Harnessing the Power of map in Python: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Harnessing the Power of map in Python: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Harnessing the Power of map in Python: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Harnessing the Power of map in Python: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Harnessing the Power of map in Python: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding the Essence of map
- 3.2 Benefits of Utilizing map
- 3.3 Practical Applications of map
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions about map
- 3.5 Tips for Effective Use of map
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Harnessing the Power of map in Python: A Comprehensive Guide

The Python programming language offers a rich set of built-in functions that streamline code and enhance efficiency. Among these, the map function stands out as a powerful tool for applying transformations to iterable objects, such as lists, tuples, or strings. This guide delves into the intricacies of map in Python, exploring its functionality, benefits, and practical applications.
Understanding the Essence of map
At its core, map acts as a bridge between a function and an iterable. It iterates through each element of the iterable, applies the specified function to each element, and generates a new iterable containing the transformed results. This process eliminates the need for explicit loops, simplifying code and promoting readability.
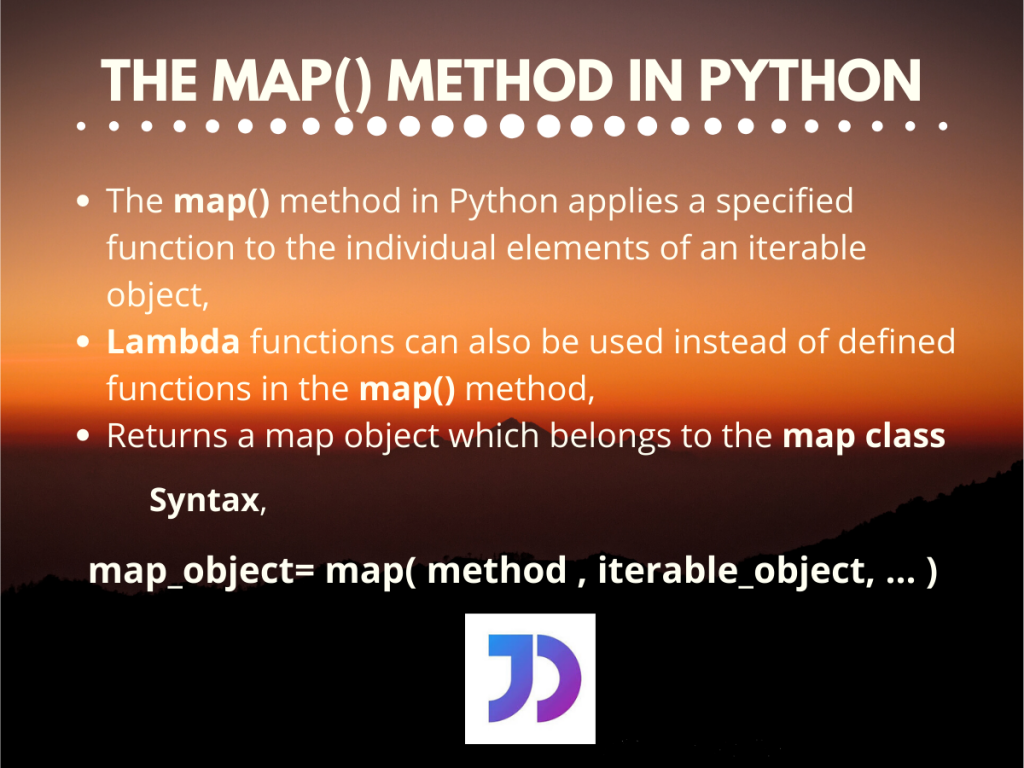
Syntax:
map(function, iterable)Here, function represents the function to be applied, and iterable refers to the sequence of elements to be processed.
Example:
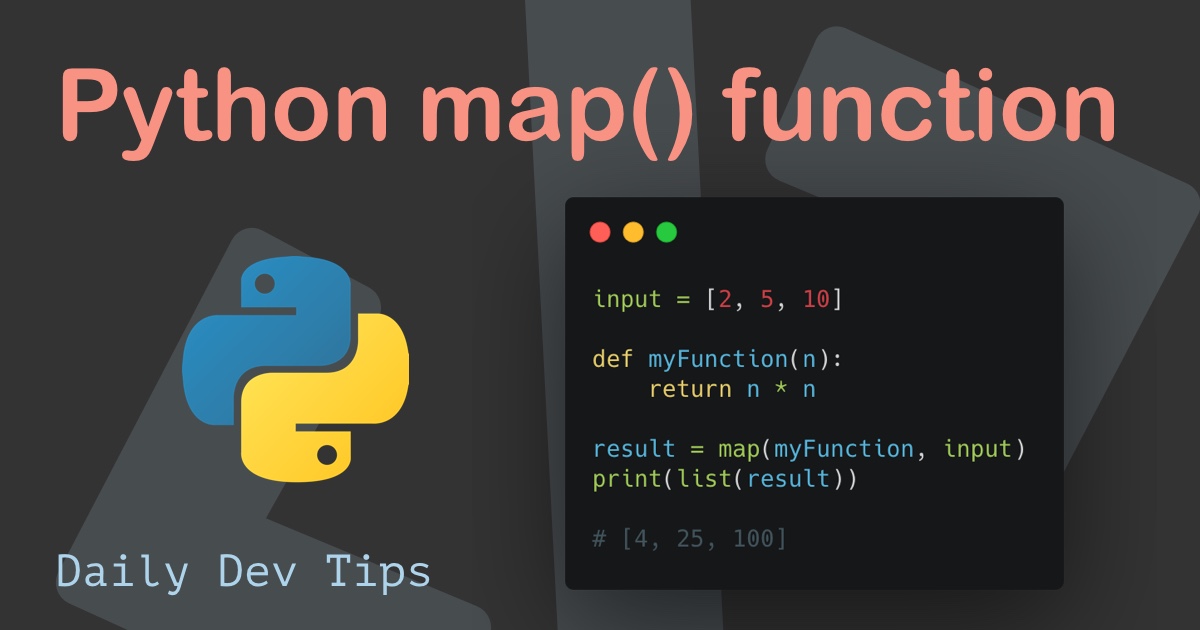
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
def square(x):
return x**2
squared_numbers = map(square, numbers)
print(list(squared_numbers)) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]In this example, square squares each element in the numbers list, and map returns an iterator containing the squared values. Converting this iterator to a list using list() allows us to observe the results.
Benefits of Utilizing map
-
Concise and Readable Code:
mapeliminates the need for explicit loops, resulting in cleaner and more concise code. This improved readability enhances code maintainability and understanding. -
Efficiency:
mapleverages Python’s internal optimization techniques, often leading to faster execution compared to manual looping. This efficiency becomes particularly noticeable when dealing with large datasets. -
Flexibility:
mapaccepts any function as input, enabling diverse transformations. It can handle functions that modify data types, perform calculations, or even apply custom logic. -
Functional Programming Paradigm:
mapaligns with the principles of functional programming, emphasizing immutability and the application of functions to data. This approach promotes code modularity and reusability.
Practical Applications of map
-
Data Transformation:
mapexcels at transforming data within lists, tuples, or other iterables. This includes tasks such as converting data types, applying mathematical operations, or manipulating strings. -
Data Validation:
mapcan be used to apply validation rules to elements within a dataset, ensuring data integrity and consistency. -
Parallel Processing: When combined with the
multiprocessingmodule,mapcan be used to distribute tasks across multiple cores, accelerating processing time for computationally intensive operations. -
Custom Function Application:
mapallows the application of user-defined functions to iterable data, enabling customized transformations tailored to specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions about map
1. What happens if the function takes multiple arguments?
map can handle functions with multiple arguments. In such cases, you need to provide multiple iterables as additional arguments to map. The function will be applied to corresponding elements from each iterable.
2. Can map be used with lambda functions?
Absolutely! Lambda functions are ideal for concise function definitions within map. They provide a succinct way to define the transformation logic directly within the map call.
3. How can I handle errors during the map operation?
map does not inherently handle exceptions raised by the applied function. To handle errors gracefully, you can use a try-except block within the function or employ the itertools.starmap function, which allows for exception handling.
4. Is map always the best choice for data transformation?
While map is a powerful tool, it might not be the optimal solution in every scenario. For instance, if you need to modify elements based on their position within the iterable, enumerate might be more appropriate.
Tips for Effective Use of map
-
Choose the Right Function: Carefully select the function to be applied based on the desired transformation. Consider lambda functions for concise logic.
-
Handle Errors Gracefully: Implement error handling mechanisms to prevent program crashes during unexpected situations.
-
Optimize for Performance: When dealing with large datasets, consider utilizing
multiprocessingfor parallel processing to enhance efficiency. -
Readability and Maintainability: Prioritize clear and concise code, ensuring that the logic behind
mapis easily understood.
Conclusion
The map function in Python empowers developers with a concise and efficient method for applying transformations to iterable objects. Its versatility, combined with its ability to simplify code and enhance performance, makes it a valuable tool in a wide range of programming scenarios. By understanding the intricacies of map and applying the provided tips, programmers can leverage its power to streamline their code and enhance the efficiency of their data manipulation tasks.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Harnessing the Power of map in Python: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!