Harnessing Efficiency: Understanding and Utilizing the Power of Map and Lambda in Python
Related Articles: Harnessing Efficiency: Understanding and Utilizing the Power of Map and Lambda in Python
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Harnessing Efficiency: Understanding and Utilizing the Power of Map and Lambda in Python. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Harnessing Efficiency: Understanding and Utilizing the Power of Map and Lambda in Python
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Harnessing Efficiency: Understanding and Utilizing the Power of Map and Lambda in Python
- 3.1 The map Function: Transforming Iterables with Grace
- 3.2 Lambda Expressions: Concise and Efficient Functions
- 3.3 The Power of Combining map and Lambda
- 3.4 Beyond Basic Transformations: Unveiling the Versatility of map and Lambda
- 3.5 FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Use
- 3.7 Conclusion: Embracing the Efficiency of map and Lambda
- 4 Closure
Harnessing Efficiency: Understanding and Utilizing the Power of Map and Lambda in Python
Python, known for its readability and versatility, offers a wealth of tools for programmers. Among these tools, the map function and lambda expressions stand out as powerful allies for streamlining code and enhancing efficiency. This article delves into the intricacies of these concepts, elucidating their individual strengths and the synergy they create when combined.
The map Function: Transforming Iterables with Grace
The map function in Python serves as a potent tool for applying a specific operation to each element within an iterable, such as a list or a tuple. It takes two arguments: a function and an iterable. The function is applied to each element of the iterable, generating a new iterable containing the results.
Consider the following scenario: You have a list of numbers and wish to square each number. Using a traditional for loop, this would require iterating through the list, squaring each element, and appending the result to a new list. This approach, while functional, can be cumbersome, especially for larger datasets.
Here’s where the map function shines. It elegantly streamlines this process, eliminating the need for explicit loops.
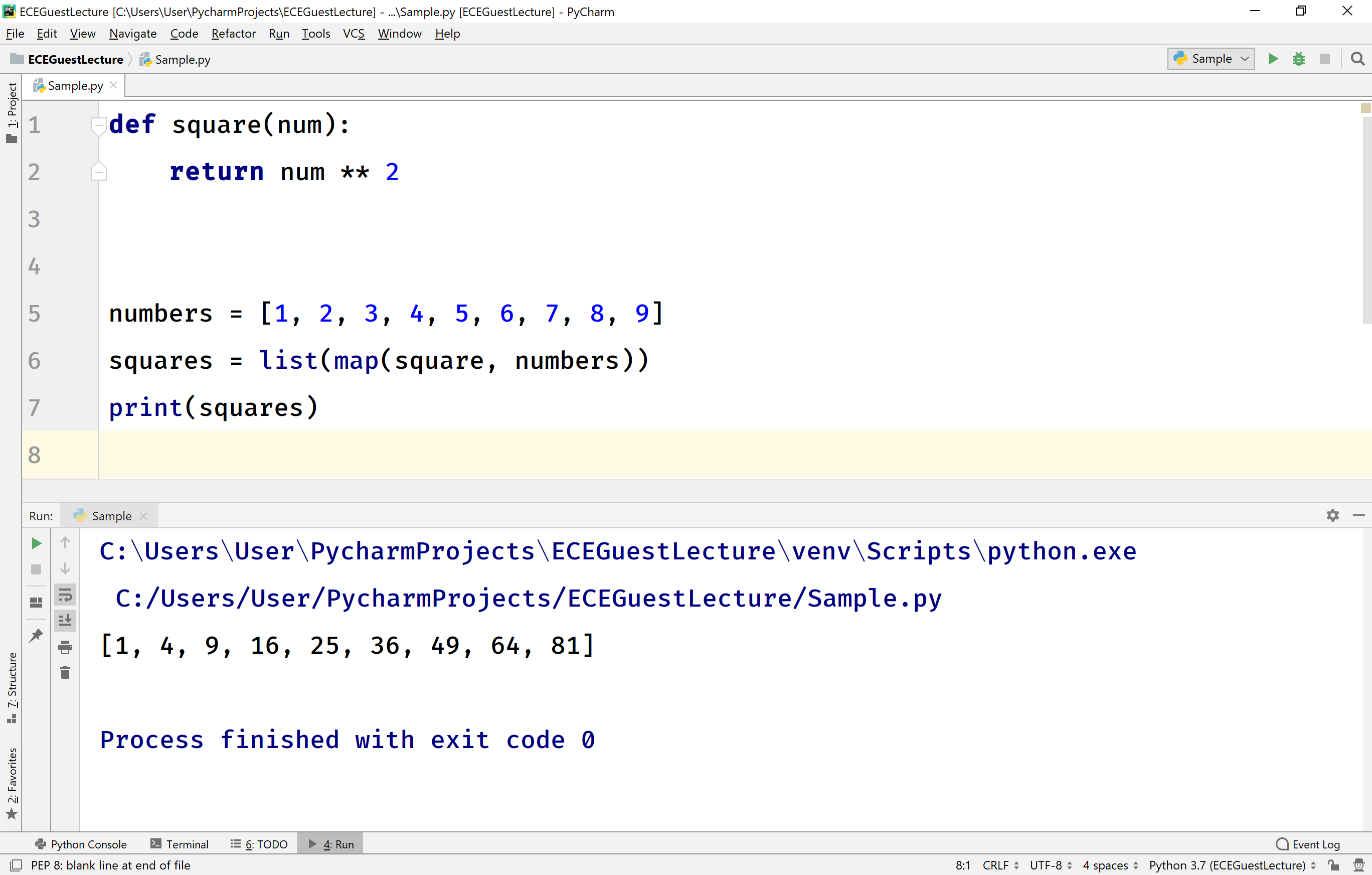
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
squared_numbers = list(map(lambda x: x**2, numbers))
print(squared_numbers) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]In this example, map applies the lambda function (explained in the next section) to each element in the numbers list. The lambda function squares each element, and the result is stored in the squared_numbers list.
Lambda Expressions: Concise and Efficient Functions
Lambda expressions, often referred to as anonymous functions, provide a concise way to define small, single-purpose functions without the need for a formal function definition using def. Their compact nature makes them ideal for use within the map function and other scenarios where a brief, reusable function is required.
The syntax of a lambda expression is straightforward: lambda arguments: expression. The arguments represent the input parameters, and the expression defines the operation to be performed on those arguments.
Returning to the previous example, the lambda expression lambda x: x**2 succinctly defines the squaring operation. It takes a single argument x and returns its square.
The Power of Combining map and Lambda
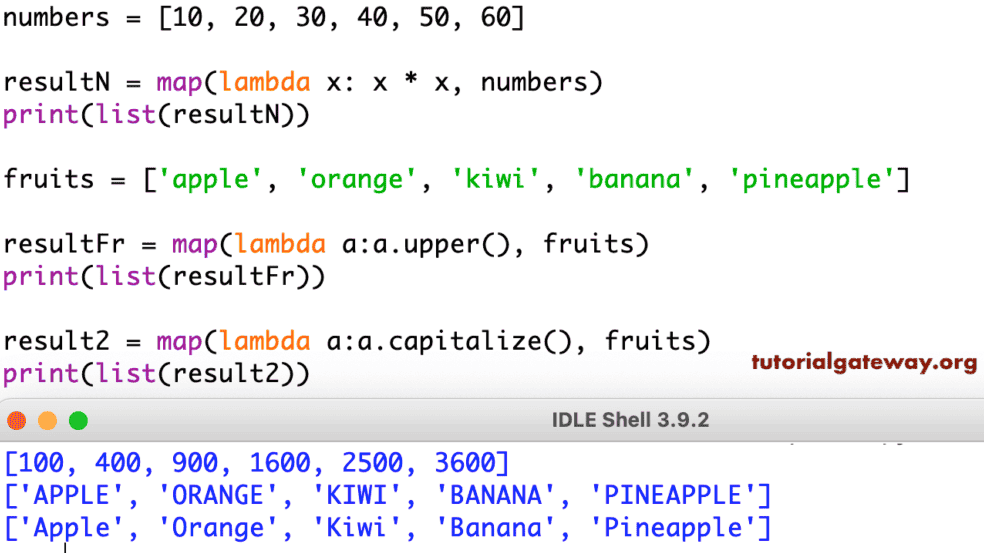
The true power of map and lambda expressions lies in their combined use. By leveraging the conciseness of lambda expressions within the `map function, one can achieve elegant and efficient code for transforming iterables.
For instance, consider the task of converting a list of strings to uppercase.
strings = ["hello", "world", "python"]
uppercase_strings = list(map(lambda x: x.upper(), strings))
print(uppercase_strings) # Output: ['HELLO', 'WORLD', 'PYTHON']This code snippet demonstrates the seamless integration of map and lambda. The map function iterates through the strings list, applying the lambda expression lambda x: x.upper() to each string, resulting in a new list containing the uppercase versions of the original strings.
Beyond Basic Transformations: Unveiling the Versatility of map and Lambda
The applications of map and lambda expressions extend far beyond simple transformations. They can be utilized in various scenarios, including:
-
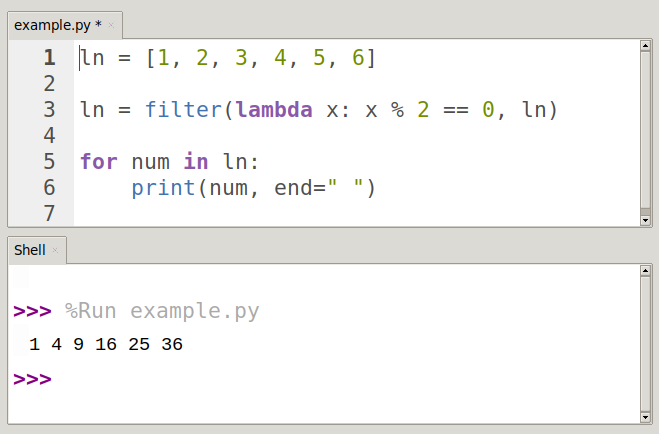
Filtering Data: By combining
mapwith a lambda function that returns a boolean value, one can filter elements from an iterable based on a specific condition. -
Applying Multiple Functions:
mapcan accept multiple iterables as arguments, allowing for the application of a function to corresponding elements from each iterable. -
Customizing Operations: Lambda expressions offer flexibility in defining complex operations, enabling the execution of customized logic on each element of an iterable.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
Q: Can map be used with multiple iterables?
A: Yes, map can accept multiple iterables as arguments. In this case, the lambda function should accept the same number of arguments as the number of iterables provided. The function will be applied to corresponding elements from each iterable.
Q: What are the benefits of using map and lambda expressions?
A: The primary benefits include:
-
Conciseness: Lambda expressions and
mapprovide a concise and elegant way to express operations on iterables, reducing the need for verboseforloops. -
Readability: The use of
mapand lambda expressions often results in more readable code, making it easier to understand the intent of the operation. -
Efficiency:
mapand lambda expressions can be more efficient than traditional loops, especially for larger datasets, as they often leverage underlying optimized implementations.
Q: When should I avoid using map and lambda expressions?
A: While powerful, map and lambda expressions are not always the best choice. Consider these scenarios:
-
Complex Logic: If the operation to be performed on each element requires complex logic, a traditional function definition using
defmight be more appropriate for readability and maintainability. -
Side Effects: If the operation involves side effects, such as modifying a global variable,
mapmight not be the most suitable approach.
Tips for Effective Use
- Keep it Concise: Lambda expressions should be kept short and focused on a single operation. Avoid complex logic within lambda functions.
- Prioritize Readability: While concise, prioritize readability. If a complex lambda expression becomes difficult to understand, consider using a traditional function definition.
-
Leverage the Power of
map: Explore the various applications ofmap, such as filtering, applying multiple functions, and customizing operations.
Conclusion: Embracing the Efficiency of map and Lambda
The map function and lambda expressions provide a powerful combination for transforming and manipulating data in Python. Their conciseness, readability, and efficiency make them invaluable tools for programmers seeking to streamline their code and enhance its performance. By understanding their individual strengths and the synergy they create when combined, developers can harness their capabilities to write more elegant and effective Python programs.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Harnessing Efficiency: Understanding and Utilizing the Power of Map and Lambda in Python. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!