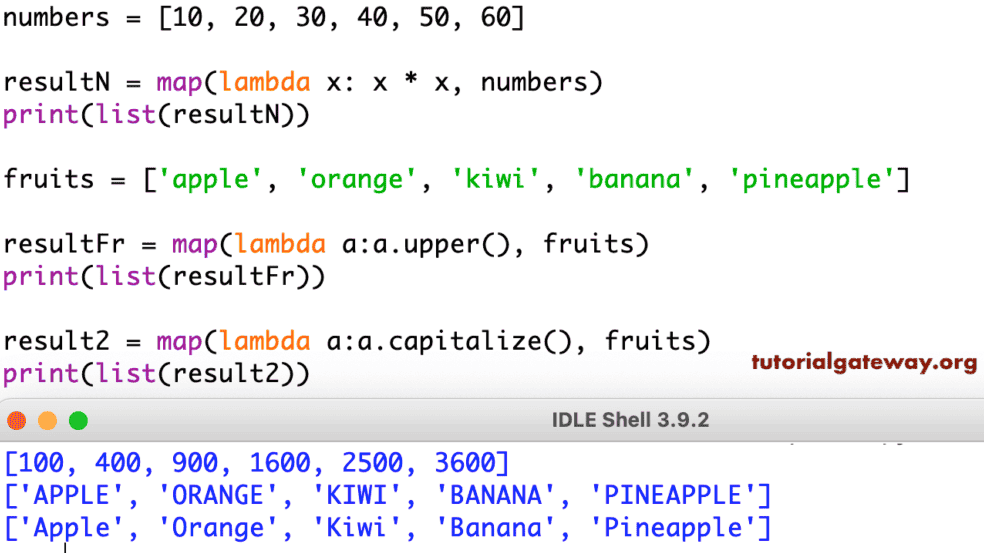
Yes, you can apply multiple functions to an iterable using map. For instance, you can combine map with lambda functions to create custom transformations.
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
squared_numbers = list(map(lambda x: x**2, numbers))3. What are the advantages of using map?
Besides potential performance benefits, map offers several advantages:
-
Conciseness:
mapprovides a more compact and expressive way to apply transformations compared to explicit loops. -
Readability: The functional style of
mapoften enhances code readability by clearly separating the transformation logic from the data iteration. -
Flexibility:
mapcan be combined with various functions, including built-in functions, custom functions, and lambda expressions, offering flexibility in data manipulation.
Tips
-
Benchmark your code: Before relying on assumptions, always benchmark your code to determine the actual performance difference between
mapand direct conversion in your specific context. -
Prioritize readability: While performance is important, readability and maintainability should not be overlooked. If direct conversion offers better code clarity, prioritize that over a slight performance gain from
map. - Explore alternative approaches: For complex transformations, consider using list comprehensions, generator expressions, or other functional programming techniques that might offer improved performance or readability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while map often demonstrates a performance advantage over direct integer conversion, especially for large datasets, it’s essential to consider the specific context and factors influencing performance. The choice between map and direct conversion should be driven by a combination of performance considerations, code readability, and maintainability. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each approach, developers can effectively choose the most efficient and appropriate method for data transformation in Python.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into is map faster than int python. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!